
Exercise3 Several methods have been developed for staining spores.Prepared slides of hacteria with stained s res will be available for student examination(spor seen as red oval bodies) DEMONSTRATION An aerobic spore-forming bacterium(Bacillus Anthracis)will be available for student examination.Please note that the presence of colorless oval areas within the bacterium should lead one to suspect that the microorganism is a spore-former B.GRAM-NEGATIVE RODS Enterobacteriaceae Family Species of the genera Escherichia,Klebsiella.Proteus.Serratia. Enterobacter.Citrobacter.Edwardsiella,Providencia,Arizona,Salmonella. Shigella are all gram-negative rods that belor teriaceae These mi ms are fou the fam estinal trac nals und normal and conditior tohumansthroush fecal contamination of water.so.food.or fomites and many species are pathogenic causing intestinal diseases,septicemia,urinary tract infections,and various opportunistic infections in hospitalized or compromised hosts (e.g.,aged,diabetic,immunosuppressed).Treatment of such infections is often complicated by the fact that many of these gram-negative rods are resistant to various antibiotics and the patients are usually debilitated or in a compromised state. Blood agar cultures of the following bacteria will be available for student examination:Escherichia coli,Proteus mirabilis,Pseudomonas aeruginosa Each group of 4 students at the lab table should work together to become familiar with these microorganisms. um.The should note that most gram-negative rods are rather indistinguishable on this medium.They appear as large,smooth,gray colonies which are usually round and convex.Nevertheless,several distinctions can be made and should be recognized by each student. Pseudomonas Escherichia coli Proteus mirabilis aeruginosa a)The spreading,swarming type growth of Proteus mirabilis which usually covers the entire agar surface is very characteristic as is the unpleasant sewage or fishy type odor. b)The very lar is quite characteristic as is the sweet or fruity odor. Streak for isolated colonies on M-H agar.(Click on above table to see images.) file://CWINDC Microb Lab Web 2001/Exercise3/exercise3.htm(4 of 7)[8/31/2002 4:30:07 PM]
Several methods have been developed for staining spores. Prepared slides of bacteria with stained spores will be available for student examination (spores seen as red oval bodies) DEMONSTRATION An aerobic spore-forming bacterium (Bacillus Anthracis) will be available for student examination. Please note that the presence of colorless oval areas within the bacterium should lead one to suspect that the microorganism is a spore-former. B. GRAM-NEGATIVE RODS Enterobacteriaceae Family Species of the genera Escherichia, Klebsiella, Proteus, Serratia, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Edwardsiella, Providencia, Arizona, Salmonella, Shigella, and Yersinia are all gram-negative rods that belong to the family Enterobacteriaceae. These microorganisms are found in the intestinal tract of man and animals under normal and disease conditions. They are transmitted to humans through fecal contamination of water, soil, food, or fomites and many species are pathogenic causing intestinal diseases, septicemia, urinary tract infections, and various opportunistic infections in hospitalized or compromised hosts (e.g., aged, diabetic, immunosuppressed). Treatment of such infections is often complicated by the fact that many of these gram-negative rods are resistant to various antibiotics and the patients are usually debilitated or in a compromised state. >>>>> Blood agar cultures of the following bacteria will be available for student examination: Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Each group of 4 students at the lab table should work together to become familiar with these microorganisms. 1. Observe and record the cultural characteristics (type of isolated colonies) of each microorganism growing on the blood agar medium. The student should note that most gram-negative rods are rather indistinguishable on this medium. They appear as large, smooth, gray colonies which are usually round and convex. Nevertheless, several distinctions can be made and should be recognized by each student. Escherichia coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa Proteus mirabilis a) The spreading, swarming type growth of Proteus mirabilis which usually covers the entire agar surface is very characteristic as is the unpleasant sewage or fishy type odor. b) The very large, flat, and irregular colonies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa which also appear to have a metallic glistening sheen is quite characteristic as is the sweet or fruity odor. Streak for isolated colonies on M-H agar. (Click on above table to see images.) Exercise 3 file:///C|/WINDOWS/Desktop/clown/Microb Lab Web 2001/Exercise3/exercise3.htm (4 of 7) [8/31/2002 4:30:07 PM]
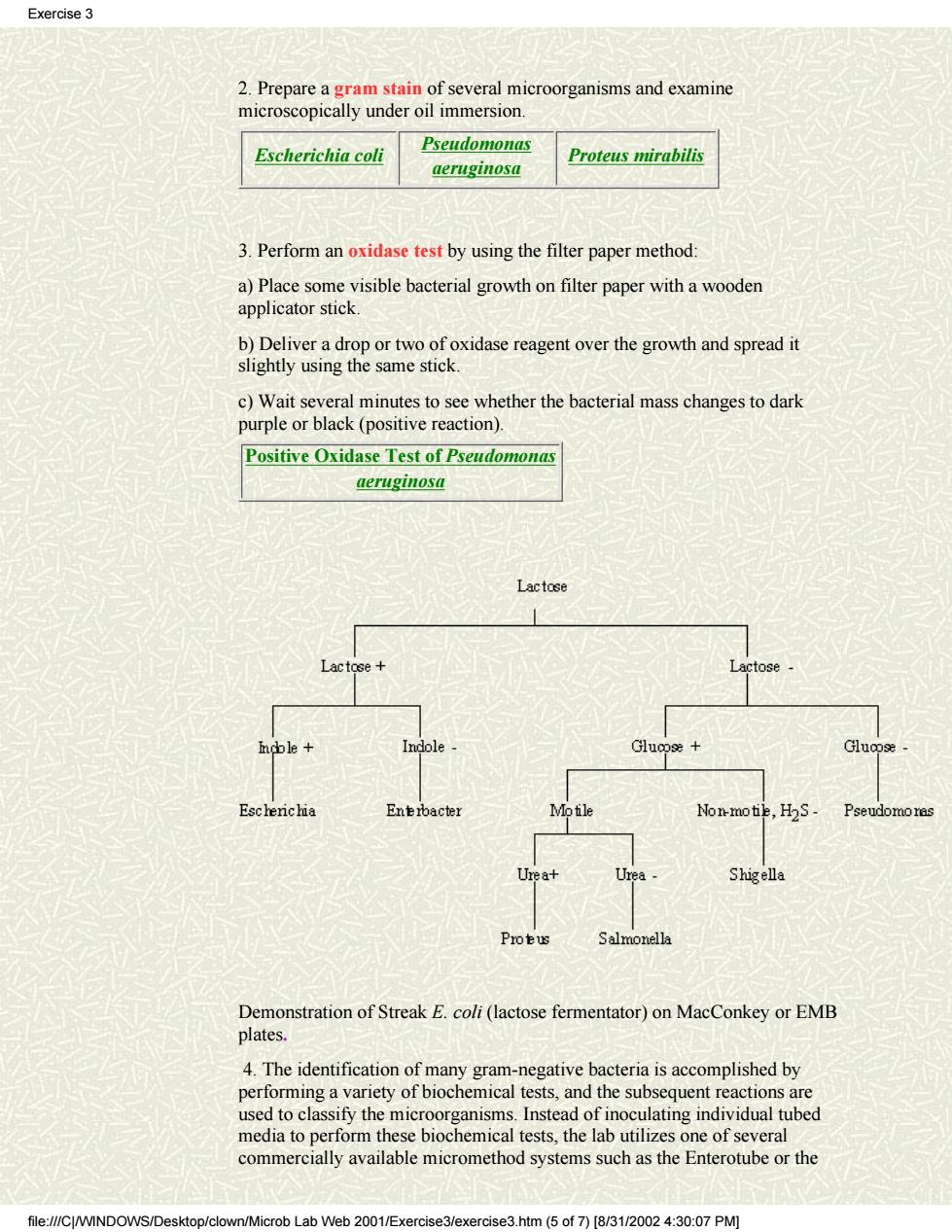
Exercise 3 2.Prepare a gram stain of several microorganisms and examine microscopically under oil immersion. Escherichia coli Pseudomona西 aeruginosa Proteus mirabilis 3.Perform an oxidase test by using the filter paper method: a)Place some visible bacterial growth on filter paper with a wooden applicator stick. b)Deliver a drop or two of oxidase reagent over the growth and spread it slightly using the same stick. c)Wait several minutes to see whether the bacterial mass changes to dark purple or black (positive reaction). Positive Oxidase Test of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lactose Demonstration of Streak E.coli(lactose fermentator)on MacConkey or EMB plates. 4.The identification of many gram-negative bacteria is accomplished by nerforming a variety of biochemical tests and the subsequent reactions are ed to clas ssify the stead of inoculating individual tubed commerialy available micromethod systems suchathe Enterotb the media e b hemical tests,the lal tiliz file://CWINDOWS/Desktop/clown/Microb Lab Web 2001/Exercise3/exercise3.htm(5 of7)[8/3/002 4:30:07 PM]
2. Prepare a gram stain of several microorganisms and examine microscopically under oil immersion. Escherichia coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa Proteus mirabilis 3. Perform an oxidase test by using the filter paper method: a) Place some visible bacterial growth on filter paper with a wooden applicator stick. b) Deliver a drop or two of oxidase reagent over the growth and spread it slightly using the same stick. c) Wait several minutes to see whether the bacterial mass changes to dark purple or black (positive reaction). Positive Oxidase Test of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Demonstration of Streak E. coli (lactose fermentator) on MacConkey or EMB plates. 4. The identification of many gram-negative bacteria is accomplished by performing a variety of biochemical tests, and the subsequent reactions are used to classify the microorganisms. Instead of inoculating individual tubed media to perform these biochemical tests, the lab utilizes one of several commercially available micromethod systems such as the Enterotube or the Exercise 3 file:///C|/WINDOWS/Desktop/clown/Microb Lab Web 2001/Exercise3/exercise3.htm (5 of 7) [8/31/2002 4:30:07 PM]
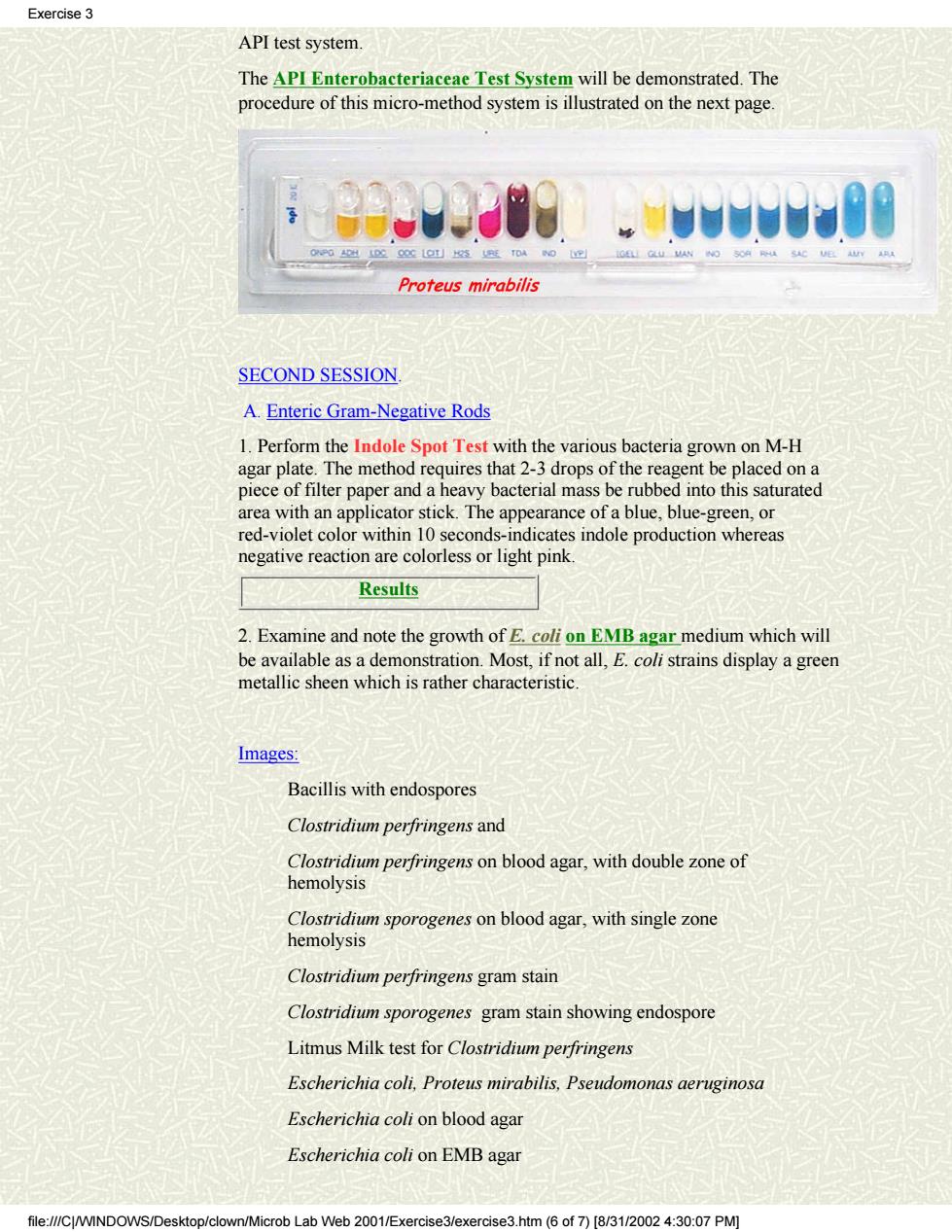
Exercise3 API test system. The API Enterobacteriaceae Test System will be demonstrated.The procedure of this micro-method system is illustrated on the next page. Proteus mirabilis SECOND SESSION. A.Enteric Gram-Negative Rods 1.Perform the Indole Spot Test with the various bacteria grown on M-H agar plate.The method requires that 2-3 drops of the reagent be placed on a piece of filter paper and a heavy bacterial mass be rubbed into this saturated area with an applicator stick.The appearance of a blue,blue-green,or red-violet color within 10 seconds-indicates indole production whereas egative reaction are colorless or light pink. Results 2.Examine and note the growth of E.coli on EMB agar medium which will be available as a demonstration.Most,if not all,E.coli strains display a green metallic sheen which is rather characteristic Images: Bacillis with endospores Clostridium perfringens and Clostridium perfringens on blood agar,with double zone of hemolysis Clostridium sporogenes on blood agar,with single zone hemolysis Clostridium perfringens gram stain Clostridium sporogenes gram stain showing endospore Litmus Milk test for Clostridium perfringens Escherichia coli.Proteus mirabilis,Pseudomonas aeruginosa Escherichia coli on blood agar Escherichia coli on EMB aga file://CJ/WINDOWS/Deskto b Lab Web 2001/Exercise3/exercise3.htm(6 of 7)[8/31/20024:30:07 PM]
API test system. The API Enterobacteriaceae Test System will be demonstrated. The procedure of this micro-method system is illustrated on the next page. SECOND SESSION. A. Enteric Gram-Negative Rods 1. Perform the Indole Spot Test with the various bacteria grown on M-H agar plate. The method requires that 2-3 drops of the reagent be placed on a piece of filter paper and a heavy bacterial mass be rubbed into this saturated area with an applicator stick. The appearance of a blue, blue-green, or red-violet color within 10 seconds-indicates indole production whereas negative reaction are colorless or light pink. Results 2. Examine and note the growth of E. coli on EMB agar medium which will be available as a demonstration. Most, if not all, E. coli strains display a green metallic sheen which is rather characteristic. Images: Bacillis with endospores Clostridium perfringens and Clostridium perfringens on blood agar, with double zone of hemolysis Clostridium sporogenes on blood agar, with single zone hemolysis Clostridium perfringens gram stain Clostridium sporogenes gram stain showing endospore Litmus Milk test for Clostridium perfringens Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa Escherichia coli on blood agar Escherichia coli on EMB agar Exercise 3 file:///C|/WINDOWS/Desktop/clown/Microb Lab Web 2001/Exercise3/exercise3.htm (6 of 7) [8/31/2002 4:30:07 PM]

Exercise3 Escherichia coli gram stain Indole test for Escherichia coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa on blood agar Pseudomonas aeruginosa on M-H aga Pseudomonas aeruginosa gram stain Indole test for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Oxidase test for Pseudomonas aeruginoso Proteus mirabilis on blood agar Proteus mirabilis on M-H agar Proteus mirabilis gram stain API enterobacteriaceae test file://CWINDOWS/Desktop/clown/Microb Lab Web 2001/Exercise3/exercise3.htm (7of7)[8/3/002 4:30:07 PM]
Escherichia coli gram stain Indole test for Escherichia coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa on blood agar Pseudomonas aeruginosa on M-H agar Pseudomonas aeruginosa gram stain Indole test for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Oxidase test for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Proteus mirabilis on blood agar Proteus mirabilis on M-H agar Proteus mirabilis gram stain API enterobacteriaceae test Exercise 3 file:///C|/WINDOWS/Desktop/clown/Microb Lab Web 2001/Exercise3/exercise3.htm (7 of 7) [8/31/2002 4:30:07 PM]

Excercise4 Bacteriology Quiz Instructions Unknown cultures will be distributed to students for examination and presumptive identification.Each student will receive two cultures a gm+cocci,a gm+rod,gm-rod)and will be required to answer the following questionnaire after some preliminary characterization. To obtain full credit for the identification of bacterial unknown,the answer sheet should be filled out using the following criteria: 1.Description of Specimen--What type of specimen(sputum,exudate,skin scraping)was used to isolate the etiologic agent and what type of infection does the patient have? Cultural Characteristics--Describe type of colonies including such things as pigmentation and the medium on which it is growing.Is there any hemolysis around colonies and what type? 3.Microscopic Characteristics--Describe gram reaction and morphological appearance of bacteria including arrangement(gram-positive rods in chains,for example). 4.Test Results--Choose relevant tests,perform these tests and report results(catalase,coagulase oxidase, etc.). 5.Presumptive Identification-All of the information above should enable one to presumptively identify the genus and perhaps the species of bacteria. 6 Tests Requested for Confirmation--What test would one request to confirm the presumptive identification(coagulase tube test,bacitracin sensitivity,optochin sensitivity,growth on bile esculin and fermentation tests,etc.)? file:///C/WINDOWS/Desktop/clown/Microb Lab Web 2001/Exercise4.htm(1 of 3)[8/31/2002 7:48:07 PM)
Bacteriology Quiz Instructions Unknown cultures will be distributed to students for examination and presumptive identification. Each student will receive two cultures ( a gm+ cocci, a gm+ rod, gm- rod) and will be required to answer the following questionnaire after some preliminary characterization. To obtain full credit for the identification of bacterial unknown, the answer sheet should be filled out using the following criteria: 1. Description of Specimen -- What type of specimen (sputum, exudate, skin scraping) was used to isolate the etiologic agent and what type of infection does the patient have? 2. Cultural Characteristics -- Describe type of colonies including such things as pigmentation and the medium on which it is growing. Is there any hemolysis around colonies and what type? 3. Microscopic Characteristics -- Describe gram reaction and morphological appearance of bacteria including arrangement (gram-positive rods in chains, for example). 4. Test Results -- Choose relevant tests, perform these tests and report results (catalase, coagulase, oxidase, etc.). 5. Presumptive Identification -- All of the information above should enable one to presumptively identify the genus and perhaps the species of bacteria. 6. Tests Requested for Confirmation -- What test would one request to confirm the presumptive identification (coagulase tube test, bacitracin sensitivity, optochin sensitivity, growth on bile esculin and fermentation tests, etc.)? Excercise4 file:///C|/WINDOWS/Desktop/clown/Microb Lab Web 2001/Exercise4.htm (1 of 3) [8/31/2002 7:48:07 PM]