Chapter 2 Cell Biology
Chapter 2 Cell Biology

2.1 Overview of the structure of microbial cells 2.2 Procaryotic cell wall 2.3 Cytoplasmic membrane 2.4 Cellular genetic information 2.5 Cytoplasmic matrix – Ribosome and Inclusions 2.6 Components external to the cell wall 2.7 Bacterial endospores 2.8 Comparison of the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell Chapter outline
2.1 Overview of the structure of microbial cells 2.2 Procaryotic cell wall 2.3 Cytoplasmic membrane 2.4 Cellular genetic information 2.5 Cytoplasmic matrix – Ribosome and Inclusions 2.6 Components external to the cell wall 2.7 Bacterial endospores 2.8 Comparison of the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell Chapter outline
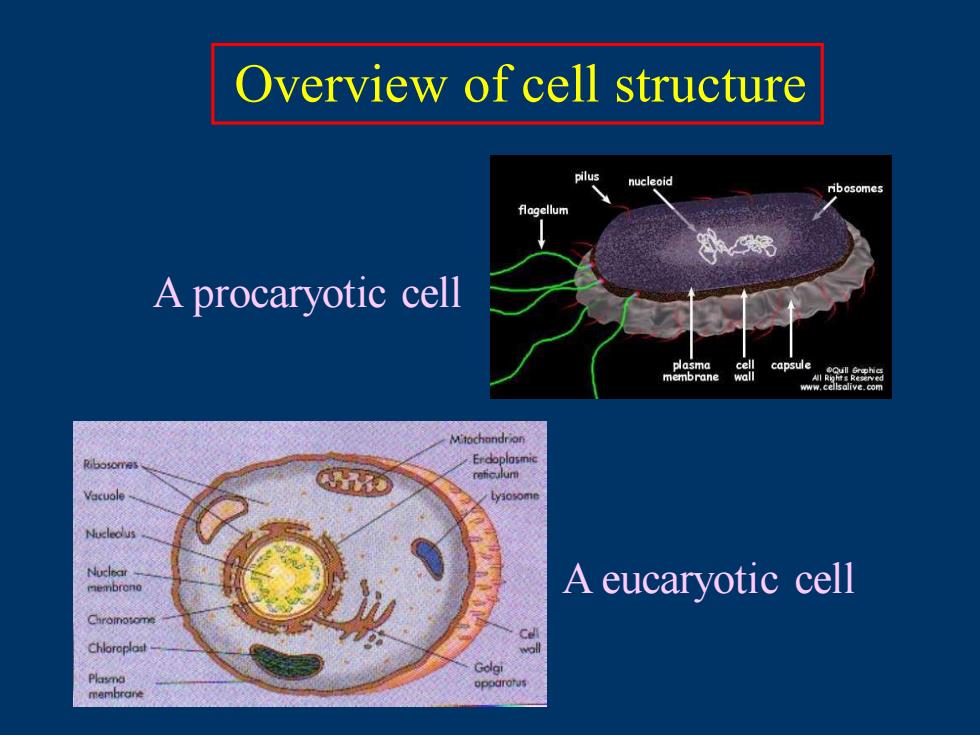
A procaryotic cell A eucaryotic cell Overview of cell structure
A procaryotic cell A eucaryotic cell Overview of cell structure

3. Their cell wall almost always contain the complex polysaccharide peptidoglycan The prokaryotic cell 1. Their genetic material (DNA) is not enclosed within a membrane and they lack other membrane – bounded organelles 2. Their DNA is not associated with histidine 4. They are very small!!
3. Their cell wall almost always contain the complex polysaccharide peptidoglycan The prokaryotic cell 1. Their genetic material (DNA) is not enclosed within a membrane and they lack other membrane – bounded organelles 2. Their DNA is not associated with histidine 4. They are very small!!
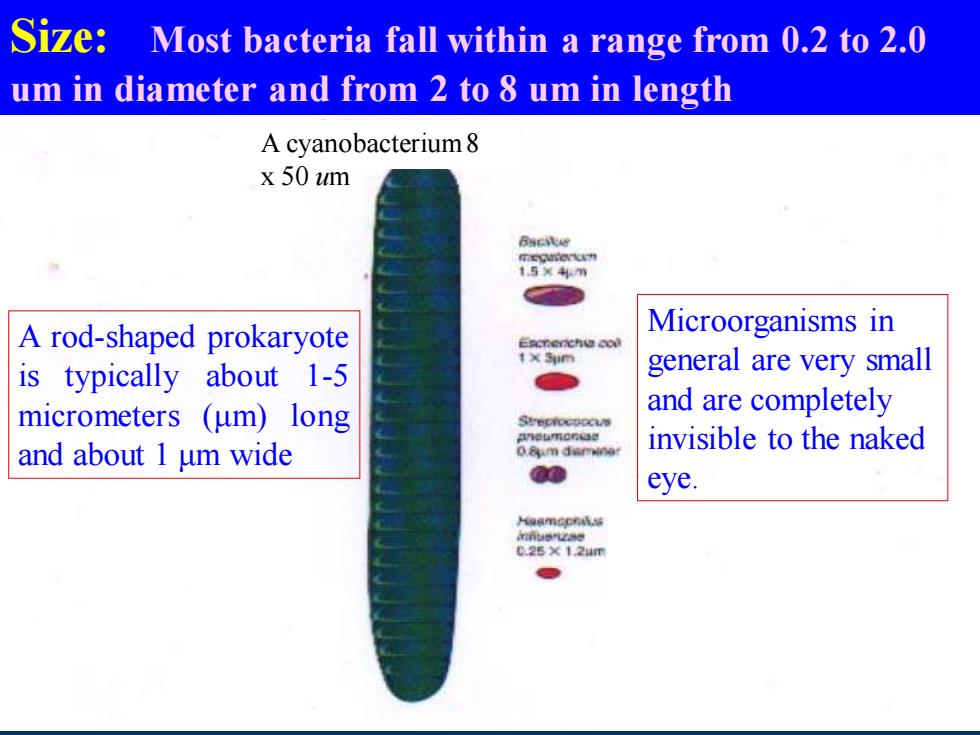
Size: Most bacteria fall within a range from 0.2 to 2.0 um in diameter and from 2 to 8 um in length A rod-shaped prokaryote is typically about 1-5 micrometers (μm) long and about 1 μm wide Microorganisms in general are very small and are completely invisible to the naked eye. A cyanobacterium 8 x 50 um
Size: Most bacteria fall within a range from 0.2 to 2.0 um in diameter and from 2 to 8 um in length A rod-shaped prokaryote is typically about 1-5 micrometers (μm) long and about 1 μm wide Microorganisms in general are very small and are completely invisible to the naked eye. A cyanobacterium 8 x 50 um