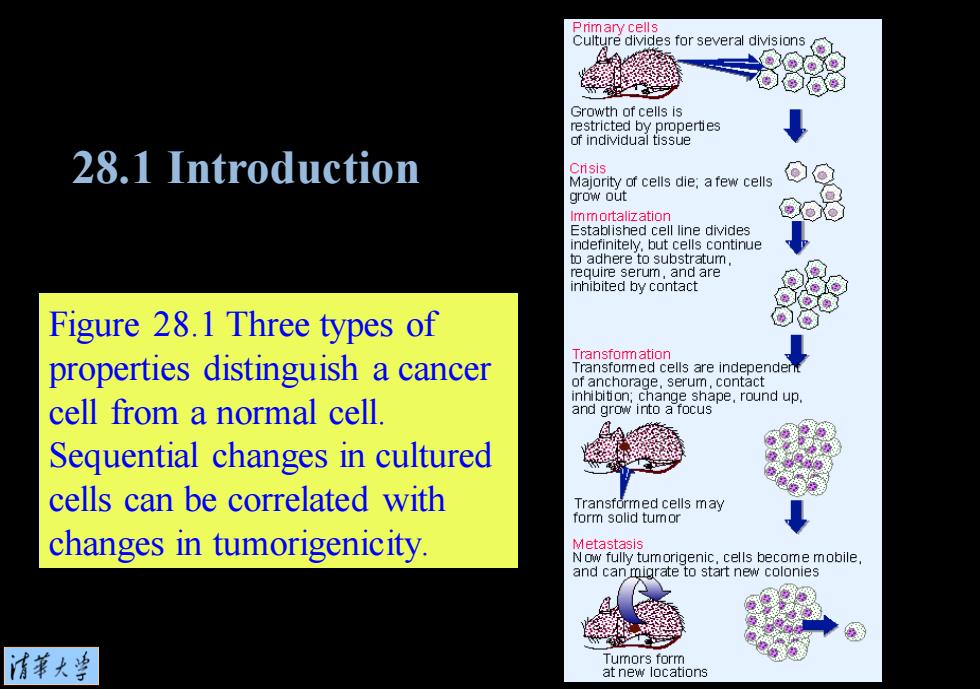
Primary cells Culture divides for several divisions Growth of cells is restricted by properties of individual tissue 28.1 Introduction Cnsis Majority of cells die;a few cells grow out Immortalization Established cell line divides indefinitely,but cells continue to adhere to substratum require serum,and are inhibited by contact Figure 28.1 Three types of properties distinguish a cancer Transfom ation Transfomed cells are independent of anchorage.serum.contact nhibiti on;change shape,round up cell from a normal cell and grow into a focus Sequential changes in cultured cells can be correlated with Transformed cells may form solid tumor changes in tumorigenicity. Metastasis Now fully tumorigenic,cells become mobile, and can migrate to start new colonies 清苇大当 Tumors form at new locations
Figure 28.1 Three types of properties distinguish a cancer cell from a normal cell. Sequential changes in cultured cells can be correlated with changes in tumorigenicity. 28.1 Introduction
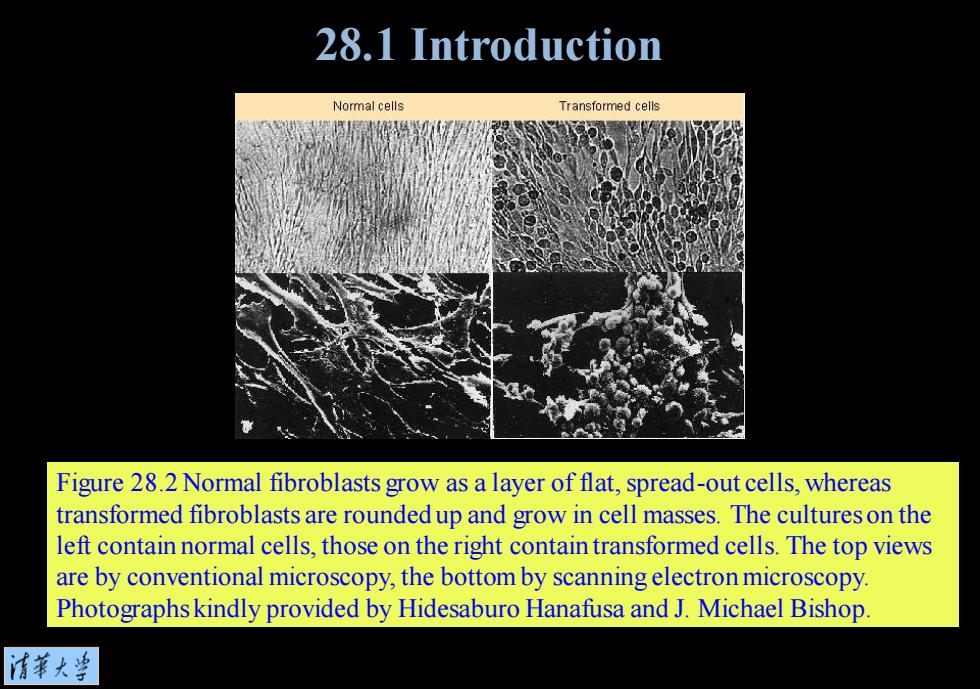
28.1 Introduction Normal cells Transformed cells Figure 28.2 Normal fibroblasts grow as a layer of flat,spread-out cells,whereas transformed fibroblasts are rounded up and grow in cell masses.The cultures on the left contain normal cells,those on the right contain transformed cells.The top views are by conventional microscopy,the bottom by scanning electron microscopy. Photographskindly provided by Hidesaburo Hanafusa and J.Michael Bishop. 情菜大当
Figure 28.2 Normal fibroblasts grow as a layer of flat, spread-out cells, whereas transformed fibroblasts are rounded up and grow in cell masses. The cultures on the left contain normal cells, those on the right contain transformed cells. The top views are by conventional microscopy, the bottom by scanning electron microscopy. Photographs kindly provided by Hidesaburo Hanafusa and J. Michael Bishop. 28.1 Introduction

28.2 Transforming viruses carry oncogenes Viral Class Genome Genome Size Oncogenes Origin of Oncogene Action of Onoogene Polyoma dsDNA 5-6kh T antigens Early viral gene inadivates tumor suppressor HPV dsDNA ~8kb E6&E7 Early viral gene inadivates tumor suppressor Adeno dsDNA ~37 kb E1A E1B Early viral gene inadivates tumor suppressor Retrovirus SSRNA 6-9kh Individual Cellular adivates oncogenic pathay (acute) Figure 28.3 Transforming viruses may carry oncogenes. 清菜大当
Figure 28.3 Transforming viruses may carry oncogenes. 28.2 Transforming viruses carry oncogenes
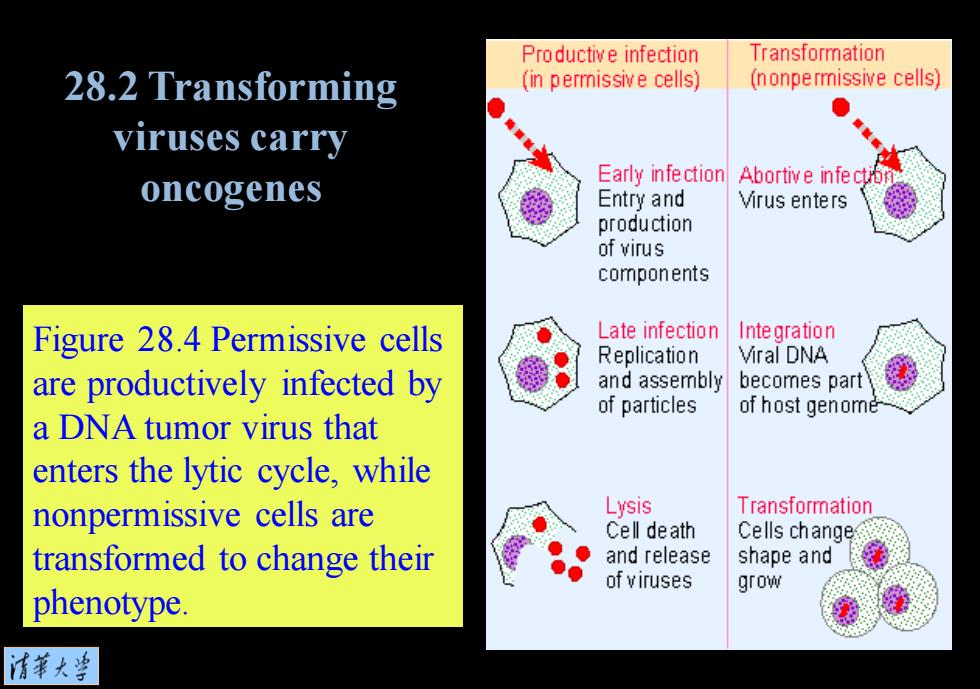
Productive infection Transformation 28.2 Transforming (in permissive cells) (nonpermissive cells) viruses carry Early infection Abortive infe ct oncogenes Entry and Virus enters production of virus components Figure 28.4 Permissive cells Late infection Integration Replication Viral DNA are productively infected by and assembly becomes part of particles of host genome a DNA tumor virus that enters the lytic cycle,while nonpermissive cells are Lysis Transformation Cell death Cells change transformed to change their and release shape and of viruses grow phenotype. 情菜大当
Figure 28.4 Permissive cells are productively infected by a DNA tumor virus that enters the lytic cycle, while nonpermissive cells are transformed to change their phenotype. 28.2 Transforming viruses carry oncogenes

28.2 Transforming late viruses carry SV40 oncogenes 价ANN Infection Adenovirus early late Figure 28.5 Cells 入10707020八N风M八N transformed by ↓ polyomaviruses or HOSt DNAROCOUU入入NN adenoviruses have viral Integratig sequences that include the N入八N入八NNNN入N early region integrated into the cellular genome.Sites of Transforming ogog integration are random. (onco-)protein SV40 T/t antigens Adenovirus E1A,E1B 清第大兰
Figure 28.5 Cells transformed by polyomaviruses or adenoviruses have viral sequences that include the early region integrated into the cellular genome. Sites of integration are random. 28.2 Transforming viruses carry oncogenes