
Some Explanatory Points Lung volume is to describe the changes of the lung volume during one breathing at static conditions,also called static lung volume. VT,VC,TLC are used at clinical.VT and VC are determined by Spirometric trace but FRC and RV by indirect method: Helium or Nitrogen analyses method
Some Explanatory Points Lung volume is to describe the changes of the lung volume during one breathing at static conditions, also called static lung volume. VT, VC, TLC are used at clinical. VT and VC are determined by Spirometric trace , but FRC and RV by indirect method: Helium or Nitrogen analyses method
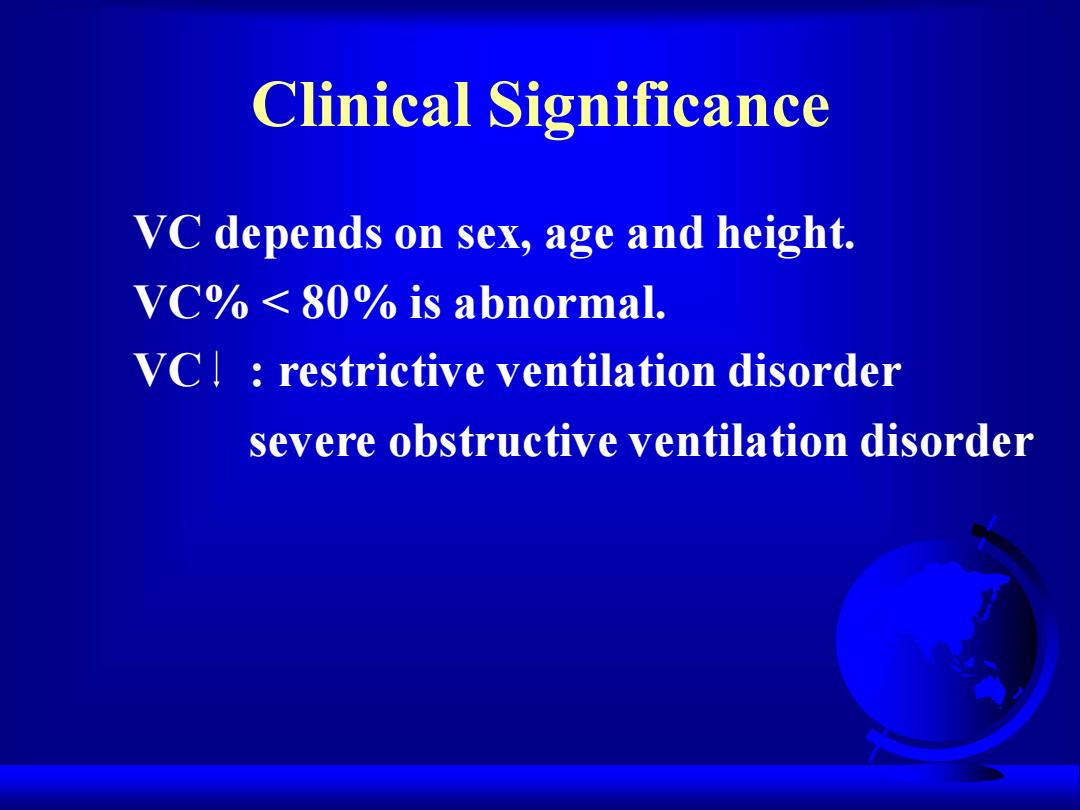
Clinical Significance VC depends on sex,age and height. VC%<80%is abnormal. VC restrictive ventilation disorder severe obstructive ventilation disorder
Clinical Significance VC depends on sex, age and height. VC% < 80% is abnormal. VC : restrictive ventilation disorder severe obstructive ventilation disorder
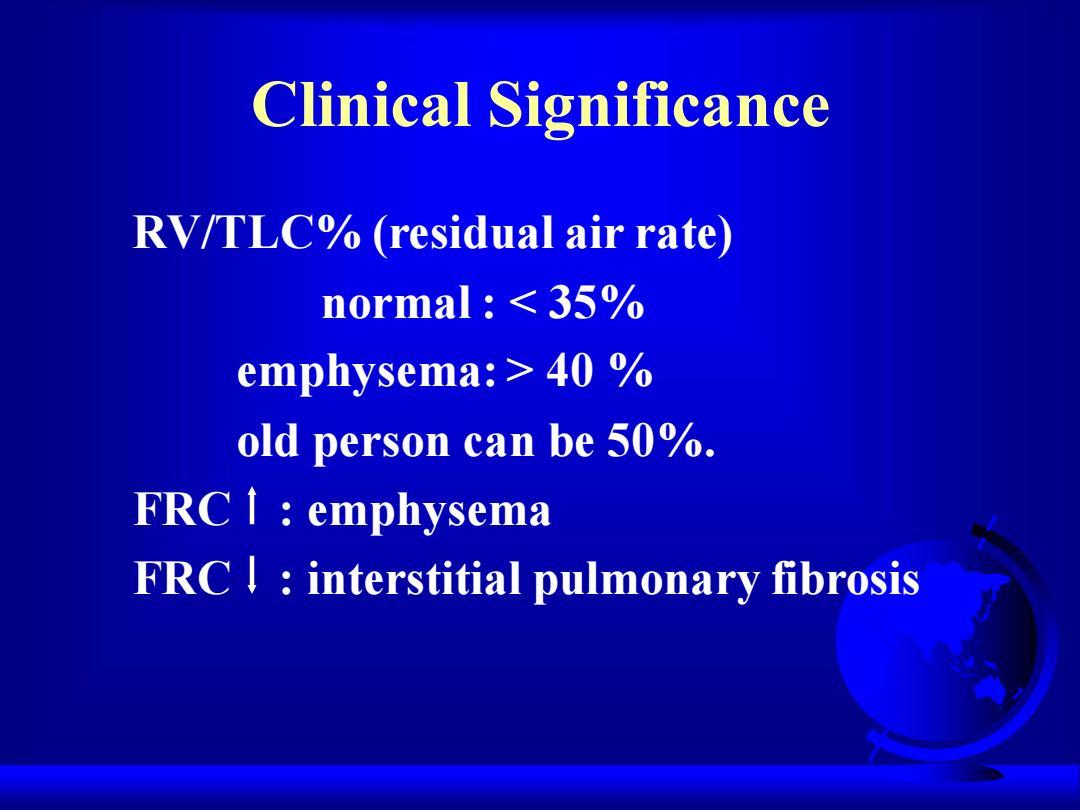
Clinical Significance RV/TLC%(residual air rate) normal 35% emphysema:40 old person can be 50%. FRC 1 emphysema FRC|interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
Clinical Significance RV/TLC% (residual air rate) normal : < 35% emphysema: > 40 % old person can be 50%. FRC : emphysema FRC : interstitial pulmonary fibrosis

Ventilation Function Test It is called as dynamic lung volumes. Fast spirometric trace to illustrate timed ventilation tests (air volume and air flow during breathing)
Ventilation Function Test It is called as dynamic lung volumes. Fast spirometric trace to illustrate timed ventilation tests (air volume and air flow during breathing)