
Chapter 2 7 Definition of“state Set of variables,with 2 properties: 1. Represent complete system info 2. If state is known at time to,it is possible to compute state for all future time. "Theory
7 Definition of “state” Set of variables, with 2 properties: 1. Represent complete system info 2. If state is known at time t0 , it is possible to compute state for all future time. Chapter 2

Chapter 2 8 Example:Differential Equation 3rd order system++3y=u 3 state variables (write as a vector): W≡ W2 ,w= W3 Theory
8 Example: Differential Equation • 3rd order system • 3 state variables (write as a vector): y y y y u 3 3 1 2 3 , w y w w w y w y Chapter 2
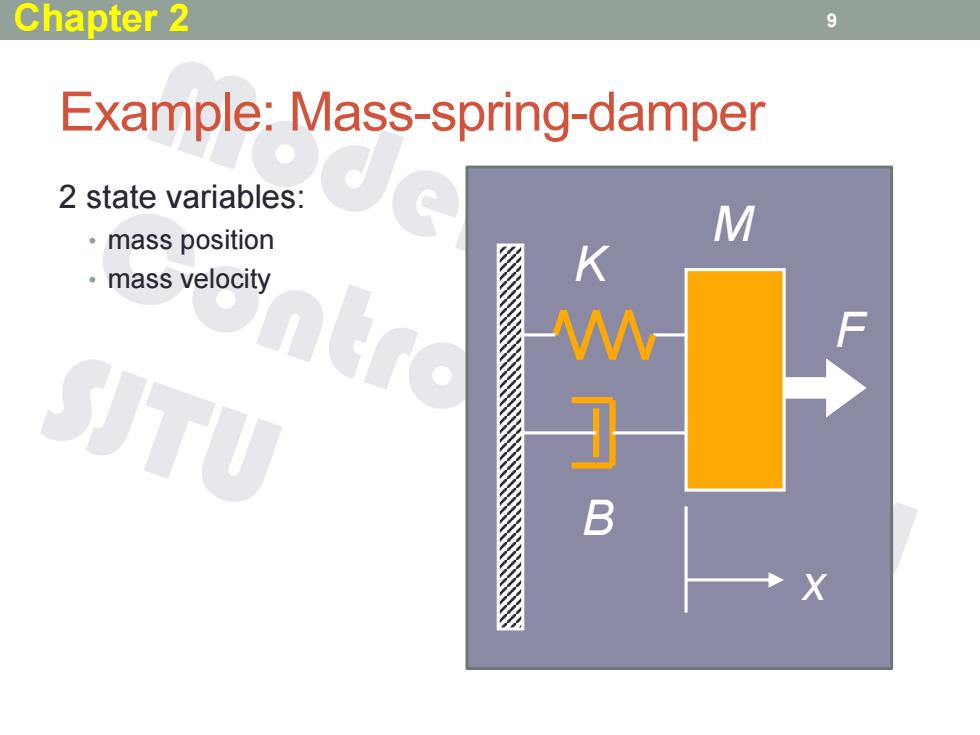
Chapter 2 9 Example:Mass-spring-damper 2 state variables: mass position M 。mass velocity K W SJTU B
9 Example: Mass-spring-damper B K M x F 2 state variables: • mass position • mass velocity Chapter 2

Chapter 2 10 Example:Mass-spring-damper 。2nd-order model M K M优+Bx+Kx=F SJTU B X
10 Example: Mass-spring-damper • 2nd-order model Mx Bx Kx F B K M x F Chapter 2
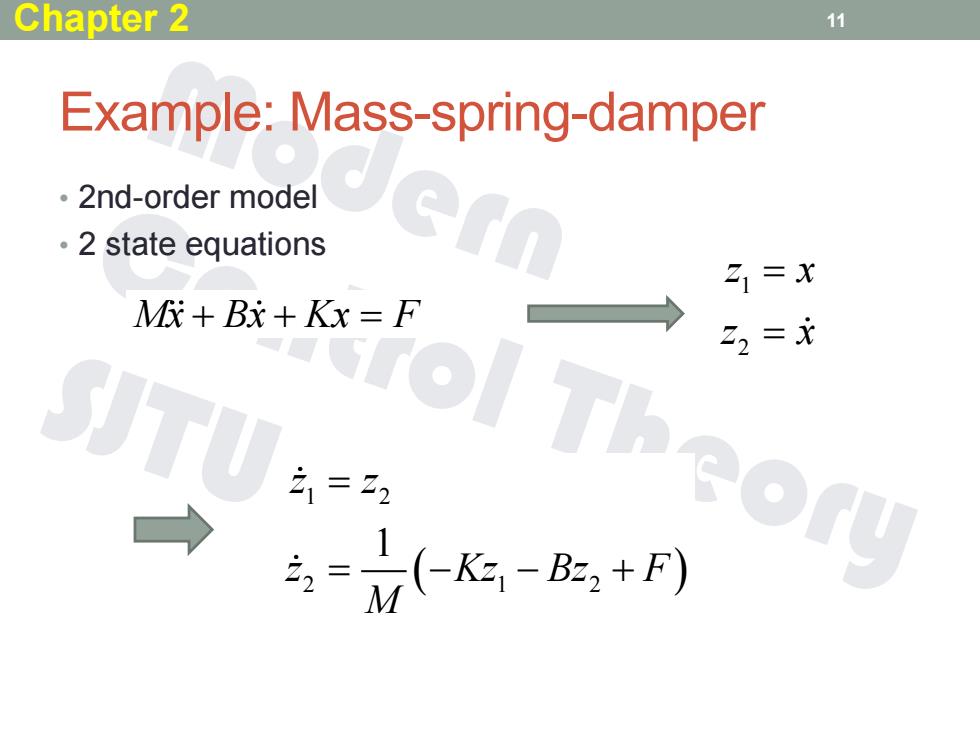
Chapter 2 11 Example:Mass-spring-damper 。2nd-order model 。2 state equations 21=X M优+Bx+Kx=F 22=X T 21=22 → ol Theory -人k-:+)
11 Example: Mass-spring-damper • 2nd-order model • 2 state equations 1 2 2 1 2 1 z z z Kz Bz F M 1 2 z x z x Mx Bx Kx F Chapter 2