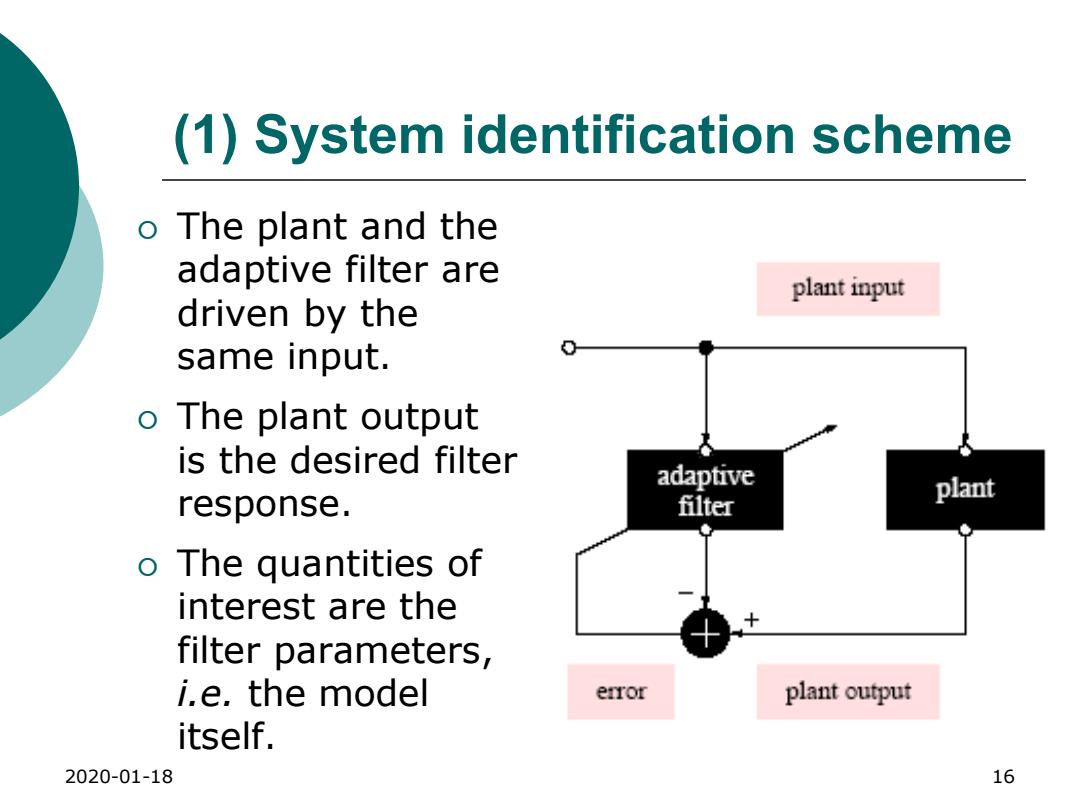
(1)System identification scheme o The plant and the adaptive filter are plant input driven by the same input. o The plant output is the desired filter adaptive response. filter plant o The quantities of interest are the filter parameters, i.e.the model error plant output itself. 2020-01-18 16
2020-01-18 16 (1) System identification scheme The plant and the adaptive filter are driven by the same input. The plant output is the desired filter response. The quantities of interest are the filter parameters, i.e. the model itself

Example o Channel dispersion introduces inter-symbol interference The signal received by a mobile is a filtered version of the original transmitted symbol sequence. o To undo the channel distortion,equalization is used at the receiver. Maximum likelihood symbol sequence estimator (Viterbi decoder)requires an (FIR)model of the channel distortion. 2020-01-18 17
2020-01-18 17 Example Channel dispersion introduces inter-symbol interference The signal received by a mobile is a filtered version of the original transmitted symbol sequence. To undo the channel distortion, equalization is used at the receiver. Maximum likelihood symbol sequence estimator (Viterbi decoder) requires an (FIR) model of the channel distortion
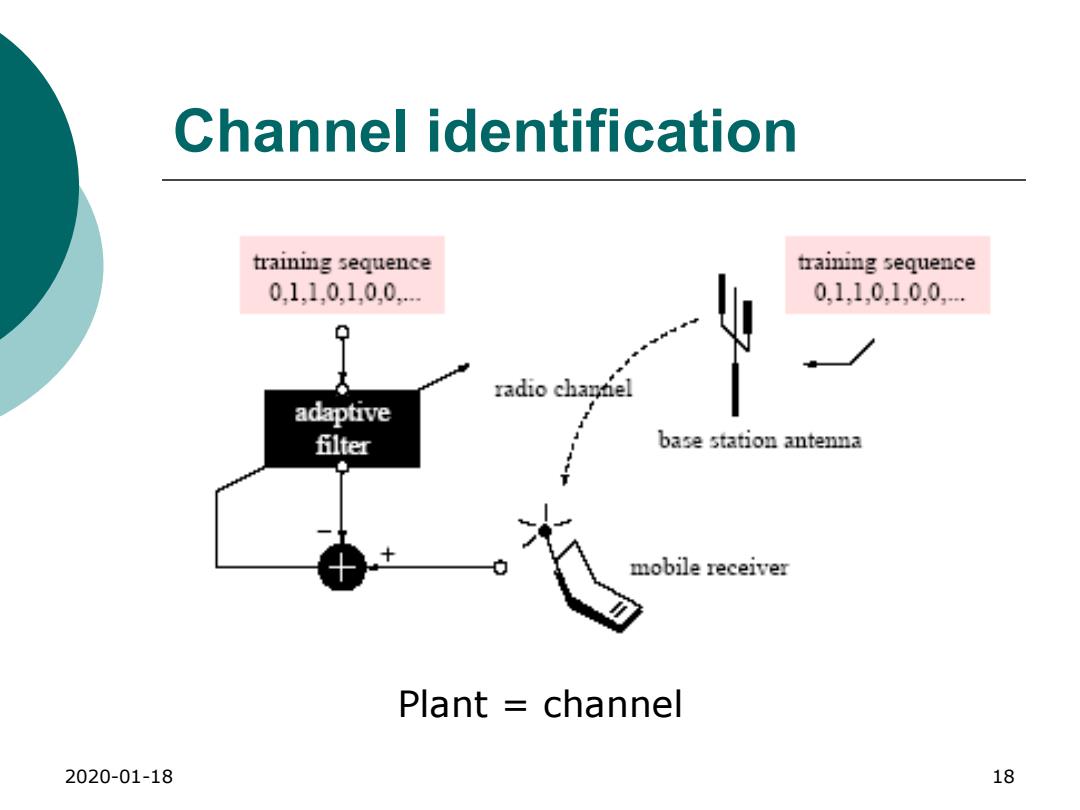
Channel identification training sequence training sequence 0,110,10,0. 0,110.10.0 N radio chantel adaptive filter base station antenna mobile receiver Plant channel 2020-01-18 18
2020-01-18 18 Channel identification Plant = channel
Training sequence:the desired signal o Transmitted periodically ● interleaved with the information symbols Defined in advance and so is known to the receiver and is used by the adaptive filtering algorithm as the desired signal o System identification The receiver sees the channel output and knows the corresponding channel input o This channel model can be used in the equalizer. 2020-01-18 19
2020-01-18 19 Training sequence: the desired signal Transmitted periodically interleaved with the information symbols Defined in advance and so is known to the receiver and is used by the adaptive filtering algorithm as the desired signal System identification The receiver sees the channel output and knows the corresponding channel input This channel model can be used in the equalizer

Blind system identification o Time-varying radio channel ●( Channel identification has to be repeated continuously o Training bits constitute a significant portion (roughly 17%)of the transmitted sequence GSM system is based on burst mode communication, where bursts of 148 bits each are transmitted.Each burst has a 26 bit training sequence,which is used to update the channel model. o Fewer training bits,or even without them blind identification/estimation 2020-01-18 20
2020-01-18 20 Blind system identification Time-varying radio channel Channel identification has to be repeated continuously Training bits constitute a significant portion (roughly 17%) of the transmitted sequence GSM system is based on burst mode communication, where bursts of 148 bits each are transmitted. Each burst has a 26 bit training sequence, which is used to update the channel model. Fewer training bits, or even without them blind identification/estimation