Centralized or Distributed Systems? ·Fact: 一 centralized systems are far simpler than distributed ones. But: -Fault-tolerance forces distribution -Physical position of sensors and computers also forces distribution -Efficiency sometimes requires distribution Real-Time Predictability Must ensure end-to-end deadlines are met before system deployment
Centralized or Distributed Systems? • Fact: – centralized systems are far simpler than distributed ones. • But: – Fault-tolerance forces distribution – Physical position of sensors and computers also forces distribution – Efficiency sometimes requires distribution • Real-Time Predictability – Must ensure end-to-end deadlines are met before system deployment

Distributed architecture USTC Temporal contracts Node Both the network and ECU resources are shared - Placing deadlines on each component network arbitration scheme Event Static(cyclic)scheduling Processing Message Message occurs begins generated ready for ·LIN ◆transmission Node response time Priority-based arbitration CAN(Controller Area Network) Network Source Event Node Node Destination Node Node Node Response Network Response Node Response End-to-End Deadline
Distributed architecture • Temporal contracts – Both the network and ECU resources are shared – Placing deadlines on each component • network arbitration scheme – Static (cyclic) scheduling • LIN – Priority-based arbitration • CAN (Controller Area Network) Source Node Destination Node
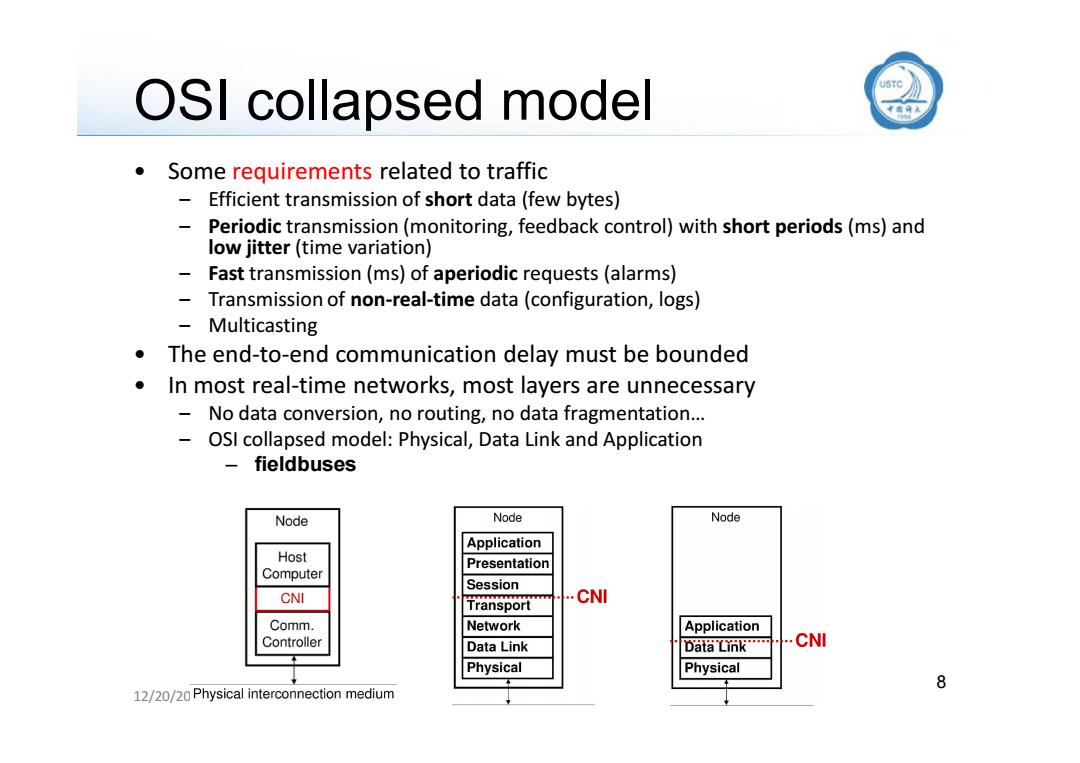
OSI collapsed model sc》 Some requirements related to traffic Efficient transmission of short data(few bytes) Periodic transmission(monitoring,feedback control)with short periods(ms)and low jitter(time variation) Fast transmission(ms)of aperiodic requests(alarms) Transmission of non-real-time data(configuration,logs) - Multicasting The end-to-end communication delay must be bounded In most real-time networks,most layers are unnecessary No data conversion,no routing,no data fragmentation... OSI collapsed model:Physical,Data Link and Application fieldbuses Node Node Node Application Host Presentation Computer Session CNI Transport CNI Comm. Network Application Controller Data Link Data Link CNI Physical Physical 8 12/20/20 Physical interconnection medium
8 12/20/2016 OSI collapsed model • Some requirements related to traffic – Efficient transmission of short data (few bytes) – Periodic transmission (monitoring, feedback control) with short periods (ms) and low jitter (time variation) – Fast transmission (ms) of aperiodic requests (alarms) – Transmission of non-real-time data (configuration, logs) – Multicasting • The end-to-end communication delay must be bounded • In most real-time networks, most layers are unnecessary – No data conversion, no routing, no data fragmentation… – OSI collapsed model: Physical, Data Link and Application – fieldbuses
Physical Layer features 》 In many cases low cost of the cabling scheme is fundamental! Is simplifies cabling Makes unnecessary for the protocol to perform routing -It facilitates a consistent reception of the same information in broadcast mode It facilitates the achievement of a consistent order in the reception of the messages. 9 12/20/2016
9 12/20/2016 Physical Layer features • In many cases low cost of the cabling scheme is fundamental! – Is simplifies cabling – Makes unnecessary for the protocol to perform routing – It facilitates a consistent reception of the same information in broadcast mode – It facilitates the achievement of a consistent order in the reception of the messages
Data Link Layer features USTC ·Addressing Direct addressing:The sender and receiver(s)are explicitly identified in every transaction,using physical addresses (as in Ethernet) - Indirect(source)addressing:The message contents are explicitly identified(e.g.temperature of sensor X).Receivers that need the message,retrieve it from the network(as in CAN and WorldFIP) Indirect(time-based)addressing:The message is identified by the time instantat which it is transmitted(as in TTP) Logical Link Control (LLC) transmission error control Medium Access Control (MAC) -Which is fundamental for RT response 10 12/20/2016
10 12/20/2016 Data Link Layer features • Addressing – Direct addressing: The sender and receiver(s) are explicitly identified in every transaction, using physical addresses (as in Ethernet) – Indirect (source) addressing: The message contents are explicitly identified (e.g. temperature of sensor X). Receivers that need the message, retrieve it from the network (as in CAN and WorldFIP) – Indirect (time-based) addressing: The message is identified by the time instantat which it is transmitted (as in TTP) • Logical Link Control (LLC) – transmission error control • Medium Access Control (MAC) – Which is fundamental for RT response