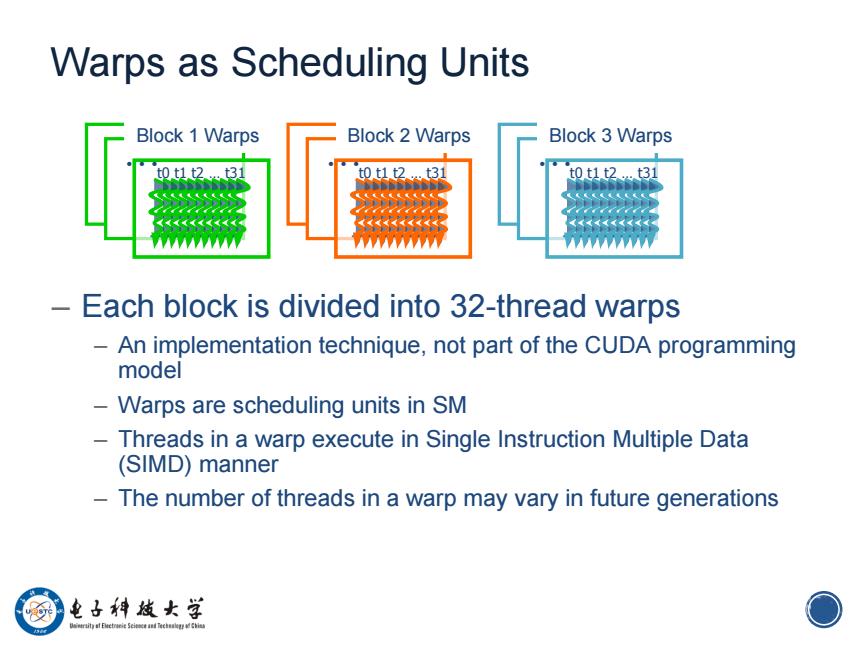
Warps as Scheduling Units Block 1 Warps Block 2 Warps Block 3 Warps t0t1t2.t31 0.t1t to t1 t2...t31 一 Each block is divided into 32-thread warps An implementation technique,not part of the CUDA programming model - Warps are scheduling units in SM Threads in a warp execute in Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD)manner The number of threads in a warp may vary in future generations 电子科妓女学 O
6 Warps as Scheduling Units – Each block is divided into 32-thread warps – An implementation technique, not part of the CUDA programming model – Warps are scheduling units in SM – Threads in a warp execute in Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) manner – The number of threads in a warp may vary in future generations … …t0 t1 t2 … t31 … …t0 t1 t2 … t31 Block 1 Warps Block 2 Warps … …t0 t1 t2 … t31 Block 3 Warps
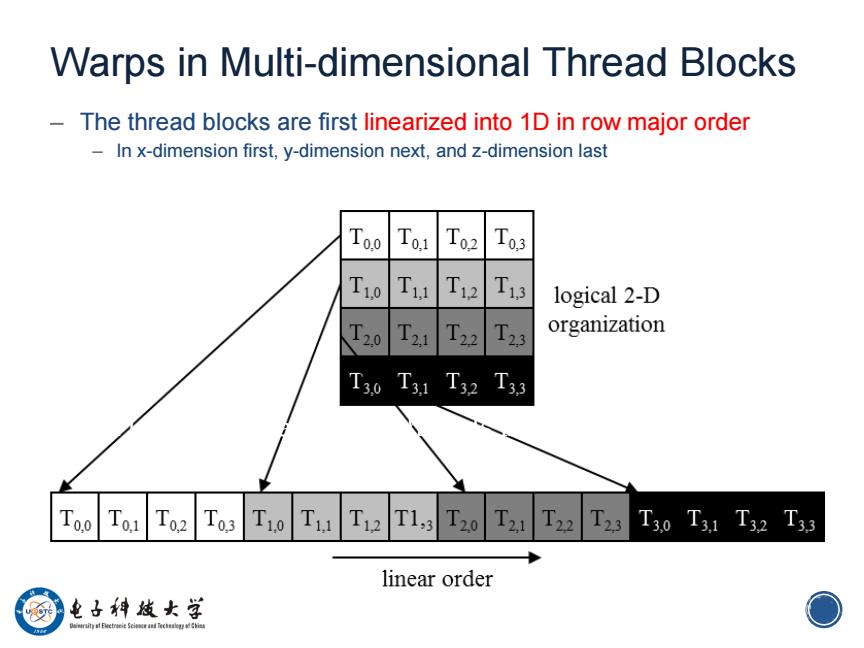
Warps in Multi-dimensional Thread Blocks The thread blocks are first linearized into 1D in row major order In x-dimension first,y-dimension next,and z-dimension last Too Tol T02 T03 T10 T11 T12 T13 logical 2-D T20 T21 T22 T23 organization T30T31T32T33 T00 T01 T02T031 T2T13T20 T21T22T23T30T31T32T33 linear order 例 电子神越女学 O
7 Warps in Multi-dimensional Thread Blocks – The thread blocks are first linearized into 1D in row major order – In x-dimension first, y-dimension next, and z-dimension last 7 Figure 6.1: Placing 2D threads into linear order

Blocks are partitioned after linearization Linearized thread blocks are partitioned Thread indices within a warp are consecutive and increasing Warp 0 starts with Thread 0 -Partitioning scheme is consistent across devices Thus you can use this knowledge in control flow However,the exact size of warps may change from generation to generation DO NOT rely on any ordering within or between warps If there are any dependencies between threads,you must _syncthreads()to get correct results(more later). 电子科妓女学
8 Blocks are partitioned after linearization – Linearized thread blocks are partitioned – Thread indices within a warp are consecutive and increasing – Warp 0 starts with Thread 0 – Partitioning scheme is consistent across devices – Thus you can use this knowledge in control flow – However, the exact size of warps may change from generation to generation – DO NOT rely on any ordering within or between warps – If there are any dependencies between threads, you must __syncthreads() to get correct results (more later)
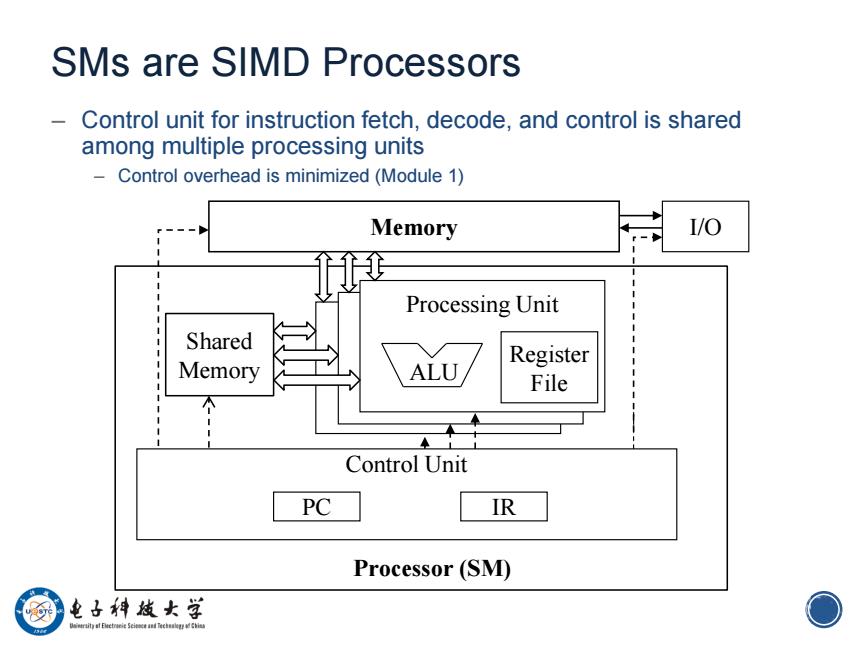
SMs are SIMD Processors Control unit for instruction fetch,decode,and control is shared among multiple processing units Control overhead is minimized (Module 1) Memory I/O Processing Unit Shared Memory ALU/ Register File Control Unit PC IR Processor (SM) 电子神越女学 Uaimraity at Eleetreie Scieeand Teclegd O
9 SMs are SIMD Processors – Control unit for instruction fetch, decode, and control is shared among multiple processing units – Control overhead is minimized (Module 1) Memory Processing Unit I/O ALU Processor (SM) Shared Memory Register File Control Unit PC IR
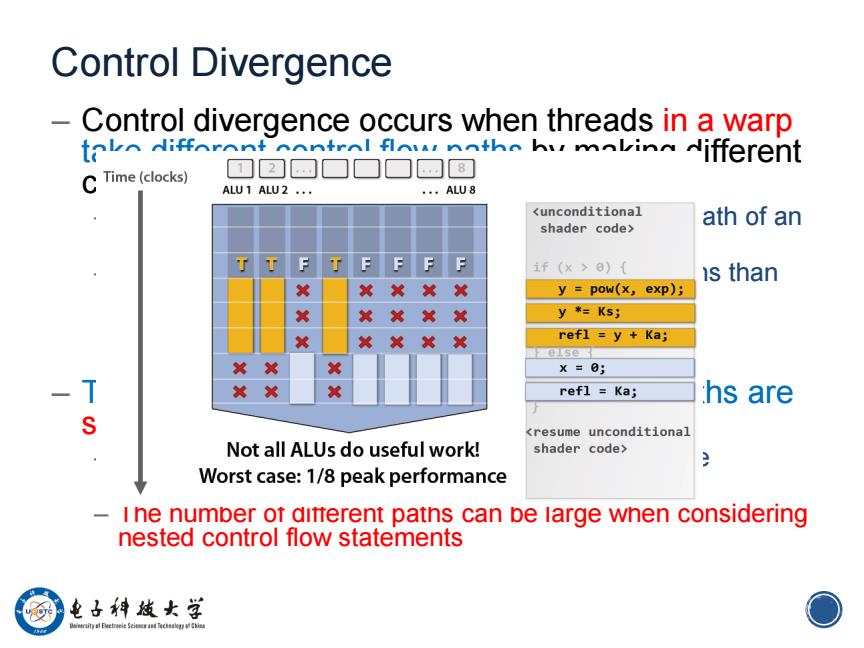
Control Divergence Control divergence occurs when threads in a warp toko Nifforont control flownth hy mokin Nifferent C Time(clocks) ALU1 ALU2 .. ·ALU8 <unconditional ath of an shader code> TT F T FFF P 1f(×>0)( is than X y pow(x,exp); X XX然 y *Ks; X XXXX refl =y Ka; else X然 X X=0; x refl Ka; hs are <resume unconditional Not all ALUs do useful work! shader code> Worst case:1/8 peak performance i ne numper ot ditterent patns can be large when considering nested control flow statements 电子神越女学 0
10 Control Divergence – Control divergence occurs when threads in a warp take different control flow paths by making different control decisions – Some take the then-path and others take the else-path of an if-statement – Some threads take different number of loop iterations than others – The execution of threads taking different paths are serialized in current GPUs – The control paths taken by the threads in a warp are traversed one at a time until there is no more. – The number of different paths can be large when considering nested control flow statements