
Measuring Demand Uncertainty Assume that demand for each period i,i=1,...,L is normally distributed with a mean D;and standard deviation oi Let pii be the correlation coefficient of demand between periods i and j. The total demand during L periods is normally distributed with a mean of D,.and a standard deviation of oL, Du=2n.L=V含+2grw SEIEE AU406 11
+ - SEIEE AU406 11 Measuring Demand Uncertainty Assume that demand for each period 𝑖, 𝑖 = 1, … , 𝐿 is normally distributed with a mean 𝐷𝑖and standard deviation 𝜎𝑖 Let 𝜌𝑖𝑗 be the correlation coefficient of demand between periods 𝑖 and 𝑗. The total demand during 𝐿 periods is normally distributed with a mean of 𝐷𝐿 and a standard deviation of 𝜎𝐿
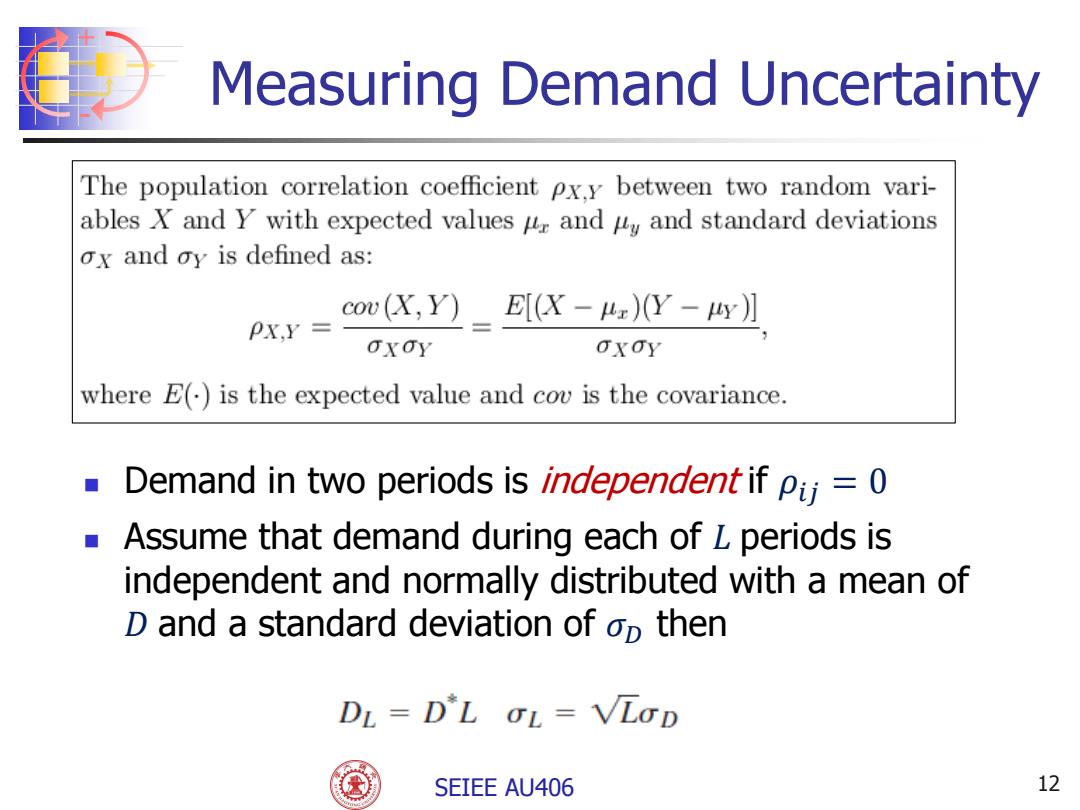
Measuring Demand Uncertainty The population correlation coefficient Px.y between two random vari- ables X and Y with expected values ur and y and standard deviations ox and oy is defined as: cov(X,Y) E[X-)Y-4y】 PX.Y= OxOY OxOY where E()is the expected value and cov is the covariance. Demand in two periods is independent if pii =0 Assume that demand during each of L periods is independent and normally distributed with a mean of D and a standard deviation of op then DL=D'L OL=VLOD SEIEE AU406 12
+ - SEIEE AU406 Demand in two periods is independent if 𝜌𝑖𝑗 = 0 Assume that demand during each of 𝐿 periods is independent and normally distributed with a mean of 𝐷 and a standard deviation of 𝜎𝐷 then 12 Measuring Demand Uncertainty
Measuring Product Availability Product availability:a firm's ability to fill a customer's order out of available inventory Stockout:a customer order arrives when product is not available Product fill rate (fr):fraction of demand that is satisfied from product in inventory Order fill rate:fraction of orders that are filled from available inventory Cycle service level:fraction of replenishment cycles that end with all customer demand met SEIEE AU406 13
+ - SEIEE AU406 13 Measuring Product Availability Product availability: a firm’s ability to fill a customer’s order out of available inventory Stockout: a customer order arrives when product is not available Product fill rate (fr): fraction of demand that is satisfied from product in inventory Order fill rate: fraction of orders that are filled from available inventory Cycle service level: fraction of replenishment cycles that end with all customer demand met
Replenishment Policies Replenishment policy:decisions regarding when to reorder and how much to reorder Continuous review:inventory is continuously monitored and an order of size Q is placed when the inventory level reaches the reorder point ROP Periodic review:inventory is checked at regular(periodic) intervals and an order is placed to raise the inventory to a specified threshold (the order-up-to"level) SEIEE AU406 14
+ - SEIEE AU406 14 Replenishment Policies Replenishment policy: decisions regarding when to reorder and how much to reorder Continuous review: inventory is continuously monitored and an order of size Q is placed when the inventory level reaches the reorder point ROP Periodic review: inventory is checked at regular (periodic) intervals and an order is placed to raise the inventory to a specified threshold (the “order-up-to” level)
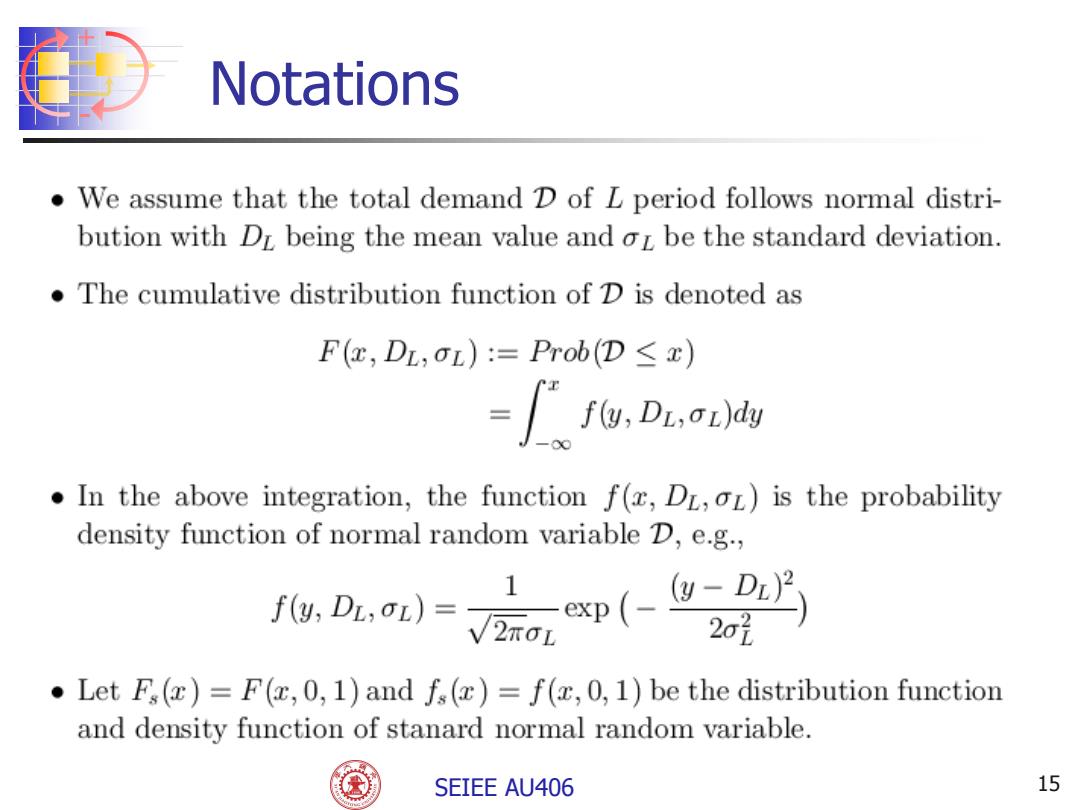
Notations We assume that the total demand D of L period follows normal distri- bution with DL being the mean value and oL be the standard deviation. The cumulative distribution function of D is denoted as F(,DL;OL):=Prob(D<t) =f,DLsat)dy In the above integration,the function f(,DL,oL)is the probability density function of normal random variable D,e.g., 0.-Vaw(-2 .Let Fs()=F(,0,1)and fs()=f(x,0,1)be the distribution function and density function of stanard normal random variable. SEIEE AU406 15
+ - SEIEE AU406 Notations 15