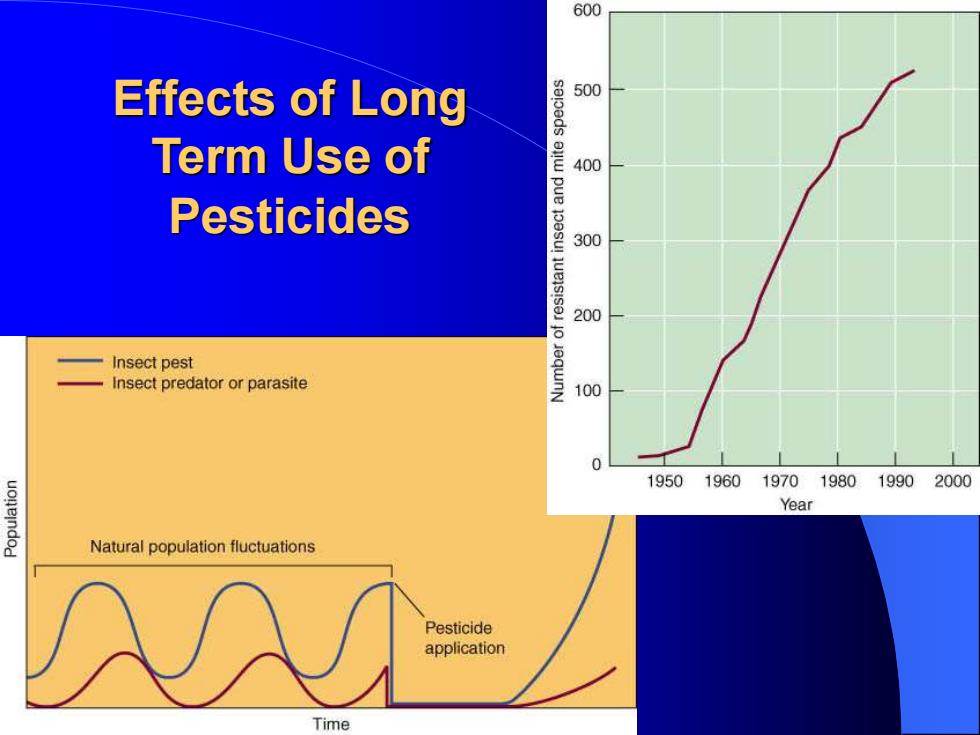
Effects of Long Term Use of Pesticides
Effects of Long Term Use of Pesticides
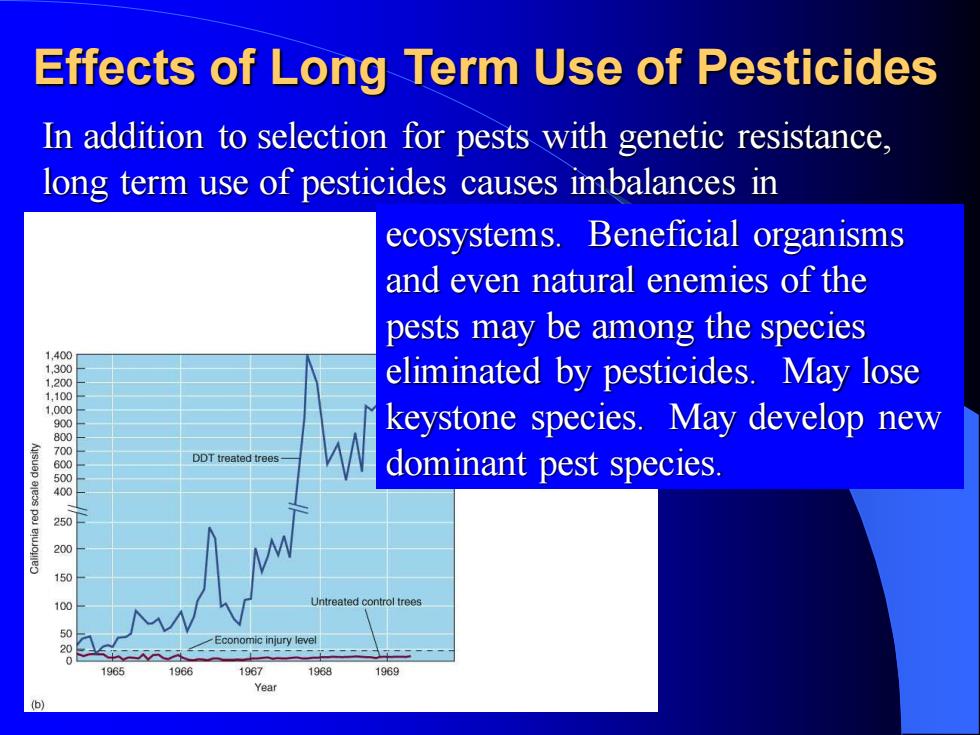
Effects of Long Term Use of Pesticides In addition to selection for pests with genetic resistance, long term use of pesticides causes imbalances in ecosystems. Beneficial organisms and even natural enemies of the pests may be among the species eliminated by pesticides. May lose keystone species. May develop new dominant pest species
Effects of Long Term Use of Pesticides In addition to selection for pests with genetic resistance, long term use of pesticides causes imbalances in ecosystems. Beneficial organisms and even natural enemies of the pests may be among the species eliminated by pesticides. May lose keystone species. May develop new dominant pest species
USA Loss of Crops to Pest Since 1940s there has been a 33 fold increase in use of pesticides in the USA. Percentage of USA Crops Lost Annually to Pest Interval Insects Diseases Weeds 1989 - 1999 13.0% 12.0% 12.0% 1974 13.0 12.0 8.0 1951 - 1960 12.9 12.2 8.5 1942 - 1951 7.1 10.5 13.8
USA Loss of Crops to Pest Since 1940s there has been a 33 fold increase in use of pesticides in the USA. Percentage of USA Crops Lost Annually to Pest Interval Insects Diseases Weeds 1989 - 1999 13.0% 12.0% 12.0% 1974 13.0 12.0 8.0 1951 - 1960 12.9 12.2 8.5 1942 - 1951 7.1 10.5 13.8

Effects of Long Term Use of Pesticides In 1987 the American Consumers Union compiled a list of 50 active ingredients of pesticides used around the home and found that 66% had been inadequately tested to determine whether they could cause cancer, 72% inadequately test for mutations, 62% for birth defects, 64% for adverse effects on reproduction, and 98% for neurobehavioral effects. Human exposure to pesticides produces cancers, deaths (~67,000/year in USA), sterility, and endocrine disorders. Persistence of man-made pesticides in the environment indicates a long term environmental issue
Effects of Long Term Use of Pesticides In 1987 the American Consumers Union compiled a list of 50 active ingredients of pesticides used around the home and found that 66% had been inadequately tested to determine whether they could cause cancer, 72% inadequately test for mutations, 62% for birth defects, 64% for adverse effects on reproduction, and 98% for neurobehavioral effects. Human exposure to pesticides produces cancers, deaths (~67,000/year in USA), sterility, and endocrine disorders. Persistence of man-made pesticides in the environment indicates a long term environmental issue

Alternatives to Pesticides 1. Rotation of crops and interplanting of alternate rows of different crops. 2. Biological controls - use of natural predators or parasites. 3. Sterile male technique. 4. Pheromone and hormone lures. 5. Genetically modified plants (e.g., Bt plants). 6. Quarantine and post harvest irradiation
Alternatives to Pesticides 1. Rotation of crops and interplanting of alternate rows of different crops. 2. Biological controls - use of natural predators or parasites. 3. Sterile male technique. 4. Pheromone and hormone lures. 5. Genetically modified plants (e.g., Bt plants). 6. Quarantine and post harvest irradiation