
Experiment 1 Properties of the Optical Grating A diffraction grating is an optical component where dispersion happens by theory of diffraction.It consists of large numbers of parallel,equilateral,equidistant slits (or nicks).Based on diffraction gratings,the spectrograph or monochrometer is one of the basic optical spectrum instruments.It has been widely used in the study of the spectrum structure,the wavelength,intensity of the characteristic spectrum,especially the structure of matter and the qualitative/quantitative elemental analysis.In this experiment,the wavelengths of the spectral lines of sodium lamp and mercury lamp have been measured by virtue of the diffraction of grating.The diffraction angles can be measured by optical goniometer. Optical goniometer is a typical optical instrument that can accurately measure the angle, usually being used to measure refractive index,wavelength,dispersion rate and to observe spectrum and so on.Because of the high precision and complexity of this device,we must adjust the goniometer strictly according to certain rules to get accurate results.The ideas,methods and techniques of the optical goniometer are typical in optical instruments which is helpful to handle the operation of more complex optical instruments. 【Objectives】 1.The basic operations on the optical goniometer. 2.Measure the vertex angle of the prism. 3. Observe the dispersion phenomenon of the mercury lamp using the prism. Measure the characteristic parameters of the grating 5. Understand the diffraction phenomena in the grating 6. Measure the wavelength of the spectral lines in the visible spectrum region of sodium lamp and mercury lamp. 【Principle】 1.How to measure the vertex angle of the prism Prism is shown in the figure 1.Its cross-section is equilateral triangle.Surface ABD and ACD are nonopaque optical surface. The angle between those surfaces is called vertex angle of prism; Other surface is the frosted glass surface which is called bottom surface. (1)Auto-corrected method B 你èΨ Figure 2 shows the schematic of using auto-corrected method to measure the vertex angle of prism.Use the telescope Figure 1 Prism itself to produce parallel light.First,rotating the telescope (or platform)to let the reflected"image of surface ABD fall on the up-cross point of+"on the reticule.At this condition,the optical axis of the telescope is perpendicular to the ABD surface. Write down the angle0 02 read on the dial.Second,rotate the telescope to let the reflected" image from surface ACD coincident with the up-cross point of+,write down the number0 and 02'.We can get the vertex angle a=180- p=2g+p,)=2K-0)+(g-8,】 (1) (2)Reflection method Figure 3 shows the schematic of using reflection method to measure the vertex angle of prism. Put the prism on the platform and let the parallel light from the collimator shot onto the two surfaces of prism.The reflected light from left side can be observed at position I using the telescope.Adjust the fine-tuning screw of telescope to make the vertical line of+"overlap with the reflected image of the slit.Write down the angle and 2.Rotate the telescope to position II and carry out the same procedure to get angle 'and 2'.We have vertex angle:
1 Experiment 1 Properties of the Optical Grating A diffraction grating is an optical component where dispersion happens by theory of diffraction. It consists of large numbers of parallel, equilateral, equidistant slits (or nicks). Based on diffraction gratings, the spectrograph or monochrometer is one of the basic optical spectrum instruments. It has been widely used in the study of the spectrum structure, the wavelength, intensity of the characteristic spectrum, especially the structure of matter and the qualitative/quantitative elemental analysis. In this experiment, the wavelengths of the spectral lines of sodium lamp and mercury lamp have been measured by virtue of the diffraction of grating. The diffraction angles can be measured by optical goniometer. Optical goniometer is a typical optical instrument that can accurately measure the angle, usually being used to measure refractive index, wavelength, dispersion rate and to observe spectrum and so on. Because of the high precision and complexity of this device, we must adjust the goniometer strictly according to certain rules to get accurate results. The ideas, methods and techniques of the optical goniometer are typical in optical instruments which is helpful to handle the operation of more complex optical instruments. 【Objectives】 1. The basic operations on the optical goniometer. 2. Measure the vertex angle of the prism. 3. Observe the dispersion phenomenon of the mercury lamp using the prism. 4. Measure the characteristic parameters of the grating. 5. Understand the diffraction phenomena in the grating. 6. Measure the wavelength of the spectral lines in the visible spectrum region of sodium lamp and mercury lamp. 【Principle】 1. How to measure the vertex angle of the prism Prism is shown in the figure 1. Its cross-section is equilateral triangle. Surface ABD and ACD are nonopaque optical surface. The angle between those surfaces is called vertex angle of prism; Other surface is the frosted glass surface which is called bottom surface. (1)Auto-corrected method Figure 2 shows the schematic of using auto-corrected method to measure the vertex angle of prism. Use the telescope itself to produce parallel light. First, rotating the telescope (or platform) to let the reflected “十” image of surface ABD fall on the up-cross point of “╪”on the reticule. At this condition, the optical axis of the telescope is perpendicular to the ABD surface. Write down the angle θ1、θ2 read on the dial. Second, rotate the telescope to let the reflected “十” image from surface ACD coincident with the up-cross point of “╪”, write down the number θ 1 and θ2′. We can get the vertex angle α=180°-ϕ [ ] 2 1 2 1 ϕ = (ϕ1 +ϕ 2 )= (θ1 ′ −θ1 )+(θ 2 ′ −θ 2 ) (1) (2)Reflection method Figure 3 shows the schematic of using reflection method to measure the vertex angle of prism. Put the prism on the platform and let the parallel light from the collimator shot onto the two surfaces of prism. The reflected light from left side can be observed at position I using the telescope. Adjust the fine-tuning screw of telescope to make the vertical line of “╪” overlap with the reflected image of the slit. Write down the angle ϕ1 and ϕ2. Rotate the telescope to position II and carry out the same procedure to get angle ϕ1′and ϕ2′. We have vertex angle: Figure 1 Prism D

a=g=2[g-m)+(g-0】 (2) 24 B A Figure2 Auto-corrected method Figure 3 Reflection method 2.Measure the refractive index from the minimum angle of deviation of the monochromatic light We can determine the refractive index n through the reflection and refraction laws of light n=sinh sin(omin +a) 2 (3) siniz sin i,i2,omin are the angle of incidence,angle of refraction and the minimum angle of deviation of a certain monochromatic light,respectively.a is the vertex angle of prism. 3.Grating diffraction As shown in figure 4,a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure,which consists of large numbers of parallel,equidistant slits. A grating assume the number of slits is N,the width of a slit is a,the width of an aphotic zone between two slits is b,then the distance between two slits is d=a+b that is defined as the grating constant. According to the Fraunhofer diffraction theory, when a beam of parallel light is incident perpendicularly onto a grating,optical interference occurs between each slit and at the same time diffraction occurs in each slit.N sets of the Figure 4 light path of the diffraction of diffraction pattern from N slits will overlap perfectly grating after passing through the optical lens.In Fig.1,when the angle of diffraction satisfies the grating equation dsin=-k(k=O,±l,±2,-),two light beams from any two slits are constructive interference and results in a very sharp and bright principal maximum stripe. 4.Grating spectrum A set of the sharp and bright principal maximum stripes formed by the grating diffraction of the monochromatic light is called the grating diffraction spectrum of this monochromatic light. If we use a polychromatic light,the angular position of the spectral line with the same order
2 [( ) ( )] 4 1 2 ϕ1 ϕ1 ϕ 2 ϕ 2 ϕ α = = ′ − + ′ − (2) 2.Measure the refractive index from the minimum angle of deviation of the monochromatic light We can determine the refractive index n through the reflection and refraction laws of light α δ α 2 1 sin ( ) 2 1 sin sin sin min 2 1 + = = i i n (3) i1,i2,δmin are the angle of incidence, angle of refraction and the minimum angle of deviation of a certain monochromatic light, respectively. α is the vertex angle of prism. 3. Grating diffraction As shown in figure 4, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure, which consists of large numbers of parallel, equidistant slits. A grating assume the number of slits is N, the width of a slit is a, the width of an aphotic zone between two slits is b, then the distance between two slits is d=a+b that is defined as the grating constant. According to the Fraunhofer diffraction theory, when a beam of parallel light is incident perpendicularly onto a grating, optical interference occurs between each slit and at the same time diffraction occurs in each slit. N sets of the diffraction pattern from N slits will overlap perfectly after passing through the optical lens. In Fig. 1, when the angle of diffraction satisfies the grating equation dsinθ=kλ (k=0, +1, +2, …), two light beams from any two slits are constructive interference and results in a very sharp and bright principal maximum stripe. 4. Grating spectrum A set of the sharp and bright principal maximum stripes formed by the grating diffraction of the monochromatic light is called the grating diffraction spectrum of this monochromatic light. If we use a polychromatic light, the angular position of the spectral line with the same order θ d O d P Figure 4 light path of the diffraction of grating Figure 2 Auto-corrected method Figure 3 Reflection method
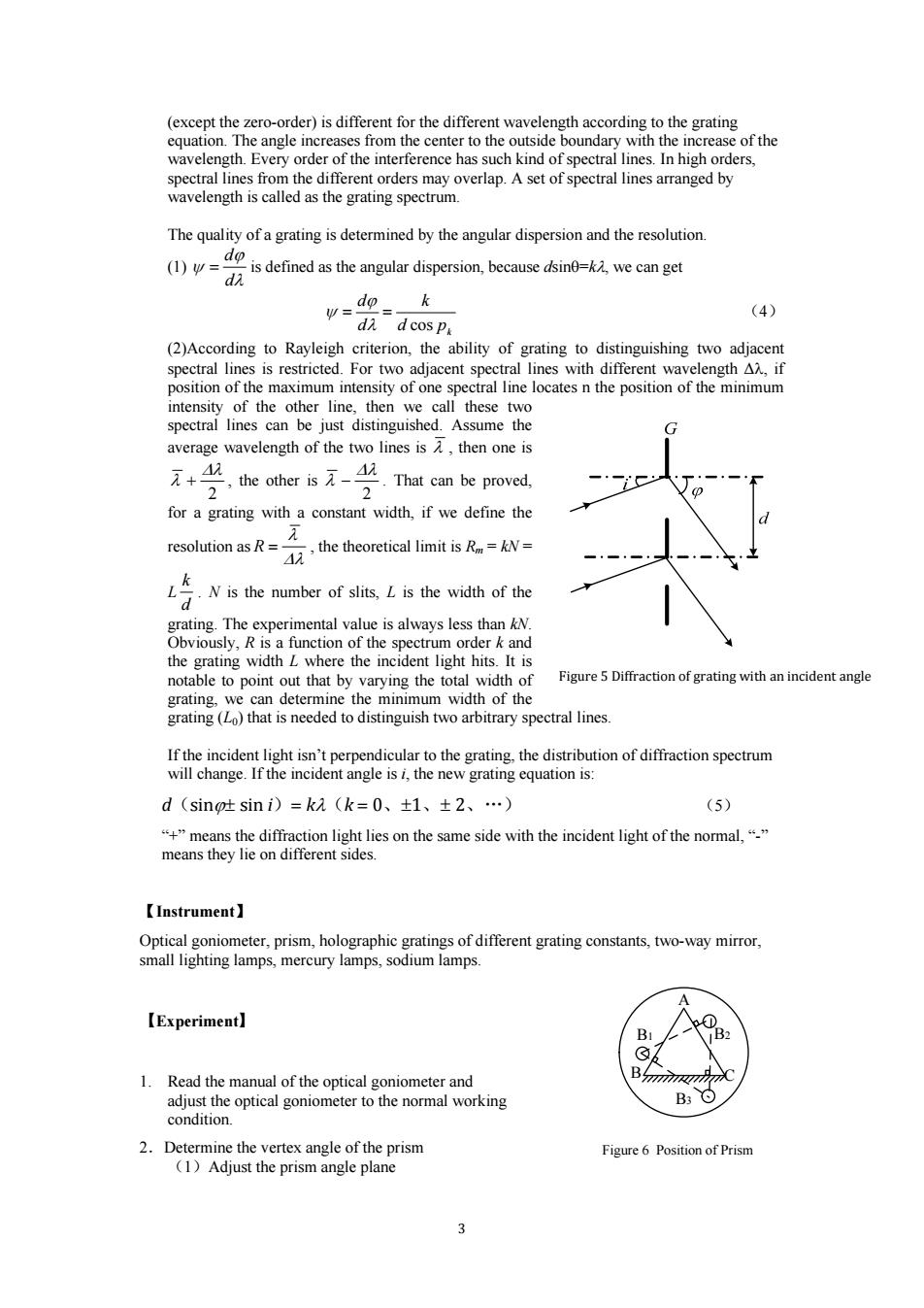
(except the zero-order)is different for the different wavelength according to the grating equation.The angle increases from the center to the outside boundary with the increase of the wavelength.Every order of the interference has such kind of spectral lines.In high orders, spectral lines from the different orders may overlap.A set of spectral lines arranged by wavelength is called as the grating spectrum. The quality of a grating is determined by the angular dispersion and the resolution. d. (1)w= is defined as the angular dispersion,because dsin=k,we can get d w=d迎=k (4) di dcos p (2)According to Rayleigh criterion,the ability of grating to distinguishing two adjacent spectral lines is restricted.For two adjacent spectral lines with different wavelength AA,if position of the maximum intensity of one spectral line locates n the position of the minimum intensity of the other line,then we call these two spectral lines can be just distinguished.Assume the G average wavelength of the two lines is A,then one is 2,the other is元-42 元+4 2 That can be proved, for a grating with a constant width,if we define the resolution as R=- the theoretical limit iskN N is the number of slits,L is the width of the grating.The experimental value is always less than kN. Obviously,R is a function of the spectrum order k and the grating width L where the incident light hits.It is notable to point out that by varying the total width of Figure 5 Diffraction of grating with an incident angle grating,we can determine the minimum width of the grating(Lo)that is needed to distinguish two arbitrary spectral lines. If the incident light isn't perpendicular to the grating,the distribution of diffraction spectrum will change.If the incident angle is i,the new grating equation is: d(sin吐sini)=k(k=0、±1、±2、…) (5) “+”means the diffraction light lies on the same side with the incident light of the normal,.“_” means they lie on different sides. 【Instrument】 Optical goniometer,prism,holographic gratings of different grating constants,two-way mirror, small lighting lamps,mercury lamps,sodium lamps. 【Experiment] Bi 1.Read the manual of the optical goniometer and adjust the optical goniometer to the normal working B3 ⊙ condition 2.Determine the vertex angle of the prism Figure 6 Position of Prism (1)Adjust the prism angle plane
3 (except the zero-order) is different for the different wavelength according to the grating equation. The angle increases from the center to the outside boundary with the increase of the wavelength. Every order of the interference has such kind of spectral lines. In high orders, spectral lines from the different orders may overlap. A set of spectral lines arranged by wavelength is called as the grating spectrum. The quality of a grating is determined by the angular dispersion and the resolution. (1) λ ϕ ψ d d = is defined as the angular dispersion, because dsinθ=kλ, we can get k d p k d d cos = = λ ϕ ψ (4) (2)According to Rayleigh criterion, the ability of grating to distinguishing two adjacent spectral lines is restricted. For two adjacent spectral lines with different wavelength Δλ, if position of the maximum intensity of one spectral line locates n the position of the minimum intensity of the other line, then we call these two spectral lines can be just distinguished. Assume the average wavelength of the two lines is λ , then one is 2 Δλ λ + , the other is 2 Δλ λ − . That can be proved, for a grating with a constant width, if we define the resolution as Δλ λ R = , the theoretical limit is Rm = kN = L d k . N is the number of slits, L is the width of the grating. The experimental value is always less than kN. Obviously, R is a function of the spectrum order k and the grating width L where the incident light hits. It is notable to point out that by varying the total width of grating, we can determine the minimum width of the grating (L0) that is needed to distinguish two arbitrary spectral lines. If the incident light isn’t perpendicular to the grating, the distribution of diffraction spectrum will change. If the incident angle is i, the new grating equation is: d(sinϕ± sin i)= kλ(k = 0、±1、± 2、…) (5) “+” means the diffraction light lies on the same side with the incident light of the normal, “-” means they lie on different sides. 【Instrument】 Optical goniometer, prism, holographic gratings of different grating constants, two-way mirror, small lighting lamps, mercury lamps, sodium lamps. 【Experiment】 1. Read the manual of the optical goniometer and adjust the optical goniometer to the normal working condition. 2.Determine the vertex angle of the prism (1)Adjust the prism angle plane Figure 5 Diffraction of grating with an incident angle B1 A B C B2 B3 Figure 6 Position of Prism

Put the prism on the loading platform and use the two refractive surfaces of prism instead of the two reflecting surfaces of the two-way mirror.Use auto-correcting method to adjust by the telescope that has already been adjusted.In order to facilitate adjustment.the prism in the position of the loading platform can refer to figure 6. Adjust the loading platform to make the AB surface target to the telescope.Adjusting the screws B2 of the platform,make the up-cross point of+"and the reflected""image has nearly half of the coincidence.Spinning the stage again,make the other refractive surface AC of the prism target to the telescope,adjust until correct.Repeat the checking several times, until the two reflective surfaces both correct when rotating the platform (2)After the adjustment,measure the vertex angle of the prism using the reflection method, repeated six times to find the average of the vertex angle,calculate the uncertainty and show the accurate measurement results.Make the data excel by yourself. 3.observe the dispersion phenomenon of the prism to the mercury lamp (Selected as the content) (1)Prism placed in the loading platform,the optical goniometer collimator pointed at the exit window of the low pressure mercury lamp,let the strongest and uniform light emit from the collimator. (2)Seen from figure 7,observe light bias situation to determine the refraction of light outgoing directions.Along the outgoing direction of light may be observed with your eyes first, slightly rotating the disc of scale to drive the platform when observed shot of the color spectrum, finds a monochromatic spectrum,continue to scale disc rotation,note that this single chromatography line out of the shot when the corresponding angle of deviation of the change, choose a direction to make the angle of deviation decreases slowly rotating loading platform,see the lines move backwards,where is the position of minimum deviation angle. 入射光束 出射光束 人kmin 最 泰方向 向角 出射方向 Figure 7 Minimum deviation angle (3)Find that monochromatic spectrum through the telescope and carefully rotate loading platform,the line's movement (note that the cross hair in the telescope field of view at this time should always be able to trace the lines),so that the monochromatic spectrum is just a reversal in the telescope field of view (where the telescope axis orientation is the minimum deviation position of the monochromatic spectrum). (4)Read the azimuth reading dual vernier on the 0 and 0'. (5)Followed by measuring the mercury lamp spectrum yellow,green,blue,purple,four kinds of monochromatic spectral lines in the minimum deviation angle of the azimuth reading. (6)Remove the prism.Make the cross hair aim at slit midpoint,read the corresponding readings of the two verniers 0o and 0o'. (7)according to 6min=[(-6)+('-')]/2,calculate the minimum angle of deviation min.Repeated measurements to calculate the average value of min.Measure the angle a and minimum angle of deviation min substituted into (3),calculate the refractive index of each monochromatic light. 4
4 Put the prism on the loading platform and use the two refractive surfaces of prism instead of the two reflecting surfaces of the two-way mirror. Use auto-correcting method to adjust by the telescope that has already been adjusted. In order to facilitate adjustment, the prism in the position of the loading platform can refer to figure 6. Adjust the loading platform to make the AB surface target to the telescope. Adjusting the screws B2 of the platform, make the up-cross point of"╪" and the reflected “十” image has nearly half of the coincidence. Spinning the stage again, make the other refractive surface AC of the prism target to the telescope, adjust until correct. Repeat the checking several times, until the two reflective surfaces both correct when rotating the platform. (2)After the adjustment, measure the vertex angle of the prism using the reflection method, repeated six times to find the average of the vertex angle, calculate the uncertainty and show the accurate measurement results. Make the data excel by yourself. 3.observe the dispersion phenomenon of the prism to the mercury lamp(Selected as the content) (1) Prism placed in the loading platform, the optical goniometer collimator pointed at the exit window of the low pressure mercury lamp, let the strongest and uniform light emit from the collimator. (2) Seen from figure 7, observe light bias situation to determine the refraction of light outgoing directions. Along the outgoing direction of light may be observed with your eyes first, slightly rotating the disc of scale to drive the platform when observed shot of the color spectrum, finds a monochromatic spectrum, continue to scale disc rotation, note that this single chromatography line out of the shot when the corresponding angle of deviation of the change, choose a direction to make the angle of deviation decreases slowly rotating loading platform, see the lines move backwards, where is the position of minimum deviation angle. Figure 7 Minimum deviation angle (3) Find that monochromatic spectrum through the telescope and carefully rotate loading platform, the line's movement (note that the cross hair in the telescope field of view at this time should always be able to trace the lines), so that the monochromatic spectrum is just a reversal in the telescope field of view (where the telescope axis orientation is the minimum deviation position of the monochromatic spectrum). (4) Read the azimuth reading dual vernier on the θ and θ′. (5) Followed by measuring the mercury lamp spectrum yellow, green, blue, purple, four kinds of monochromatic spectral lines in the minimum deviation angle of the azimuth reading. (6) Remove the prism. Make the cross hair aim at slit midpoint, read the corresponding readings of the two verniers θ0 and θ0′. (7) according to δ min= [(θ − θ0 )+( θ ′‐ θ0′)] /2, calculate the minimum angle of deviation δmin. Repeated measurements to calculate the average value of δmin. Measure the angle α and minimum angle of deviation δmin substituted into (3), calculate the refractive index of each monochromatic light

4.Determine four main parameters of the grating:the grating constant(d),the angular dispersion V,the resolution R with a given width of slits. 5.Measure the sodium double visible spectra lines(D1,D2 lines)using the sodium lamp,the wavelength of He-Ne laser and spectra line of mercury lamp by grating.The accuracy must be E元≤0.1% 6. Determine the highest order of each spectral line.Write down the sequence of the spectral lines for each order of the diffraction.Determine the angular width of each spectral line. 7.Compare the grating spectrum with the prism spectrum 【Attention】 1.Do not touch the surface of prism and grating and Pay attention to avoid breaking the prism and grating 2.Read the azimuth of telescope correctly. 【Prelab question】 1.Which the main components of optical goniometer?What is their role? 2.What is the relationship of telescope,collimator,loading platform and dial?Described the requirements of the adjustment briefly. 3.Why self-corrected method can be used to adjust the telescope to accept light parallel to the vertical central axis of the normal working condition?How to adjust? 4.Why use successive approximation of half adjustment method to adjust the telescope optical axis and optical goniometer center perpendicular?How to use successive approximation of half adjustment method? 【Review question】 1.Reflection method for measuring the vertex angle of the prism,why have to placed the vertex angle A near the center of the loading platform?Try to plot and explain. 2.Try to plot and explain,when the telescope or the reflecting surface normal of two-way mirror is not perpendicular to the central axis,once per rotation of two-way mirror 180,describe the possible relative position of cross hair and the cross-shaped image and their variation. 3.If angle-measurement accuracy of optical goniometer is 1',try to derivate the vertex angle A, the minimum angle of deviation min and the error formula of refractive index n,and estimate the accuracy of n 4.Comparing the grating spectrum with the prism spectrum. 5.According to the symmetry of the“+”and“.”spectrum of the same diffraction order,. determine the position of the grating;Try to adjust the grating to the proper position.If the diffraction angles of"+"and""spectrums aren't the same,please estimate the incident angle (Deviation from normal incident) 6.Using a black card to decrease the grating slit number N,how will the diffraction pattern change?Determine the minimum gating width Lp that is needed to resolve the double sodium lines (D.D,lines):Comparing with the theoretical value. 7.Design an experiment to measure the wavelengths of a light emitting diode(LED). 8.Using a grating(with a given d)to observe any spectral line of He-Ne laser,sodium lamp or mercury lamp,please estimate the highest order of diffraction that we can observe. 9.Is the highest diffraction order the same for the different wavelength using the same grating? Is the spectrum width the same for the different wavelength?Is the spectrum width the same for a single wavelength at the different diffraction order?Why?
5 4. Determine four main parameters of the grating: the grating constant (d), the angular dispersion ψ, the resolution R with a given width of slits. 5. Measure the sodium double visible spectra lines (D1, D2 lines) using the sodium lamp, the wavelength of He-Ne laser and spectra line of mercury lamp by grating. The accuracy must be Eλ ≤ 0.1%. 6. Determine the highest order of each spectral line. Write down the sequence of the spectral lines for each order of the diffraction. Determine the angular width of each spectral line. 7. Compare the grating spectrum with the prism spectrum. 【Attention】 1.Do not touch the surface of prism and grating and Pay attention to avoid breaking the prism and grating. 2.Read the azimuth of telescope correctly. 【 Prelab question】 1. Which the main components of optical goniometer? What is their role? 2. What is the relationship of telescope, collimator, loading platform and dial? Described the requirements of the adjustment briefly. 3. Why self-corrected method can be used to adjust the telescope to accept light parallel to the vertical central axis of the normal working condition? How to adjust? 4. Why use successive approximation of half adjustment method to adjust the telescope optical axis and optical goniometer center perpendicular? How to use successive approximation of half adjustment method? 【 Review question】 1. Reflection method for measuring the vertex angle of the prism, why have to placed the vertex angle A near the center of the loading platform? Try to plot and explain. 2. Try to plot and explain, when the telescope or the reflecting surface normal of two-way mirror is not perpendicular to the central axis, once per rotation of two-way mirror 180 °, describe the possible relative position of cross hair and the cross-shaped image and their variation. 3. If angle-measurement accuracy of optical goniometer is 1', try to derivate the vertex angle A, the minimum angle of deviation δmin and the error formula of refractive index n, and estimate the accuracy of n. 4. Comparing the grating spectrum with the prism spectrum. 5. According to the symmetry of the “+” and “-” spectrum of the same diffraction order, determine the position of the grating; Try to adjust the grating to the proper position. If the diffraction angles of “+” and “-” spectrums aren’t the same, please estimate the incident angle (Deviation from normal incident) 6. Using a black card to decrease the grating slit number N, how will the diffraction pattern change? Determine the minimum gating width LD that is needed to resolve the double sodium lines (D1, D2 lines); Comparing with the theoretical value. 7. Design an experiment to measure the wavelengths of a light emitting diode (LED). 8. Using a grating (with a given d) to observe any spectral line of He-Ne laser, sodium lamp or mercury lamp, please estimate the highest order of diffraction that we can observe. 9. Is the highest diffraction order the same for the different wavelength using the same grating? Is the spectrum width the same for the different wavelength? Is the spectrum width the same for a single wavelength at the different diffraction order? Why?