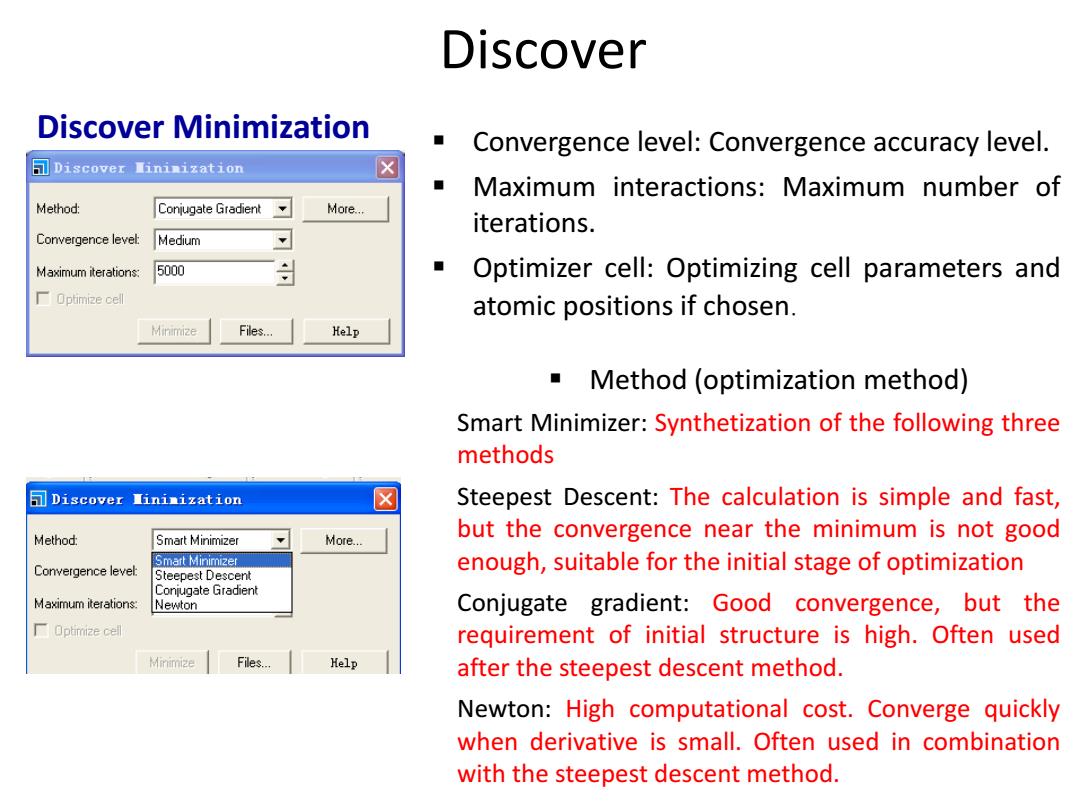
Discover Discover Minimization Convergence level:Convergence accuracy level. Discover Nininization ■ Maximum interactions:Maximum number of Method: Conjugate Gradient More... iterations. Convergence level: Medium Maximum iterations: 5000 Optimizer cell:Optimizing cell parameters and 厂Optimia2ecel atomic positions if chosen. Minimize Files..… Help Method (optimization method) Smart Minimizer:Synthetization of the following three methods Discover Iininization Steepest Descent:The calculation is simple and fast, Method: Smart Minimizer More... but the convergence near the minimum is not good Smart Minimizer Convergence level: enough,suitable for the initial stage of optimization Steepest Descent Conjugate Gradient Maximum iterations: Newton Conjugate gradient:Good convergence,but the Optimize cell requirement of initial structure is high.Often used Minimize Files... Help after the steepest descent method. Newton:High computational cost.Converge quickly when derivative is small.Often used in combination with the steepest descent method
Discover Minimization Method (optimization method) Smart Minimizer: Synthetization of the following three methods Steepest Descent: The calculation is simple and fast, but the convergence near the minimum is not good enough, suitable for the initial stage of optimization Conjugate gradient: Good convergence, but the requirement of initial structure is high. Often used after the steepest descent method. Newton: High computational cost. Converge quickly when derivative is small. Often used in combination with the steepest descent method. Convergence level: Convergence accuracy level. Maximum interactions: Maximum number of iterations. Optimizer cell: Optimizing cell parameters and atomic positions if chosen. Discover

Discover Discover Molecular Ensemble Dynamics\Dynamics > Temperature Discover Molecular Dynamics Pressure Dynamics Stress >Number of steps Ensemble NVT More... > Time step Temperature: 300.0 K Thermostat... Pressure: 0.0 >Dynamics time:Number of steps XTime GPa Barostat.. Number of steps: 5000 step Time step: 1.0 fs Trajectory Dynamics time: 5.0 ps Trajectory Save: Save: Full Coordinates Frame output every: 250 日steps Restart ■Final Structure ■Use restart data ■Full(all Run Files... Frame output every:output a frame of Help crystal structue every 5000 steps if it is set to 5000
Discover Molecular Dynamics\Dynamics Ensemble Temperature Pressure Number of steps Time step Dynamics time: Number of steps×Time step Trajectory Save: Coordinates Final Structure Full (all) Frame output every:output a frame of crystal structue every 5000 steps if it is set to 5000 Discover
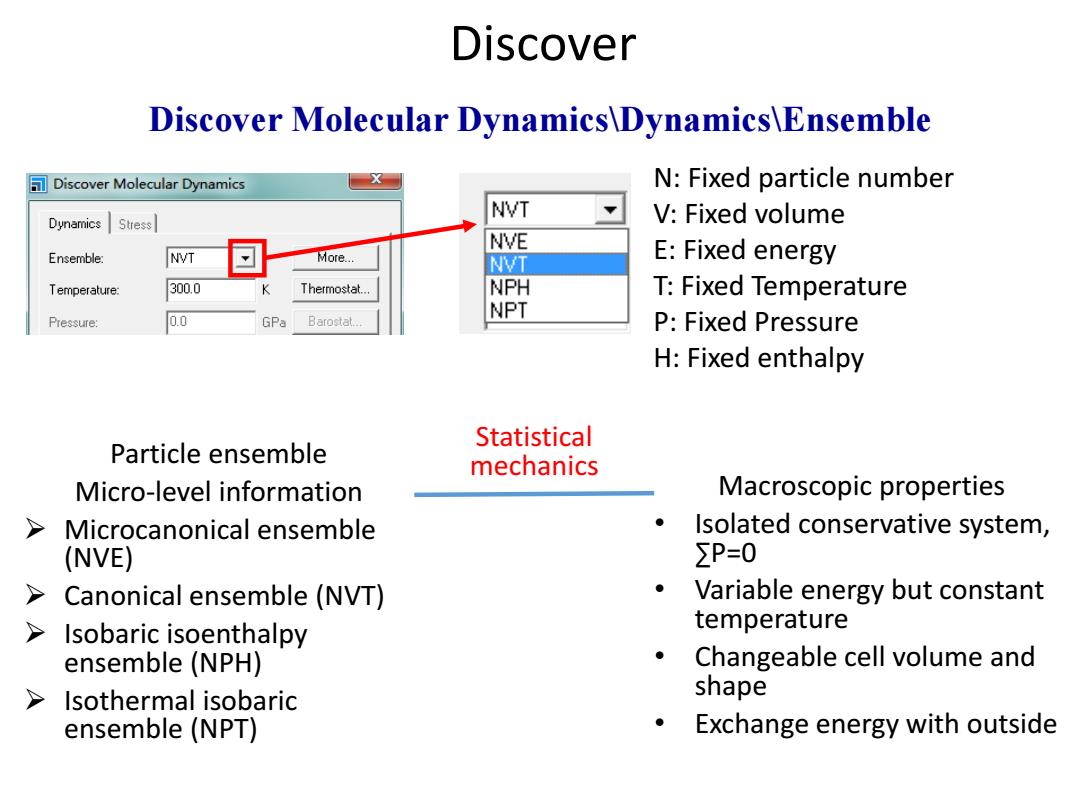
Discover Discover Molecular Dynamics\Dynamics\Ensemble Discover Molecular Dynamics N:Fixed particle number NVT Dynamics Stress V:Fixed volume NVE Ensemble: NVT More... NVT E:Fixed energy Temperature: 300.0 Thermostat... NPH T:Fixed Temperature NPT Pressure: 0.0 GPa Barostat... P:Fixed Pressure H:Fixed enthalpy Statistical Particle ensemble mechanics Micro-level information Macroscopic properties Microcanonical ensemble Isolated conservative system, (NVE) ∑P=0 > Canonical ensemble (NVT) Variable energy but constant > Isobaric isoenthalpy temperature ensemble (NPH) Changeable cell volume and Isothermal isobaric shape ensemble (NPT) Exchange energy with outside
N: Fixed particle number V: Fixed volume E: Fixed energy T: Fixed Temperature P: Fixed Pressure H: Fixed enthalpy Discover Discover Molecular Dynamics\Dynamics\Ensemble Particle ensemble Micro-level information Microcanonical ensemble (NVE) Canonical ensemble (NVT) Isobaric isoenthalpy ensemble (NPH) Isothermal isobaric ensemble (NPT) Macroscopic properties • Isolated conservative system, ∑P=0 • Variable energy but constant temperature • Changeable cell volume and shape • Exchange energy with outside Statistical mechanics
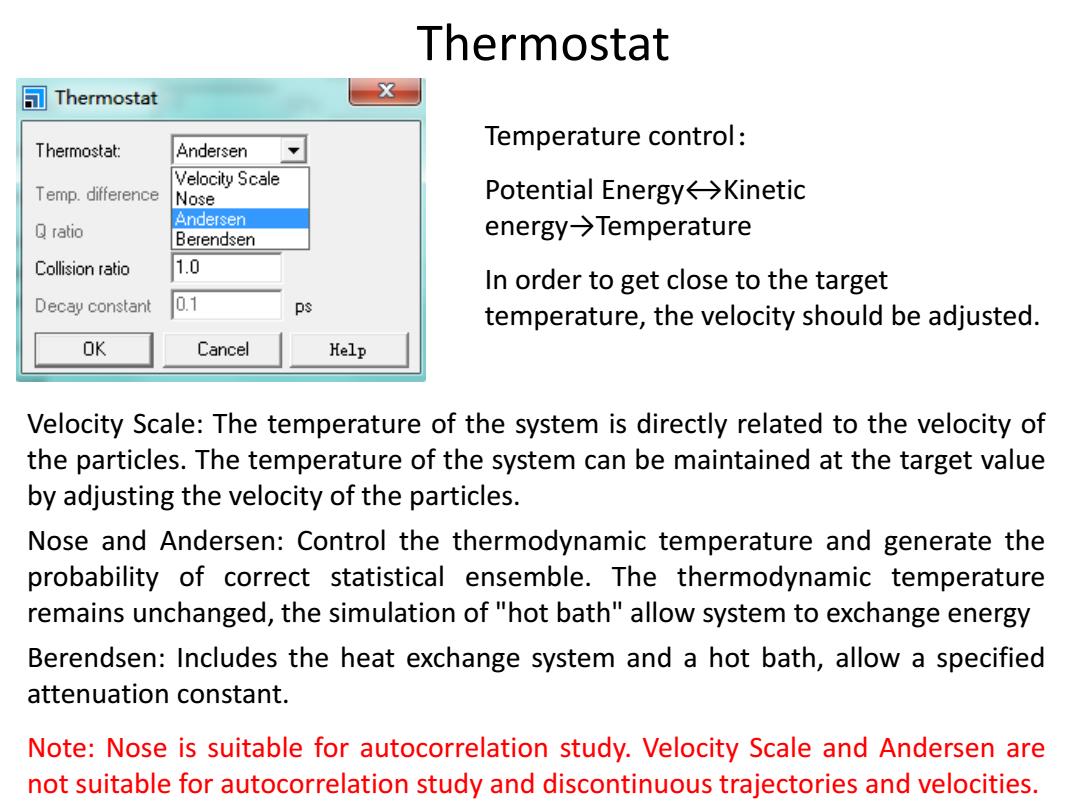
Thermostat Thermostat X Temperature control: Thermostat: Andersen Velocity Scale Temp.difference Nose Potential Energy←→Kinetic Andersen ratio Berendsen energy→Temperature Collision ratio 1.0 In order to get close to the target Decay constant 0.1 ps temperature,the velocity should be adjusted. OK Cancel Kelp Velocity Scale:The temperature of the system is directly related to the velocity of the particles.The temperature of the system can be maintained at the target value by adjusting the velocity of the particles. Nose and Andersen:Control the thermodynamic temperature and generate the probability of correct statistical ensemble.The thermodynamic temperature remains unchanged,the simulation of "hot bath"allow system to exchange energy Berendsen:Includes the heat exchange system and a hot bath,allow a specified attenuation constant. Note:Nose is suitable for autocorrelation study.Velocity Scale and Andersen are not suitable for autocorrelation study and discontinuous trajectories and velocities
Velocity Scale: The temperature of the system is directly related to the velocity of the particles. The temperature of the system can be maintained at the target value by adjusting the velocity of the particles. Nose and Andersen: Control the thermodynamic temperature and generate the probability of correct statistical ensemble. The thermodynamic temperature remains unchanged, the simulation of "hot bath" allow system to exchange energy Berendsen: Includes the heat exchange system and a hot bath, allow a specified attenuation constant. Note: Nose is suitable for autocorrelation study. Velocity Scale and Andersen are not suitable for autocorrelation study and discontinuous trajectories and velocities. Thermostat Temperature control: Potential Energy↔Kinetic energy→Temperature In order to get close to the target temperature, the velocity should be adjusted

Forcite Advanced molecular mechanics and dynamics simulation program. Supporting multiple molecular force fields >Applicabale to various systems >With the development of computer hardware and software,more and more attention has been paid to it in recent years Research field > Calculating Radial Distribution Function,orientation correlation function and scattering curve Measuring distribution of distance,angle and rotation radius Giving concentration curves of specific components Plotting temperature,pressure,volume,stress and cell parameters > Giving potential energy and its components,kinetic energy and total energy for MM and MD simulations >Studying mechanical properties of materials > Computing dipole correlation function Cohesive energy density and solubility parameters of molecular Systems >Estimating mean square displacement and velocity correlation function for self-diffusion > Simulating shear limit of lubricant and lubricating ability > Observing and plotting trajectory data in learning tables.Sorting by a specific
Advanced molecular mechanics and dynamics simulation program. Forcite Supporting multiple molecular force fields Applicabale to various systems With the development of computer hardware and software, more and more attention has been paid to it in recent years Research field Calculating Radial Distribution Function, orientation correlation function and scattering curve Measuring distribution of distance, angle and rotation radius Giving concentration curves of specific components Plotting temperature, pressure, volume, stress and cell parameters Giving potential energy and its components, kinetic energy and total energy for MM and MD simulations Studying mechanical properties of materials Computing dipole correlation function Cohesive energy density and solubility parameters of molecular Systems Estimating mean square displacement and velocity correlation function for self-diffusion Simulating shear limit of lubricant and lubricating ability Observing and plotting trajectory data in learning tables. Sorting by a specific property. If sorting by energy, find the lowest energy configration