重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 2004级救 课程名称 心肌病 年级 版、麻醉 授课专业 循环系统 教师 秦俭职称副教授 授课方式※大课示教学时2 题目章节 第九章 教材名称 内科学(全国高等学校教材) 作者主编:叶任高陆再英 出版社人民卫生出版社 版次第6版 教 学 目 掌握心肌病的定义、分类、病理、临床表现、诊断、鉴别诊断及治疗原则。 的 求 教 学 联系病理生理讲述扩张型心肌病和非喉梗阻型心肌病的临床表现及超声心动图的特征性改 难 点 教 学 重 同上。 点 外语 掌握几种不同心肌病的英文名称。 要求 多媒体教学:结合病理讲解。 教学方 法手段 教研 意见 同意通过 教学组长:秦俭 2007年 辅助手段
重庆医科大学临床学院教案及讲稿 课程名称 心肌病 年级 2004 级救 援、麻醉 授课专业 循环系统 教 师 秦 俭 职称 副教授 授课方式 ※大课 示教 学时 2 题目章节 第九章 教材名称 内科学(全国高等学校教材) 作者 主编:叶任高 陆再英 出 版 社 人民卫生出版社 版次 第 6 版 教 学 目 的 要 求 掌握心肌病的定义、分类、病理、临床表现、诊断、鉴别诊断及治疗原则。 教 学 难 点 联系病理生理讲述扩张型心肌病和非喉梗阻型心肌病的临床表现及超声心动图的特征性改 变。 教 学 重 点 同上。 外语 要求 掌握几种不同心肌病的英文名称。 教学方 法手段 教研室 意见 同意通过 教学组长:秦俭 教研室主任:陶小红 2007 年 3 月 18 日 辅助手段 多媒体教学;结合病理讲解
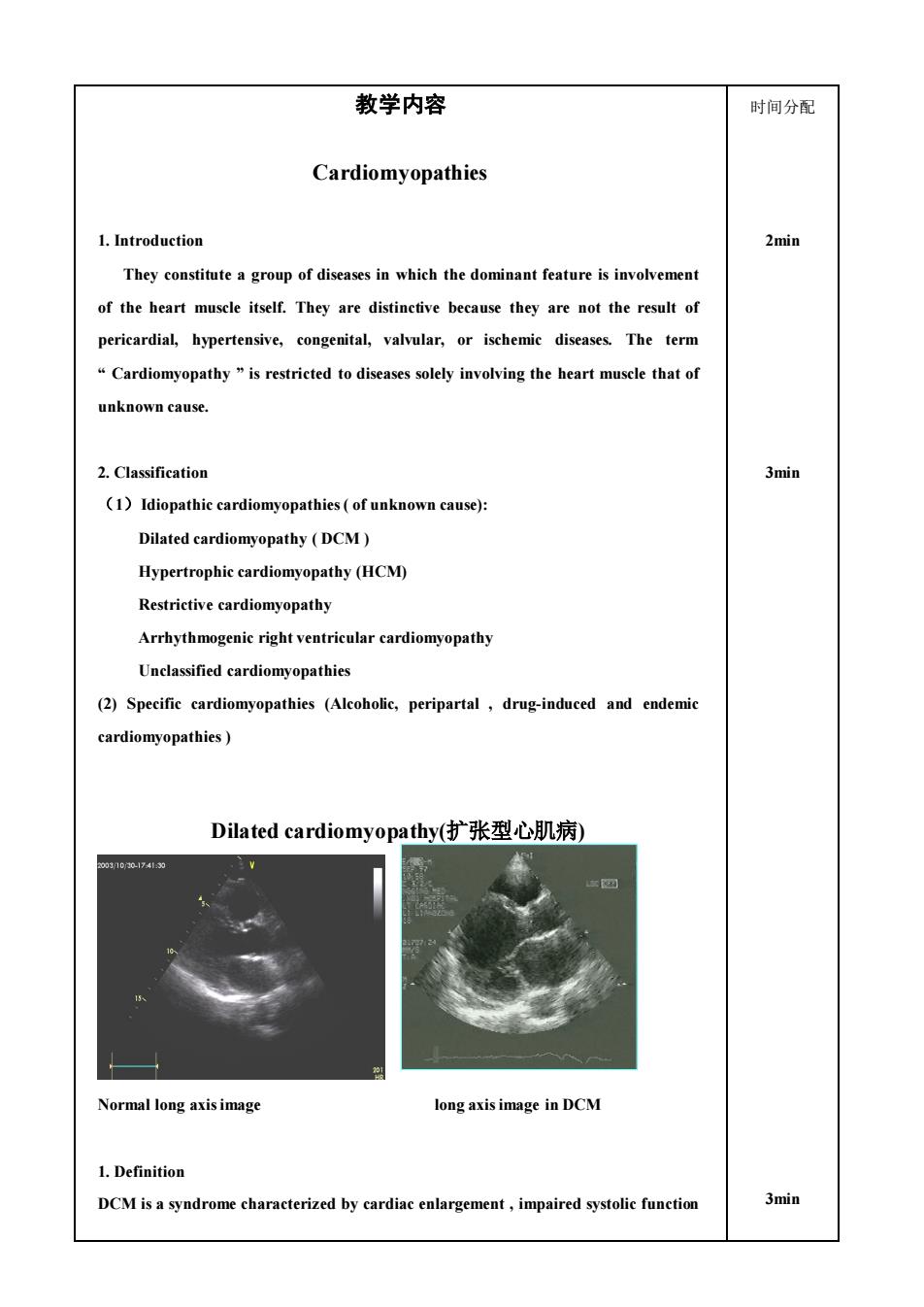
教学内容 时间分配 Cardiomyopathies 1.Introduction 2min They constitute a group of diseases in which the dominant feature is involvement of the heart muscle itself.They are distinctive because they are not the result of pericardial,hypertensive,congenital,valvular,or ischemie diseases.The term Cardiomyopathy"is restricted to diseases solely involving the heart musele that of unknown cause. 2.Classification 3min (1)Idiopathic cardiomyopathies(of unknown cause) Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy(HCM) Restrictive cardiomyopathy Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy Unclassified cardiomyopathies (2)Specific cardiomyopathies (Alcoholic,peripartal,drug-induced and endemic cardiomyopathies) Dilated cardiomyopathy(扩张型心肌病) 73 Normal long axisimage long axis image in DCM 1.Definition DCM isa syndrome characterized by cardiac,impaired systolic function 3min
教学内容 Cardiomyopathies 1. Introduction They constitute a group of diseases in which the dominant feature is involvement of the heart muscle itself. They are distinctive because they are not the result of pericardial, hypertensive, congenital, valvular, or ischemic diseases. The term “ Cardiomyopathy ” is restricted to diseases solely involving the heart muscle that of unknown cause. 2. Classification (1)Idiopathic cardiomyopathies ( of unknown cause): Dilated cardiomyopathy ( DCM ) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) Restrictive cardiomyopathy Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy Unclassified cardiomyopathies (2) Specific cardiomyopathies (Alcoholic, peripartal , drug-induced and endemic cardiomyopathies ) Dilated cardiomyopathy(扩张型心肌病) Normal long axis image long axis image in DCM 1. Definition DCM is a syndrome characterized by cardiac enlargement , impaired systolic function 时间分配 2min 3min 3min

of one or both ventricles and with or without congestive heart failure.Arrhythmia often occurs.It is most common in middle age and is almost three times more frequent in males than in females.The long-term prognosis is not good. 2.Etiology 2min The cause of disease remains unelear.But there are three possible basic mecha-nisms of damage:familial and genetic factors;viral myocarditis and other cytocoxic insults Immunological abnormalities 3.Pathology 5min Postmortem examination reveals enlargement and dilation of all four chambers;the cardiac valves and coronary arteries are nor-mal,and intracavitary thrombi are common. Histological examination reveals extensive areas of interstitial and perivascular fibrosis,myocardial cell degeneration.Small areas of necrosis are seen on occasion. 4.Clinical manifestations 10min (1)History:A.In the early stage some patients are asymptomatic and later symptoms develop gradually.B.Symptoms of congestive heart failure gradually deteriorate(usually left and right ventricular failures occur simultaneously ).C. Emboli and sudden death may occur.D.All kinds of arrhythmia may occur. (2)Physical examination: A.variable degrees of findings of congestive heart failure; B.variable degrees of cardiac enlargement; C.weakened heart sounds and fast heart rate; D.systolic murmurs due to mitral or tricuspid valvular regurgitation; E.arrhythmia. 5.Laboratory examinations 10min (1)Chest roentgenogram:generalized cardiomegaly and pulmonary vascular redistribution
of one or both ventricles and with or without congestive heart failure. Arrhythmia often occurs. It is most common in middle age and is almost three times more frequent in males than in females. The long-term prognosis is not good. 2. Etiology The cause of disease remains unclear. But there are three possible basic mecha-nisms of damage: familial and genetic factors; viral myocarditis and other cytocoxic insults; Immunological abnormalities. 3. Pathology Postmortem examination reveals enlargement and dilation of all four chambers; the cardiac valves and coronary arteries are nor-mal, and intracavitary thrombi are common. Histological examination reveals extensive areas of interstitial and perivascular fibrosis, myocardial cell degeneration. Small areas of necrosis are seen on occasion. 4. Clinical manifestations (1)History: A. In the early stage some patients are asymptomatic and later symptoms develop gradually. B. Symptoms of congestive heart failure gradually deteriorate ( usually left and right ventricular failures occur simultaneously ) . C. Emboli and sudden death may occur. D. All kinds of arrhythmia may occur. (2)Physical examination: A. variable degrees of findings of congestive heart failure; B. variable degrees of cardiac enlargement; C. weakened heart sounds and fast heart rate; D. systolic murmurs due to mitral or tricuspid valvular regurgitation; E. arrhythmia. 5. Laboratory examinations (1)Chest roentgenogram: generalized cardiomegaly and pulmonary vascular redistribution. 2min 5min 10min 10min
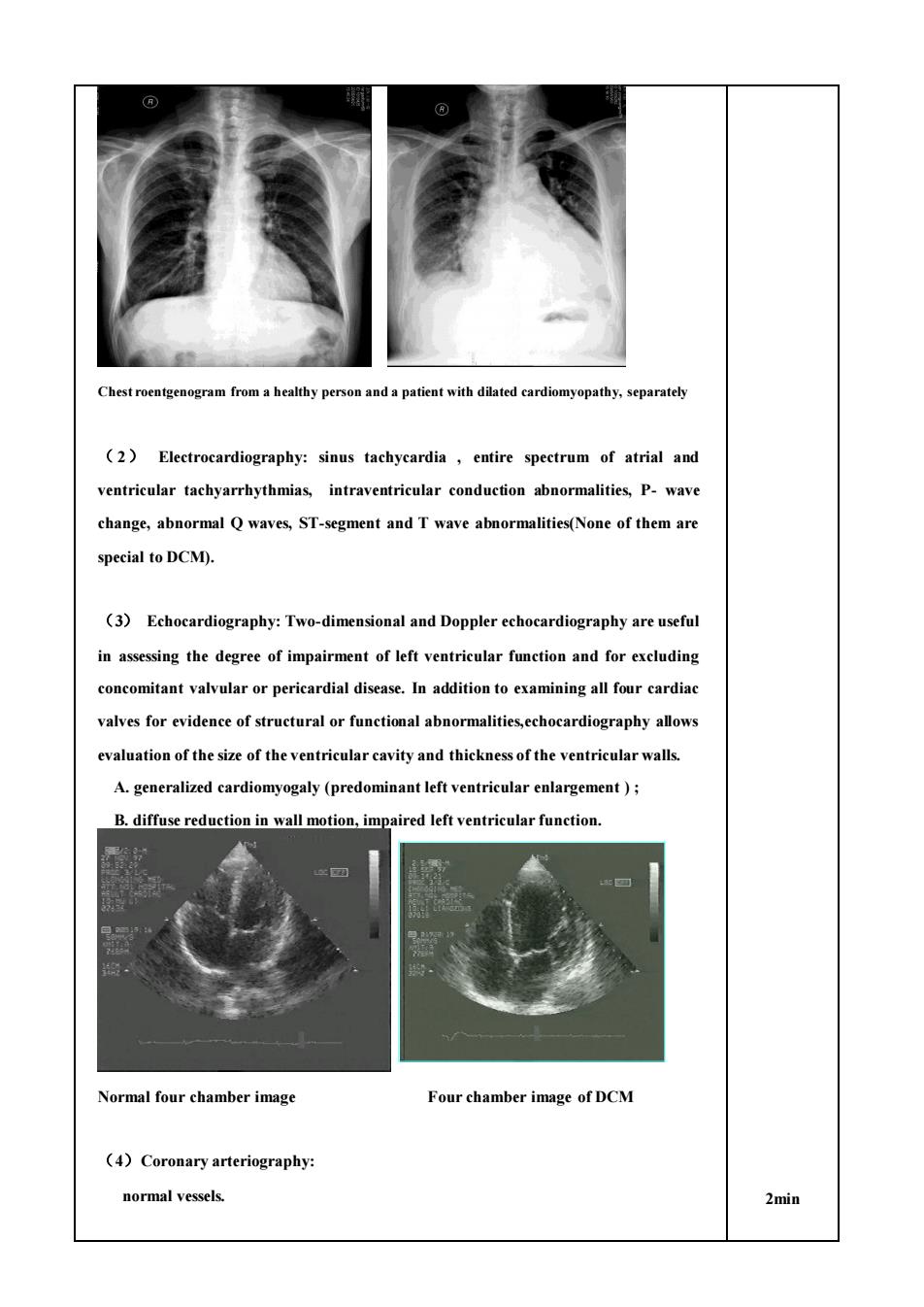
personanda patient with dilated cardiomyopathy,separately (2)Electrocardiography:sinus tachycardia,entire spectrum of atrial and ventricular tachyarrhythmias,intraventricular conduction abnormalities,P-wave change,abnormal Q waves,ST-segment and T wave abnormalities(None of them are special to DCM). (3)Echocardiography:Two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography are useful in assessing the degree of impairment of left ventricular function and for excluding concomitant valvular or pericardial disease.In addition to examining all four cardiac valves for evidence of structural or functional abnormalities,echocardiography allows evaluation of the size of the ventricular cavity and thickness of the ventricular walls. A.generalized cardiomyogaly(predominant left ventricular enlargement); B.diffuse reduction in wall motion,impaired left ventricular function. Normal four chamber image Four chamber image of DCM (4)Coronary arteriography normal vessels. 2min
Chest roentgenogram from a healthy person and a patient with dilated cardiomyopathy, separately ( 2) Electrocardiography: sinus tachycardia , entire spectrum of atrial and ventricular tachyarrhythmias, intraventricular conduction abnormalities, P- wave change, abnormal Q waves, ST-segment and T wave abnormalities(None of them are special to DCM). (3) Echocardiography: Two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography are useful in assessing the degree of impairment of left ventricular function and for excluding concomitant valvular or pericardial disease. In addition to examining all four cardiac valves for evidence of structural or functional abnormalities,echocardiography allows evaluation of the size of the ventricular cavity and thickness of the ventricular walls. A. generalized cardiomyogaly (predominant left ventricular enlargement ) ; B. diffuse reduction in wall motion, impaired left ventricular function. Normal four chamber image Four chamber image of DCM (4)Coronary arteriography: normal vessels. 2min

6.Diagnosis and differentiation (1)Clinical manifestations: Unknown cardiac enlargement,congestive hear failure,arrhythmia,without organic murmurs; (2 Echocardiography:Enlargement of four chambers,diffuse reduction in wal motion. Its diagnosis is based on the exclusion of all other known organic heart diseases, including myocarditis,rhematic heart disease,coronary heart disease,hyperten-sive heart disease,chronic pulmonary heart disease and congenital heart diseases. 3min) 7.Management Beeause the cause of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy is unknown,specific treatment is impossible.Therefore,treatment is for heart failure (1)Digitalis:easer to overdose on Digitalis. (2)Anticoagulants-recommended. Anticoagulants:Even without controlled clinical trials demonstrating their efficacy,it is recommended in patients with DCM and heart failure; (3)Antiarrhythmias: Although there is no definitive evidence that antiarrhythmatic agents prolong life or prevent sudden death in DCM,it may be appropriate to use them in the treatment of symptomatic arrhythmias.But both efficacy and toxity must be carefully monitored. (4)Cardiac transplantation. 7.Prognosis The long-term prognosis is not good.Greater ventricular enlargement and worse dysfunction tend to correlate with poorer prognosis Patients suffering from DCM usually die of heart failure and/or fatal arrhythmia
6. Diagnosis and differentiation (1) Clinical manifestations: Unknown cardiac enlargement , congestive heart failure, arrhythmia, without organic murmurs; (2) Echocardiography: Enlargement of four chambers, diffuse reduction in wall motion. ※Its diagnosis is based on the exclusion of all other known organic heart diseases , including myocarditis, rhematic heart disease, coronary heart disease, hyperten-sive heart disease, chronic pulmonary heart disease and congenital heart diseases. 7. Management Because the cause of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy is unknown, specific treatment is impossible. Therefore, treatment is for heart failure. (1) Digitalis: easer to overdose on Digitalis. (2) Anticoagulants- recommended. Anticoagulants:Even without controlled clinical trials demonstrating their efficacy, it is recommended in patients with DCM and heart failure; (3) Antiarrhythmias: Although there is no definitive evidence that antiarrhythmatic agents prolong life or prevent sudden death in DCM,it may be appropriate to use them in the treatment of symptomatic arrhythmias . But both efficacy and toxity must be carefully monitored. (4) Cardiac transplantation. 7. Prognosis The long-term prognosis is not good. Greater ventricular enlargement and worse dysfunction tend to correlate with poorer prognosis. Patients suffering from DCM usually die of heart failure and/or fatal arrhythmia. 3min) 1min