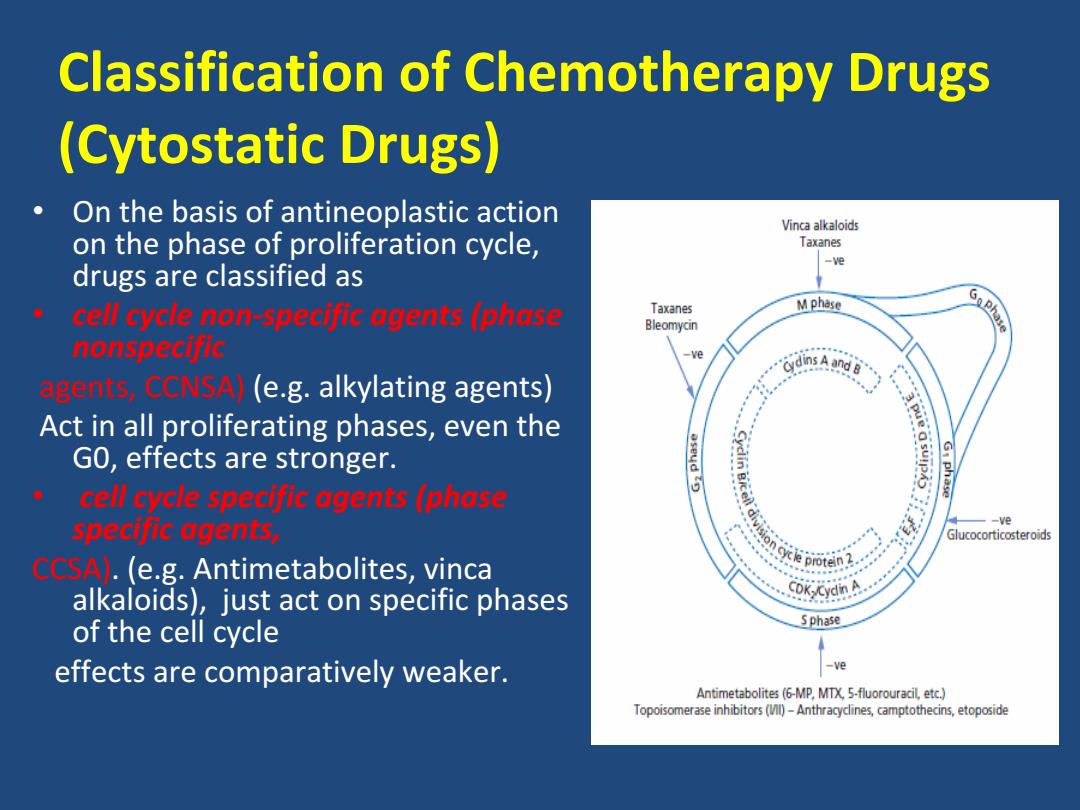
Classification of Chemotherapy Drugs (Cytostatic Drugs) On the basis of antineoplastic action Vinca alkaloids on the phase of proliferation cycle, Taxanes -ve drugs are classified as cell cycle non-specific agents (phase Taxanes Mphase Bleomycin nonspecific ve dins A and (e.g.alkylating agents) Act in all proliferating phases,even the GO,effects are stronger. cell cycle specific agents (phase specific agents, -ve Glucocorticosteroids (e.g.Antimetabolites,vinca CDK Cydin alkaloids),just act on specific phases of the cell cycle Sphase effects are comparatively weaker. -ve Antimetabolites(6-MP,MTX,5-fluorouracil,etc.) Topoisomerase inhibitors(M)-Anthracyclines,camptothecins,etoposide
Classification of Chemotherapy Drugs (Cytostatic Drugs) • On the basis of antineoplastic action on the phase of proliferation cycle, drugs are classified as • cell cycle non‐specific agents (phase nonspecific agents, CCNSA) (e.g. alkylating agents) Act in all proliferating phases, even the G0, effects are stronger. • cell cycle specific agents (phase specific agents, CCSA). (e.g. Antimetabolites, vinca alkaloids), just act on specific phases of the cell cycle effects are comparatively weaker

Cell Cycle non- Cell Cycle Specific(CCS) specific(CCNS) Fluorouracil(氟尿嘧啶) alkylating agents: 一 Mercaptopurinet(巯嘌呤) Cyclophosphamide(环磷 Methotrexate(甲氨喋呤) 酰胺), mechlorethamine(氮芥) nitrosoureas(亚硝基脲) 一 L-asparaginase(左旋天 actinomycin D(放线菌素D) 冬氨酸酶) Daunorubicin(柔红霉素), - Paclitaxel(紫杉醇) doxorubicin(阿霉素) Etoposide(依托泊苷), vincristine/vinblastine( -Cisplatin(顺铂) 长春花碱) Bleomycin(博来霉素)
• Cell Cycle Specific(CCS) – Fluorouracil(氟尿嘧啶) – Mercaptopurine(巯嘌呤) – Methotrexate(甲氨喋呤) – L ‐asparaginase(左旋天 冬氨酸酶) – Paclitaxel(紫杉醇) – vincristine/vinblastine( 长春花碱) • Cell Cycle non ‐ specific(CCNS) – alkylating agents: • Cyclophosphamide(环磷 酰胺), mechlorethamine(氮芥), nitrosoureas(亚硝基脲) – actinomycin D(放线菌素D) – Daunorubicin(柔红霉素), doxorubicin(阿霉素) – Etoposide(依托泊苷), – Cisplatin(顺铂) – Bleomycin(博来霉素)

Classification of Chemotherapy Drugs 1.alkylating agents; 。2.antimetabolites; 3.DNA-binding agents; .4.Cytotoxic Antibiotics 5.microtubular inhibitors (vinca alkaloids and taxanes); 6.topoisomerase inhibitors; 7.molecularly targeted agents;small molecules and monoclonal antibodies; 。8.hormones; 9.biological response modifiers
Classification of Chemotherapy Drugs • 1. alkylating agents; • 2. antimetabolites; • 3. DNA‐binding agents; • 4. Cytotoxic Antibiotics • 5. microtubular inhibitors (vinca alkaloids and taxanes); • 6. topoisomerase inhibitors; • 7. molecularly targeted agents; small molecules and • monoclonal antibodies; • 8. hormones; • 9. biological response modifiers

Principles of cytotoxic chemotherapy Cytotoxic drugs kill a constant percentage of cells-not a constant number. Cells have discrete periods of the cell cycle during which they are sensitive to cytotoxic drugs. Cancer chemotherapy slows progression through the cell cycle. Cytotoxic drugs are not totally selective in their toxicity to cancer cells. Cell cytotoxicity is proportional to total drug exposure. Cytotoxic drugs should be used in combination
• Principles of cytotoxic chemotherapy • Cytotoxic drugs kill a constant percentage of cells – not a constant number. • Cells have discrete periods of the cell cycle during which they are sensitive to cytotoxic drugs. • Cancer chemotherapy slows progression through the cell cycle. • Cytotoxic drugs are not totally selective in their toxicity to cancer cells. • Cell cytotoxicity is proportional to total drug exposure. • Cytotoxic drugs should be used in combination

Principles of combination chemotherapy .Develop combinations in which the drugs have: individual antineoplastic actions; non-overlapping toxicities; different mechanisms of cytotoxic effects. .The dose and schedule used must be optimized. .Combination therapy is better than single drug therapy ·because: there is improved cell cytotoxicity; heterogeneous tumour cell populations are killed; it reduces the development of resistance
Principles of combination chemotherapy • • Develop combinations in which the drugs have: • – individual antineoplastic actions; • – non‐overlapping toxicities; • – different mechanisms of cytotoxic effects. • • The dose and schedule used must be optimized. • • Combination therapy is better than single drug therapy • because: • – there is improved cell cytotoxicity; • – heterogeneous tumour cell populations are killed; • – it reduces the development of resistance