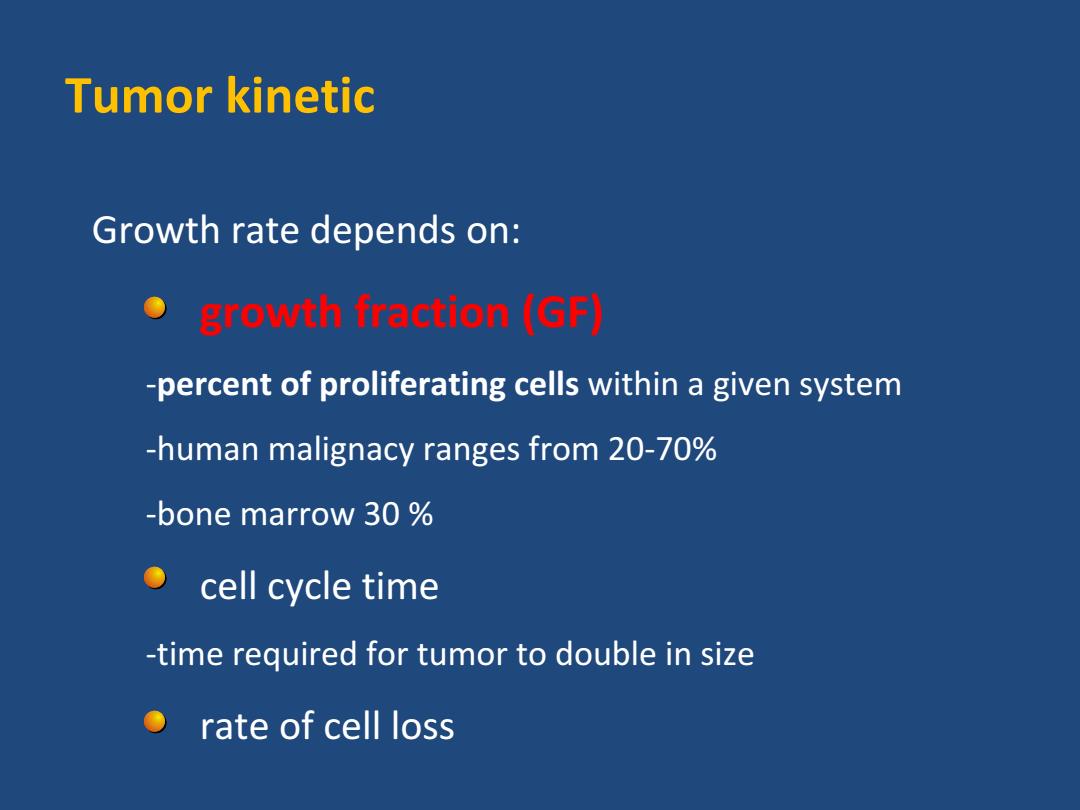
Tumor kinetic Growth rate depends on: growth fraction(GF) -percent of proliferating cells within a given system -human malignacy ranges from 20-70% -bone marrow 30% ● cell cycle time -time required for tumor to double in size rate of cell loss
Tumor kinetic Growth rate depends on: growth fraction (GF) ‐percent of proliferating cells within a given system ‐human malignacy ranges from 20‐70% ‐bone marrow 30 % cell cycle time ‐time required for tumor to double in size rate of cell loss
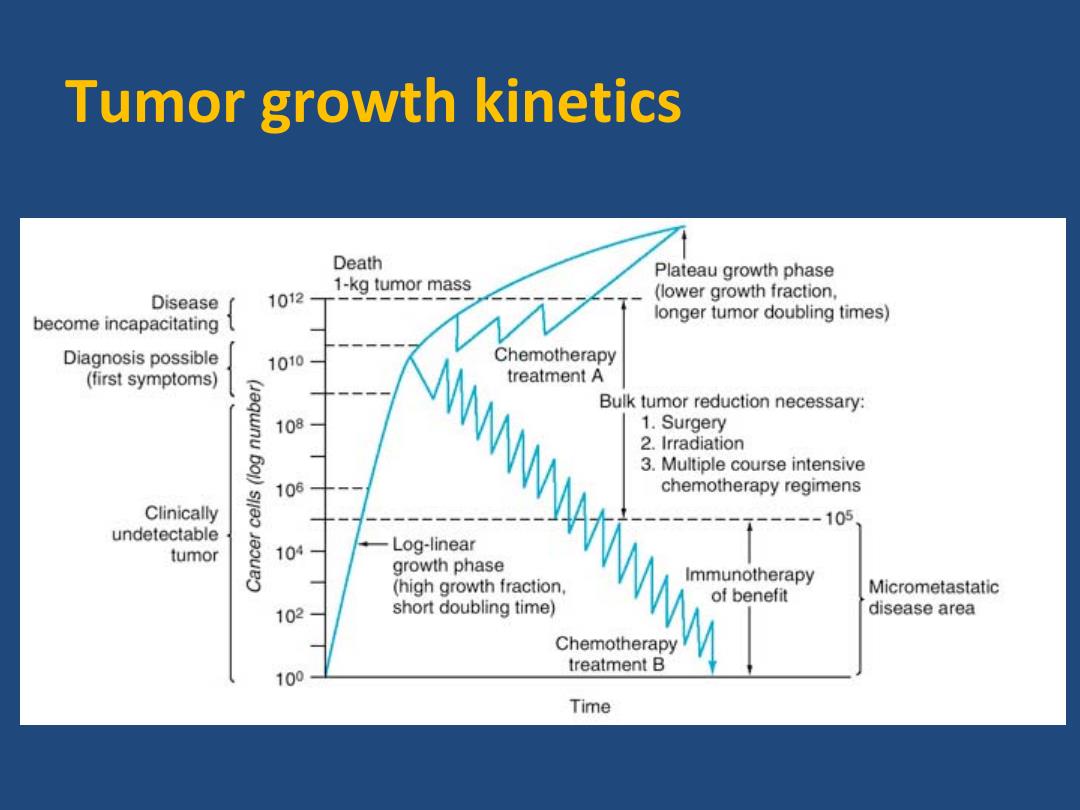
Tumor growth kinetics Death Plateau growth phase 1-kg tumor mass Disease 1012 (lower growth fraction, become incapacitating longer tumor doubling times) Diagnosis possible 1010 Chemotherapy (first symptoms) treatment A (equnu 601) Bulk tumor reduction necessary: 108 1.Surgery 2.Irradiation 3.Multiple course intensive sje5 106 chemotherapy regimens Clinically ---105 undetectable tumor 10 Log-linear 8 growth phase (high growth fraction, Immunotherapy of benefit Micrometastatic 102 short doubling time) disease area Chemotherapy treatment B 100 Time
Tumor growth kinetics
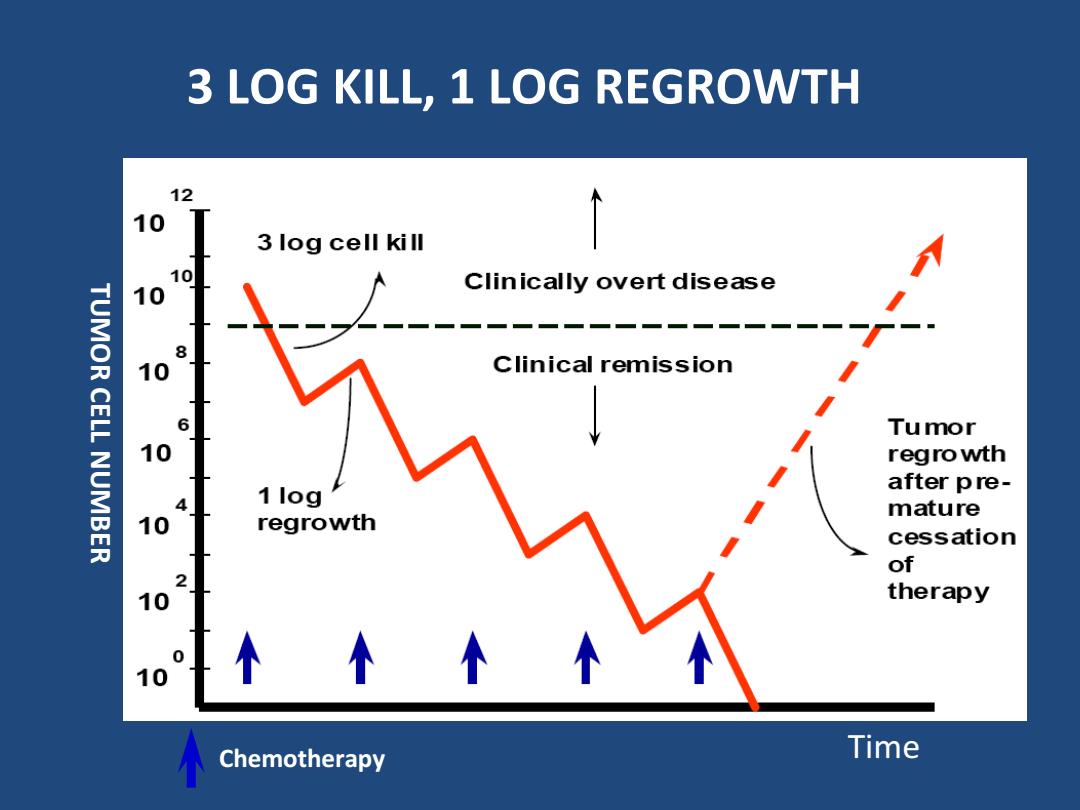
3 LOG KILL,1 LOG REGROWTH 12 10 3 log cell kill 10 10 Clinically overt disease TUMOR CELL NUMBER 8 Clinical remission 6 Tumor 10 reg ro wth 1 log after pre- mature 10 regrowth cessation of 2 10 therapy 0 10 个 Chemotherapy Time
3 LOG KILL, 1 LOG REGROWTH Time TUMOR CELL NUMBER Chemotherapy
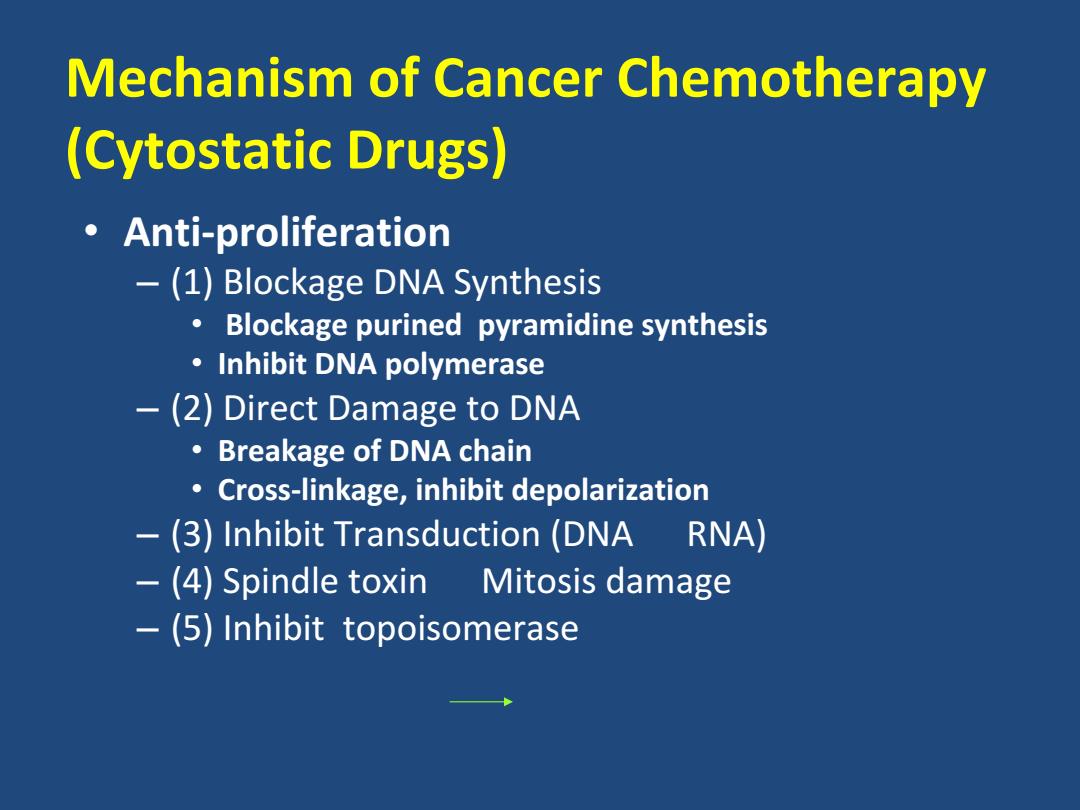
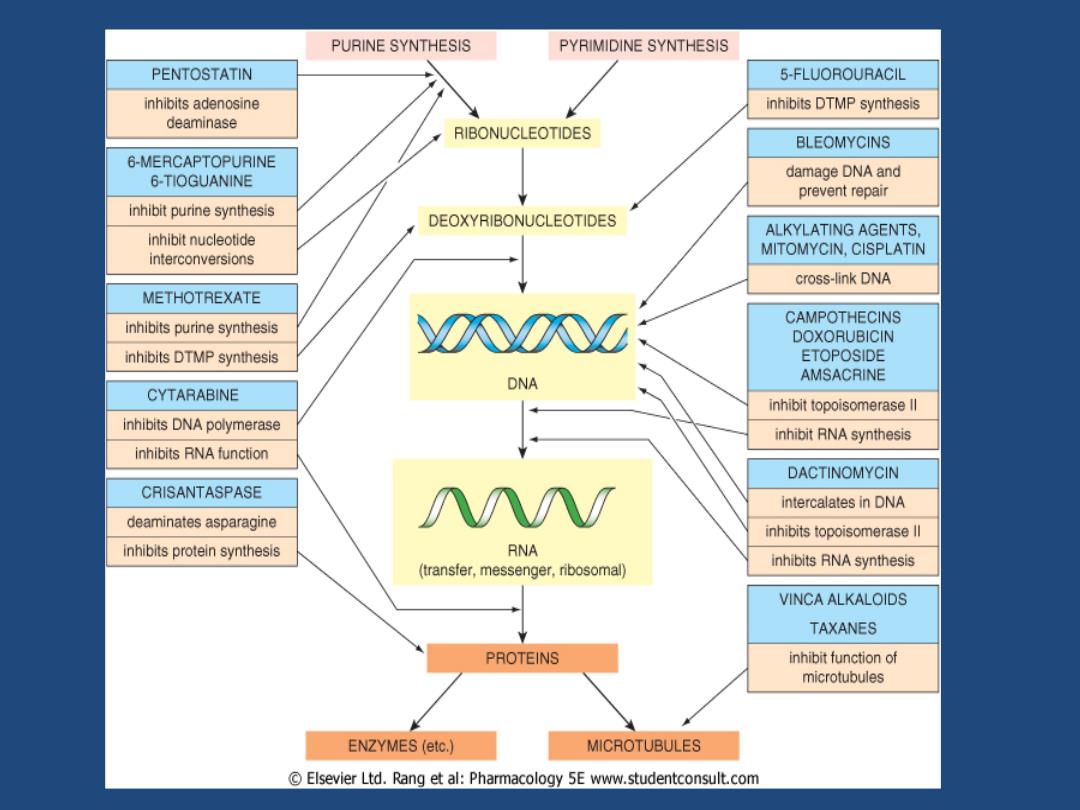
Mechanism of Cancer Chemotherapy (Cytostatic Drugs) 。Anti-proliferation -(1)Blockage DNA Synthesis Blockage purined pyramidine synthesis Inhibit DNA polymerase -(2)Direct Damage to DNA ·Breakage of DNA chain Cross-linkage,inhibit depolarization -(3)Inhibit Transduction (DNA RNA) - (4)Spindle toxin Mitosis damage -(5)Inhibit topoisomerase
Mechanism of Cancer Chemotherapy (Cytostatic Drugs) • Anti‐proliferation – (1) Blockage DNA Synthesis • Blockage purined pyramidine synthesis • Inhibit DNA polymerase – (2) Direct Damage to DNA • Breakage of DNA chain • Cross‐linkage, inhibit depolarization – (3) Inhibit Transduction (DNA RNA) – (4) Spindle toxin Mitosis damage – (5) Inhibit topoisomerase
PURINE SYNTHESIS PYRIMIDINE SYNTHESIS PENTOSTATIN 5-FLUOROURACIL inhibits adenosine inhibits DTMP synthesis deaminase RIBONUCLEOTIDES BLEOMYCINS 6-MERCAPTOPURINE 6-TIOGUANINE damage DNA and prevent repair inhibit purine synthesis DEOXYRIBONUCLEOTIDES ALKYLATING AGENTS. inhibit nucleotide MITOMYCIN,CISPLATIN interconversions cross-link DNA METHOTREXATE CAMPOTHECINS inhibits purine synthesis DOXORUBICIN inhibits DTMP synthesis ETOPOSIDE DNA AMSACRINE CYTARABINE inhibit topoisomerase ll inhibits DNA polymerase inhibit RNA synthesis inhibits RNA function DACTINOMYCIN CRISANTASPASE intercalates in DNA deaminates asparagine inhibits topoisomerase ll inhibits protein synthesis RNA inhibits RNA synthesis (transfer,messenger,ribosomal) VINCA ALKALOIDS TAXANES PROTEINS inhibit function of microtubules ENZYMES (etc.) MICROTUBULES Elsevier Ltd.Rang et al:Pharmacology 5E www.studentconsult.com