
第六章 微生物的代谢 新陈代谢:发生在活细胞中的各种分解代谢 (catabolism)和合成代谢(anabolism)的总和。 新陈代谢 = 分解代谢 + 合成代谢 分解代谢:指复杂的有机物分子通过分解代谢酶系的催 化,产生简单分子、腺苷三磷酸(ATP)形式的能量和 还原力的作用。 合成代谢:指在合成代谢酶系的催化下,由简单小分子、 ATP形式的能量和还原力一起合成复杂的大分子的过程
第六章 微生物的代谢 新陈代谢:发生在活细胞中的各种分解代谢 (catabolism)和合成代谢(anabolism)的总和。 新陈代谢 = 分解代谢 + 合成代谢 分解代谢:指复杂的有机物分子通过分解代谢酶系的催 化,产生简单分子、腺苷三磷酸(ATP)形式的能量和 还原力的作用。 合成代谢:指在合成代谢酶系的催化下,由简单小分子、 ATP形式的能量和还原力一起合成复杂的大分子的过程

•= total activity of cell; has two components 1.Anabolism - used to make new molecules •assimilative •biosynthetic •endergonic • G > 0; energy consuming 1.Catabolism - used to obtain energy •degradative •dissimulative •exergonic • G < 0; energy producing Metabolism
•= total activity of cell; has two components 1.Anabolism - used to make new molecules •assimilative •biosynthetic •endergonic • G > 0; energy consuming 1.Catabolism - used to obtain energy •degradative •dissimulative •exergonic • G < 0; energy producing Metabolism

CHAPTER OVERVIEW This chapter presents an overview of metabolism beginning with carbohydrate degradation and the aerobic generation of ATP through electron transport. Fermentation and anaerobic respiration are examined, followed by the catabolism of lipids, proteins, and amino acids. The chapter concludes with discussions of the function of inorganic molecules as electron acceptors and the trapping of energy by photosynthesis
CHAPTER OVERVIEW This chapter presents an overview of metabolism beginning with carbohydrate degradation and the aerobic generation of ATP through electron transport. Fermentation and anaerobic respiration are examined, followed by the catabolism of lipids, proteins, and amino acids. The chapter concludes with discussions of the function of inorganic molecules as electron acceptors and the trapping of energy by photosynthesis

第一节 代谢概论 一、代谢是生命的基本特征: 二、代谢通过代谢途径完成: 三、代谢途径是不平衡的稳态体系■ 四、代谢途径的形式多样 五、代谢途径有明确的细胞定位 六、代谢途径相互沟通 七、代谢途径间有能量关联 八、关键酶限制代谢途径的流量
第一节 代谢概论 一、代谢是生命的基本特征: 二、代谢通过代谢途径完成: 三、代谢途径是不平衡的稳态体系■ 四、代谢途径的形式多样 五、代谢途径有明确的细胞定位 六、代谢途径相互沟通 七、代谢途径间有能量关联 八、关键酶限制代谢途径的流量
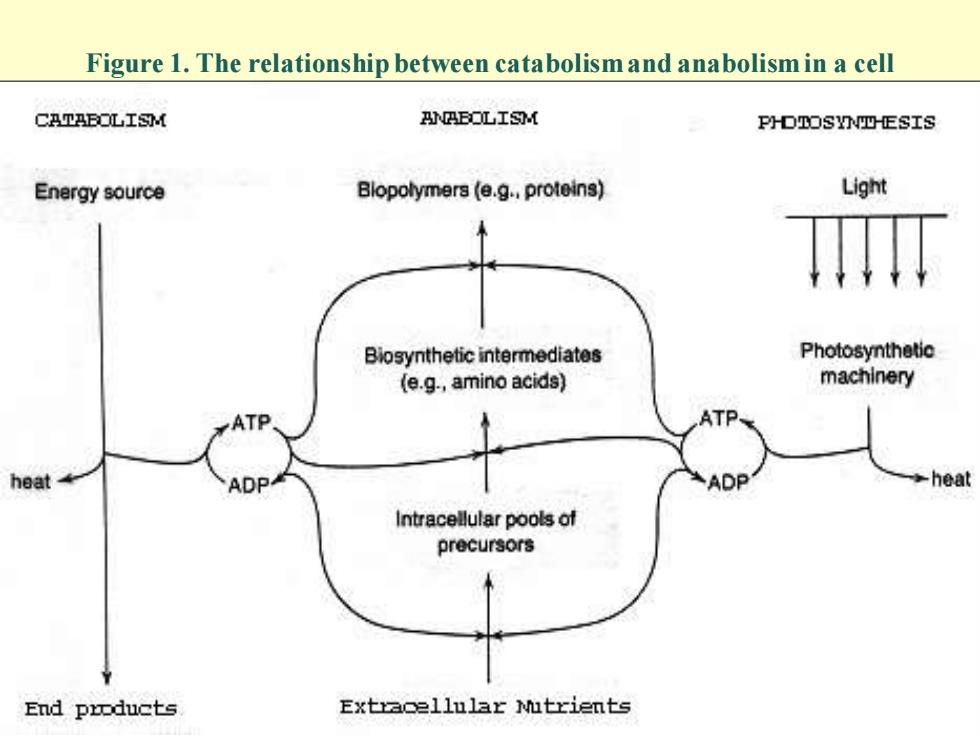
Figure 1. The relationship between catabolism and anabolism in a cell
Figure 1. The relationship between catabolism and anabolism in a cell