
Health Communication 9o LAT D1R⊙V● ●SKILEUROPY .9 主讲教师:王积龙
Health Communication 主讲教师:王积龙

Health Communication --Elaboration Likelihood Model Motivation and processing ability determine attitude change History and Orientation Petty and Cacioppo(1979) 60% discovered,in contrast to social judgment-involvement theory,that high levels of involvement do not invariably decrease persuasion
Health Communication -- Elaboration Likelihood Model Motivation and processing ability determine attitude change History and Orientation Petty and Cacioppo (1979) discovered, in contrast to social judgment-involvement theory, that high levels of involvement do not invariably decrease persuasion

Health Communication --Elaboration Likelihood Model Core Assumptions and Statements Core:The ELM is based on the idea that attitudes are important because attitudes guide decisions and other behaviors.While attitudes can result from a number of things,persuasion is a primary source.The model features two routes of persuasive influence:central and peripheral.The ELM accounts for the differences in persuasive impact produced by arguments that contain ample information and cogent reasons as compared to messages that rely on simplistic associations of negative and positive attributes to some object,action or situation. The key variable in this process is involvement,the extent to which an individual is willing and able to think'about the position advocated and its supporting materials.When people are motivated and able to think about the content of the message,elaboration is high.Elaboration involves cognitive processes such as evaluation,recall,critical judgment,and inferential judgment.When elaboration is high,the central persuasive route is likely to occur;conversely,the peripheral route is the likely result of low elaboration.Persuasion may also occur with low elaboration.The receiver is not guided by his or her assessment of the message,as in the case of the central route,but the receiver decides to follow a principle or a decision-rule which is derived from the persuasion situation
Health Communication -- Elaboration Likelihood Model Core Assumptions and Statements Core: The ELM is based on the idea that attitudes are important because attitudes guide decisions and other behaviors. While attitudes can result from a number of things, persuasion is a primary source. The model features two routes of persuasive influence: central and peripheral. The ELM accounts for the differences in persuasive impact produced by arguments that contain ample information and cogent reasons as compared to messages that rely on simplistic associations of negative and positive attributes to some object, action or situation. The key variable in this process is involvement, the extent to which an individual is willing and able to ‘think’ about the position advocated and its supporting materials. When people are motivated and able to think about the content of the message, elaboration is high. Elaboration involves cognitive processes such as evaluation, recall, critical judgment, and inferential judgment. When elaboration is high, the central persuasive route is likely to occur; conversely, the peripheral route is the likely result of low elaboration. Persuasion may also occur with low elaboration. The receiver is not guided by his or her assessment of the message, as in the case of the central route, but the receiver decides to follow a principle or a decision-rule which is derived from the persuasion situation
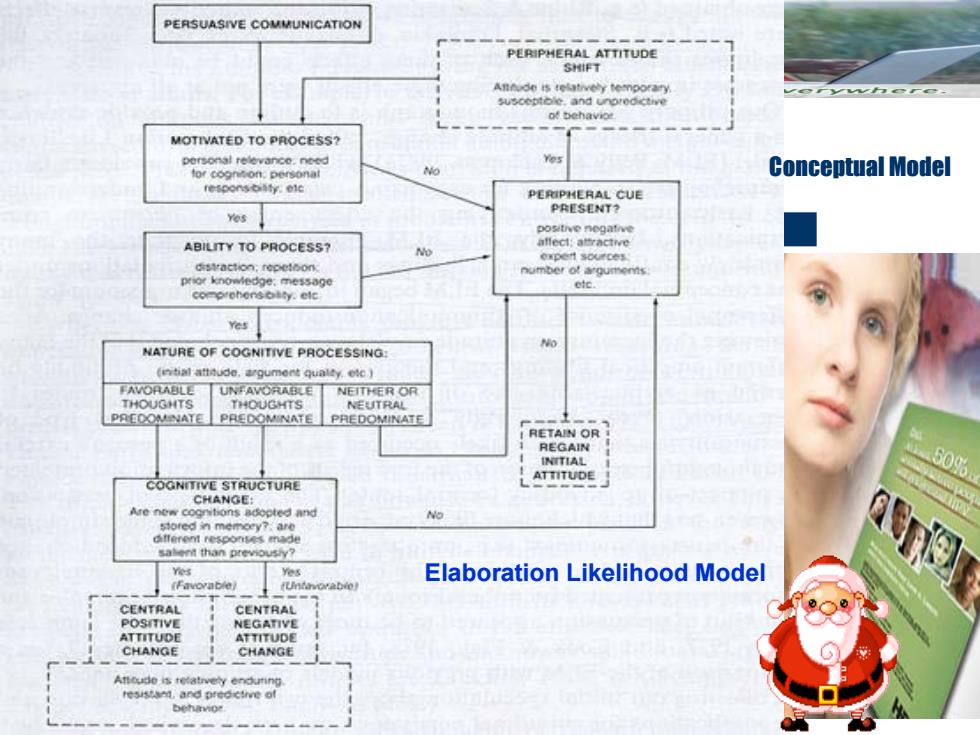
PERSUASIVE COMMUNICATION PERIPHERAL ATTITUDE 生针样于 ol behavioe MOTIVATED TO PROCESS? personal relevance:need Yes tor coonon personat No Conceptual Model PERIPHERAL CUE Yes PRESENT? positive negative ABILITY TO PROCESS? aflect:atractive 。州o0地 distraction:repetoon number of argun prior knowledge:message Yes Mo NATURE OF COGNITIVE PROCESSING LAVORABU UNFAVORABLE NEITHER OR THOUGHTS THOUGHTS NEUTRAL PREOOMINATE PREDOMINATE PREDOMINATE RETAIN OR 日ECA ATTITUDE 60% COGNITIVE STRUCTURE CHANGE: sored in memory?.are dtferent responses made a箱九n prevous小y? 阀 Yes Yes Elaboration Likelihood Model CENTR益1 CENTRAL POSTTIVE NEG去TW ATTITUDE ATTITUDE CHANGE CHANGE A韩de is end水n
Health Communication -- Elaboration Likelihood Model Conceptual Model Elaboration Likelihood Model
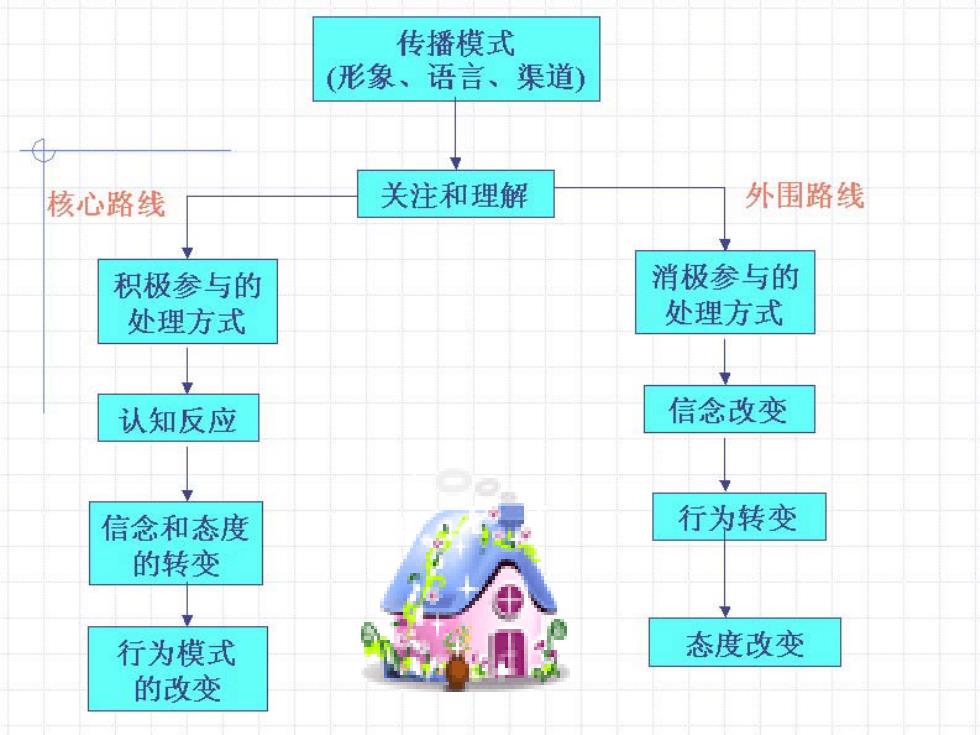
传播模式 (形象、语言、渠道) 核心路线 关注和理解 外围路线 积极参与的 消极参与的 处理方式 处理方式 认知反应 信念改变 信念和态度 行为转变 的转变 行为模式 态度改变 的改变
Health Communication -- Elaboration Likelihood Model Conceptual Model Elaboration Likelihood Model