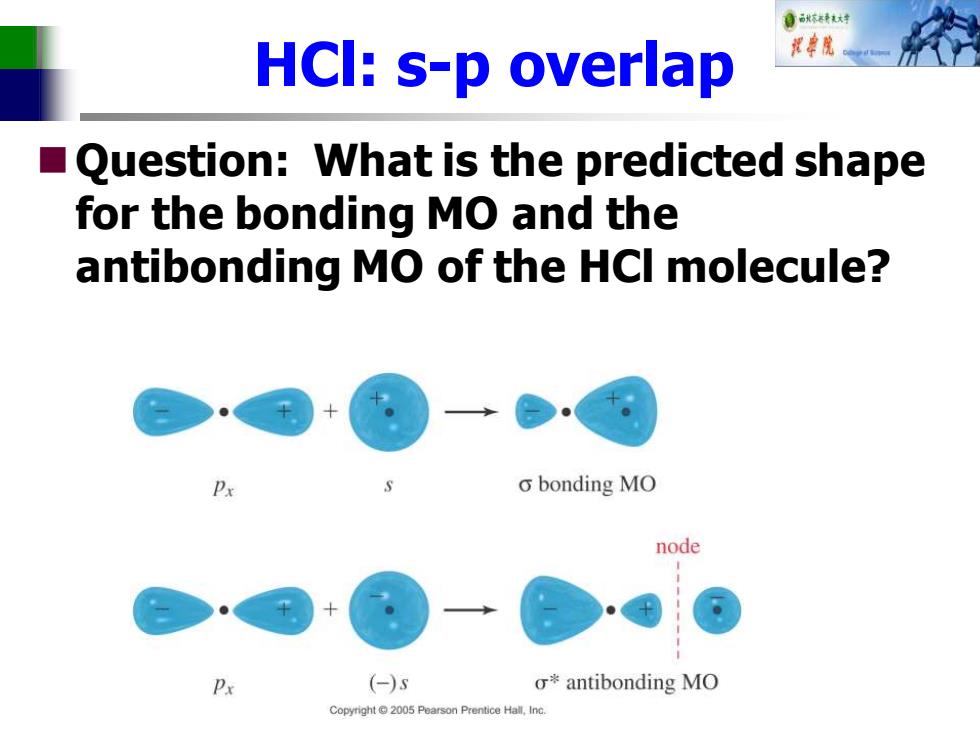
自秋不特大对 HCI:s-p overlap ■ Question:What is the predicted shape for the bonding MO and the antibonding MO of the HCI molecule? o bonding MO node Px (-)s σ*antibonding MO Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
HCl: s-p overlap ◼Question: What is the predicted shape for the bonding MO and the antibonding MO of the HCl molecule?
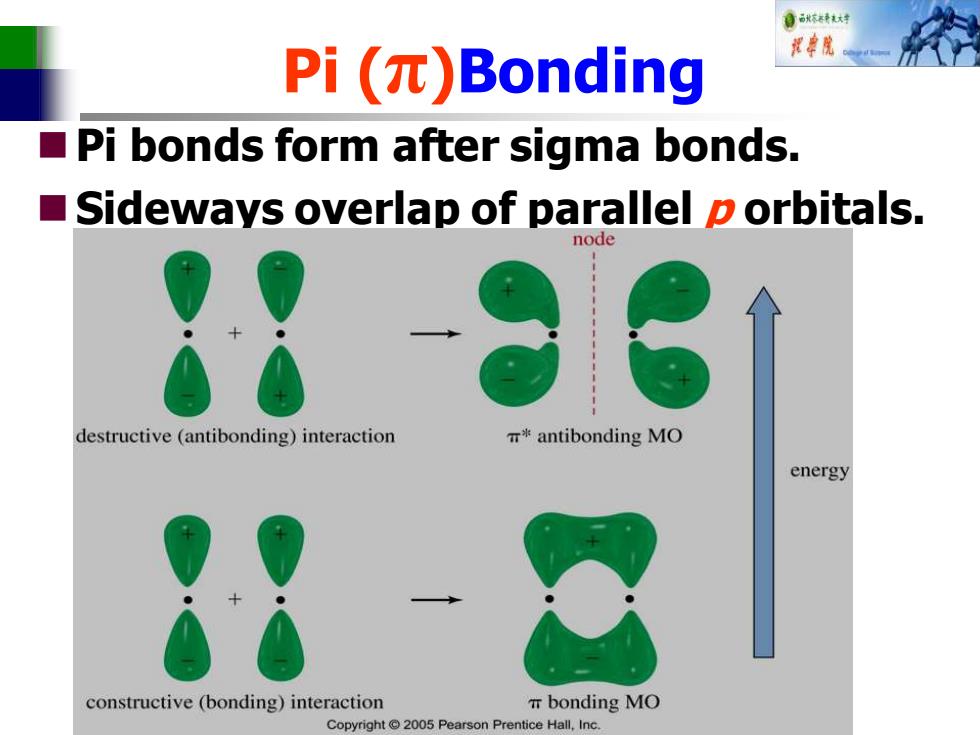
自秋精对 Pi ()Bonding 视中院 Pi bonds form after sigma bonds. ■ Sideways overlap of parallel p orbitals. node destructive (antibonding)interaction m*antibonding MO energy constructive (bonding)interaction T bonding MO Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Pi (π)Bonding ◼Pi bonds form after sigma bonds. ◼Sideways overlap of parallel p orbitals
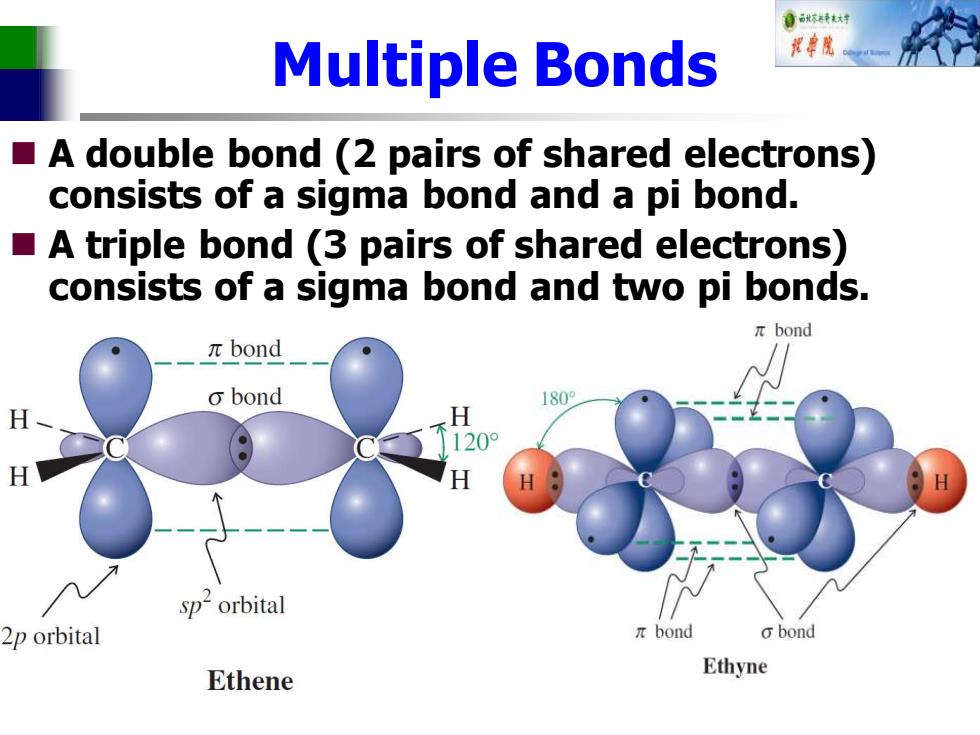
自标转对 Multiple Bonds A double bond (2 pairs of shared electrons) consists of a sigma bond and a pi bond. A triple bond (3 pairs of shared electrons) consists of a sigma bond and two pi bonds. πbond πbond o bond 1809 H H 8 120° H H sp2orbital 2p orbital πbond obond Ethene Ethyne
Multiple Bonds ◼ A double bond (2 pairs of shared electrons) consists of a sigma bond and a pi bond. ◼ A triple bond (3 pairs of shared electrons) consists of a sigma bond and two pi bonds

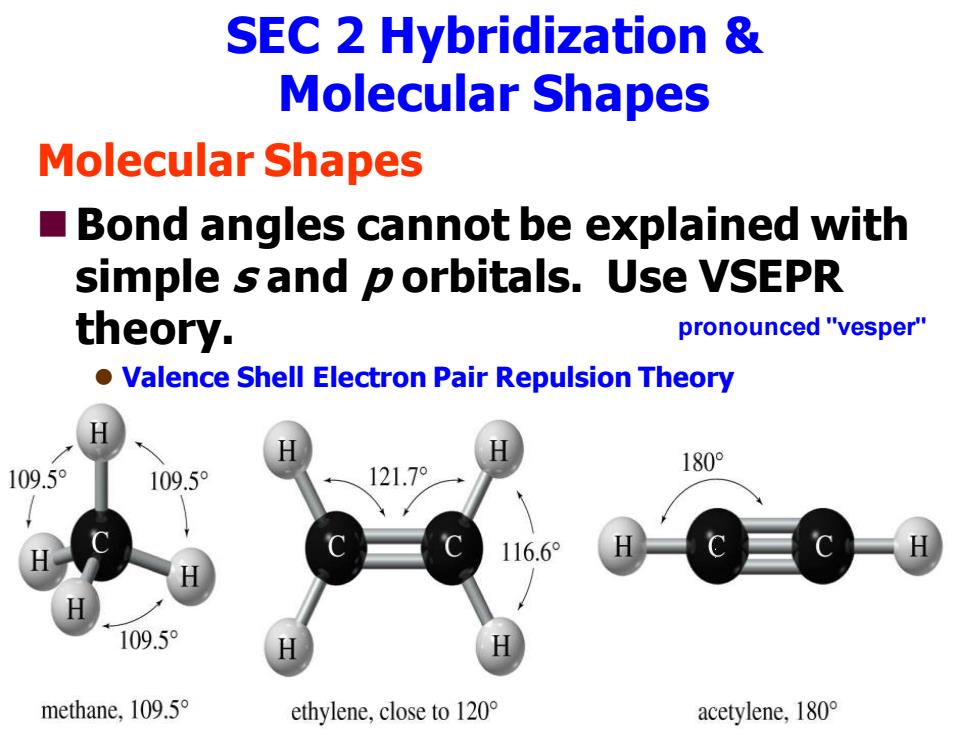
SEC 2 Hybridization Molecular Shapes Molecular Shapes ■ Bond angles cannot be explained with simple sand porbitals.Use VSEPR theory. pronounced "vesper" Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory 109.5 109.5° 121.7° 180° 116.6° 109.5° methane,109.5 ethylene,close to 120 acetylene,.I80°
SEC 2 Hybridization & Molecular Shapes Molecular Shapes ◼Bond angles cannot be explained with simple s and p orbitals. Use VSEPR theory. ⚫ Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory pronounced "vesper