
IRONMETABOLISM.Dietary iron- High in iron·Red meat/ liverkidney/ oily fish- Average iron.Beans /fortifiedcereals/dark greenvegetables/driedfruit/nutsand seeds- Poor in iron.Mi1k(1.5vs0.5mg/L)HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOG, CHILDREN'SHOSPITAL
• Dietary iron –High in iron • Red meat/ liver kidney/ oily fish –Average iron • Beans / fortified cereals/ dark green vegetables/ dried fruit/ nuts and seeds –Poor in iron • Milk (1.5 vs 0.5mg/L) IRON METABOLISM HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY, CHILDREN’S H O S P I T A L

IRONMETABOLISM·Iron absorption1-20%general absorption10-25%-Meat/fish/ chicken1%-Cereals/vegetables50%/10%-Breast/cow' s milkHEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY,CHILDREN SHOSPITAL
• Iron absorption general absorption –M e a t/ fish/ chicken 1-2 0% 1 0-25% –Cereals/vegetables 1% –Breast/cow’s milk 5 0 % /10% IRON METABOLISM HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY, CHILDREN’S H O S P I T A L
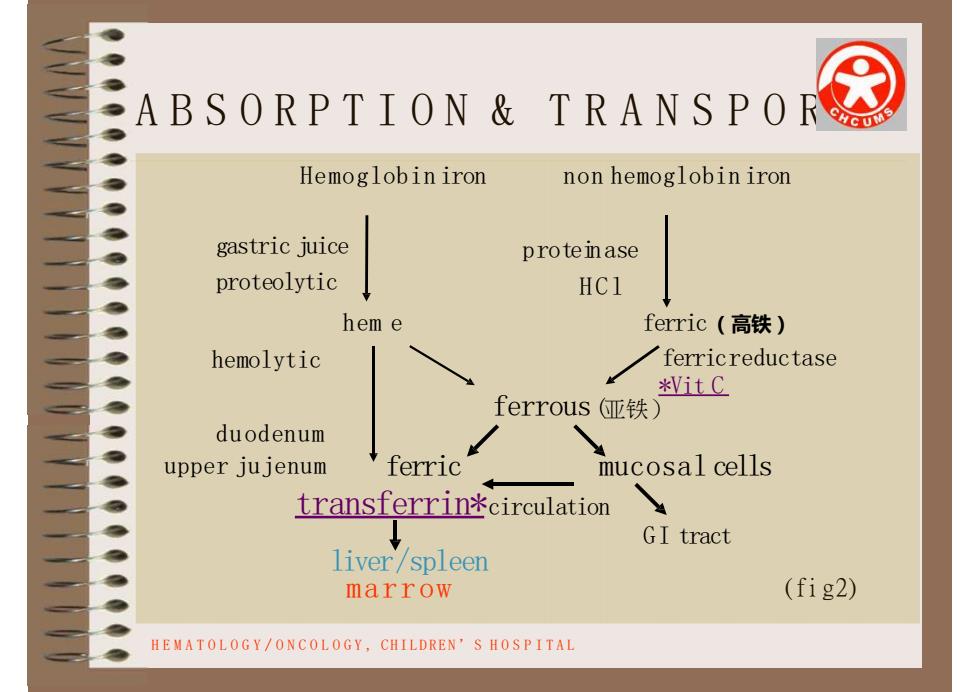
ABSORPTION&TRANSPORHemoglobinironnon hemoglobinirongastric juiceproteinaseproteolyticHC1hem eferric(高铁)ferricreductasehemolytic*VitCferrous亚铁)duodenummucosal cellsferricupper jujenumtransferrin*circulationGI tractliver/spleen(fig2)marrowHEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY,CHILDREN'SHOSPITAL
A B S O R P T I O N & TRANSPOR T Hemoglobin iron non hemoglobin iron proteinase HCl gastric juice proteolytic hem e hemolytic ferric(高铁) ferricreductase *Vit C ferrous(亚铁) duodenum upper jujenum ferric mucosal cells GI tract transferrin*circulation liver/spleen marrow ( f i g2) HEMATOLOGY/ONCOLOGY, CHILDREN’S H O S P I T A L
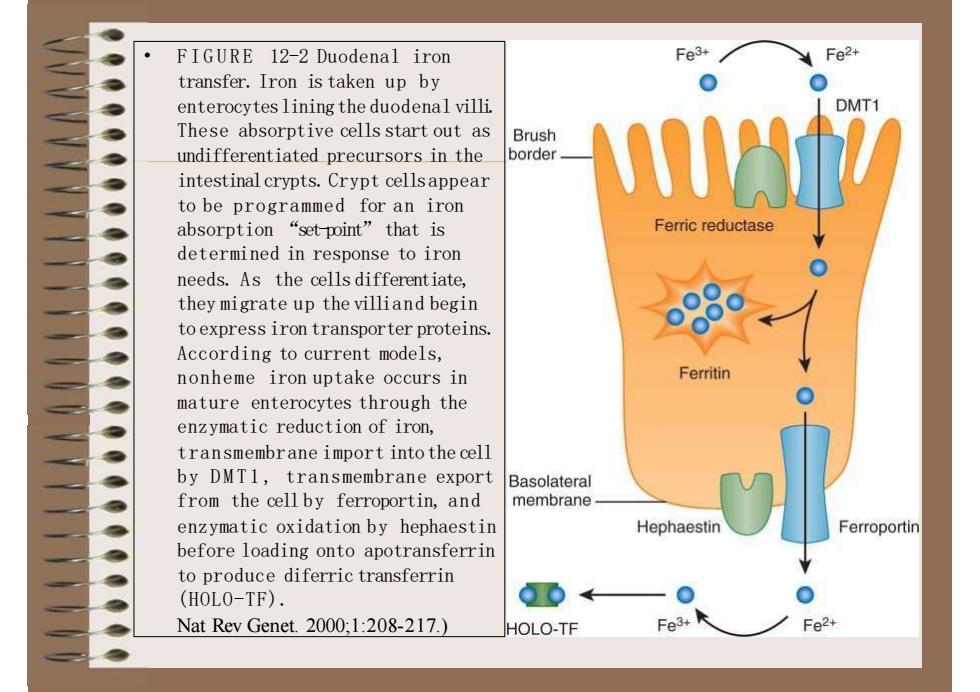
Fe3+Fe2+FIGURE 12-2Duodenal irontransfer. Iron istaken up byODMT1enterocytesliningtheduodenal villiThese absorptive cells start out asBrushmanborderundifferentiated precursorsin theintestinalcrypts.Cryptcellsappeartobe programmed foran ironFerricreductaseabsorption “set point"that isdetermined in response to ironneeds. As the cells differentiate,theymigrate up thevilliand begintoexpressirontransporterproteins.According to current models,Ferritinnonheme iron uptake occurs inmature enterocytes through theenzymatic reduction of iron,transmembraneimportintothecellby DMTl,transmembrane exportBasolateralfrom the cellby ferroportin, andmembraneenzymatic oxidation by hephaestinHephaestinFerroportinbeforeloading onto apotransferrinto produce diferric transferrinQOO(HOLO-TF).Fe3+Fe2+Nat Rev Genet. 2000;1:208-217.)HOLO-TF
• FIGURE 12-2 Duodenal iron transfer. Iron is taken up by enterocytesliningthe duodenal villi. These absorptive cells start out as undifferentiated precursors in the intestinalcrypts.Crypt cellsappear to be programmed for an iron absorption “set-point” that is determined in response to iron needs. As the cells differentiate, they migrate up the villiand begin to express iron transporter proteins. According to current models, nonheme iron uptake occurs in mature enterocytes through the enzymatic reduction of iron, transmembrane import intothe cell by DMT1, transmembrane export from the cell by ferroportin, and enzymatic oxidation by hephaestin before loading onto apotransferrin to produce diferric transferrin (HOLO-TF). Nat Rev Genet. 2000;1:208-217.)
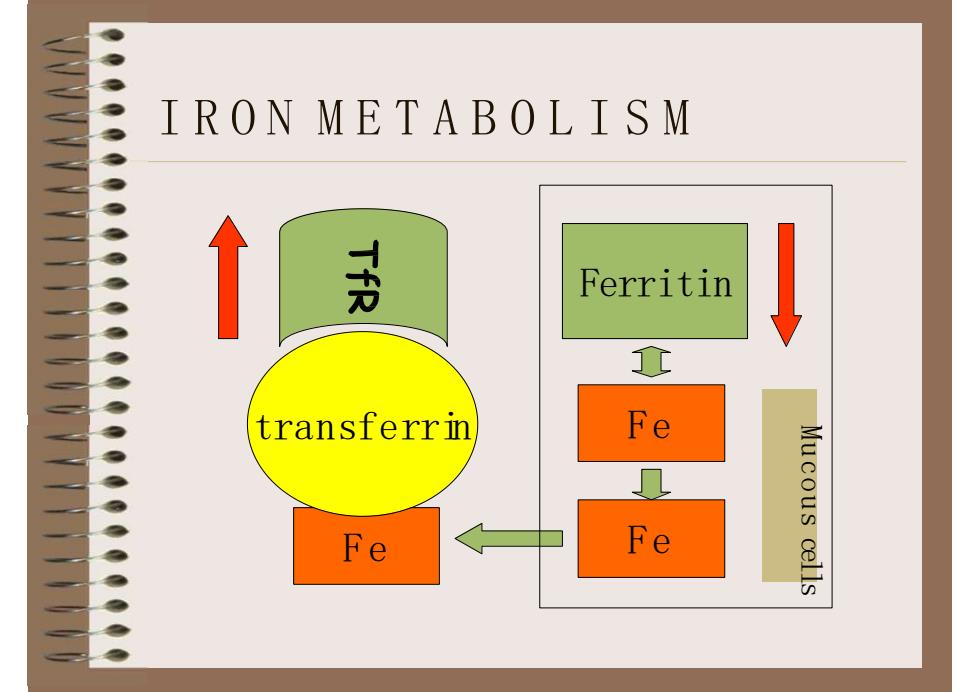
-IRONMETABOLISMTfRFerritin工FetransferrinMucous cellsFeFe
Ferritin Fe transferrin Fe Fe IRON METABOLISM Mucous cells