
>Substitutes-Two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the quantity demanded of the other. >Complements-Two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to a decrease in the quantity demanded of the other
➢ Substitutes-Two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the quantity demanded of the other. ➢ Complements-Two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to a decrease in the quantity demanded of the other

2.2 The Market Mechanism Equilibrium(or market-clearing)price-Price that equates the quantity supplied to the quantity demanded. >Market mechanism-Tendency in a free market for price to change until the market clears. >Surplus-Situation in which the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded. >Shortage-Situation in which the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied
2.2 The Market Mechanism ➢ Equilibrium(or market-clearing)price-Price that equates the quantity supplied to the quantity demanded. ➢ Market mechanism-Tendency in a free market for price to change until the market clears. ➢ Surplus-Situation in which the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded. ➢ Shortage-Situation in which the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied
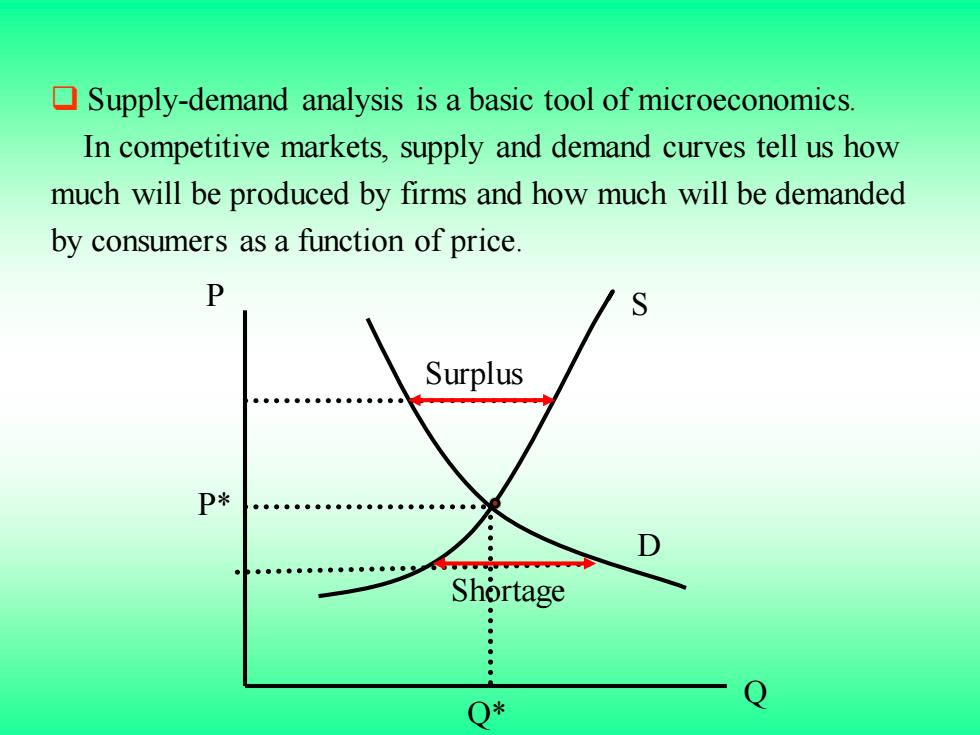
Supply-demand analysis is a basic tool of microeconomics. In competitive markets,supply and demand curves tell us how much will be produced by firms and how much will be demanded by consumers as a function of price. Surplus Shortage : : Q*
❑ Supply-demand analysis is a basic tool of microeconomics. In competitive markets, supply and demand curves tell us how much will be produced by firms and how much will be demanded by consumers as a function of price. Q P Q* P* S D Surplus Shortage