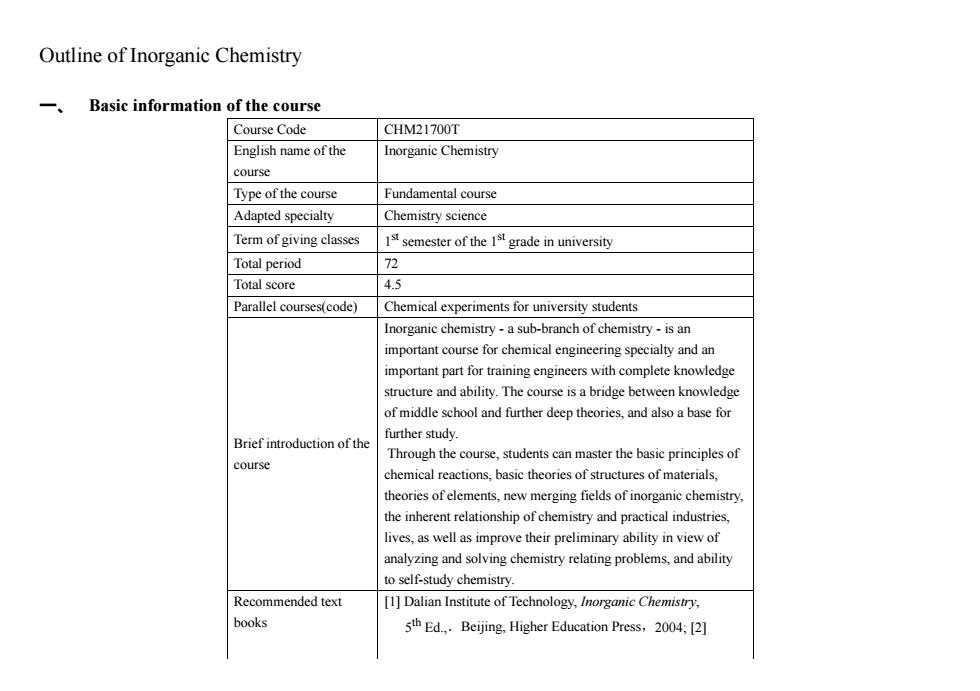
Outline of Inorganic Chemistry 一、 Basic information of the course Course Code CHM21700T English name of the Inorganic Chemistry course Type of the course Fundamental course Adapted specialty Chemistry science Term of giving classes 1ssemester of the 1st grade in university Total period 72 Total score 4.5 Parallel courses(code) Chemical experiments for university students Inorganic chemistry-a sub-branch of chemistry-is an important course for chemical engineering specialty and an important part for training engineers with complete knowledge structure and ability.The course is a bridge between knowledge of middle school and further deep theories,and also a base for further study. Brief introduction of the Through the course,students can master the basic principles of course chemical reactions,basic theories of structures of materials, theories of elements,new merging fields of inorganic chemistry, the inherent relationship of chemistry and practical industries, lives,as well as improve their preliminary ability in view of analyzing and solving chemistry relating problems,and ability to self-study chemistry. Recommended text [1]Dalian Institute of Technology,Inorganic Chemistry, books 5thEd.Beijing.Higher Education Press,2004;[2]
Outline of Inorganic Chemistry 一、 Basic information of the course Course Code CHM21700T English name of the course Inorganic Chemistry Type of the course Fundamental course Adapted specialty Chemistry science Term of giving classes 1 st semester of the 1st grade in university Total period 72 Total score 4.5 Parallel courses(code) Chemical experiments for university students Brief introduction of the course Inorganic chemistry - a sub-branch of chemistry - is an important course for chemical engineering specialty and an important part for training engineers with complete knowledge structure and ability. The course is a bridge between knowledge of middle school and further deep theories, and also a base for further study. Through the course, students can master the basic principles of chemical reactions, basic theories of structures of materials, theories of elements, new merging fields of inorganic chemistry, the inherent relationship of chemistry and practical industries, lives, as well as improve their preliminary ability in view of analyzing and solving chemistry relating problems, and ability to self-study chemistry. Recommended text books [1] Dalian Institute of Technology, Inorganic Chemistry, 5 th Ed.,.Beijing, Higher Education Press,2004; [2]

Raymond Chang.Chemistry,9h edition,McGraw Hill Education,1999 [1]Oxtoby,Gillis,Nachtrieb.Principhes of Modern Chemistry (Fifth).U.S.A.Thomson.2002 [2]C.E.Housecroft and A.G.Sharpe,Inorganic Chemistry,3rd edition,Pearson Education/Prentice Hall [3]F.A.Cotton,G.Wilkinson,C.A.Murillo,and M. Bochmann,Advanced Inorganic Chemistry,Six Edition, Willey Interscience,1999 [4]M.S.Silberberg,Chemistry-The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change,hed,,McGraw Hill,Boston,2006 [5]G.Rayner-Canham,T.Overton,Descriptive Inorganic References Chemistry,4h ed,Freeman&Co.New York,2006. 扩充性无机化学中文优秀教材 [山傅献彩主编大学化学(上、下册).北京:高等教育出版 社,1999. [2]吉林大学,武汉大学,南开大学等校编,宋天佑等,无 机化学,(上、下册),高等教育出版社,2005. [3]唐有祺主编.当代无机化学前沿.北京:中国致公出版 社,1997. [4唐有祺,王夔主编化学与社会.北京:高等教育出版 社,1997. 二、Targets of the course education 1.Aims of the course in view of moral character
Raymond Chang, Chemistry, 9th edition,McGraw Hill Education, 1999. References [1] Oxtoby, Gillis, Nachtrieb. Principhes of Modern Chemistry. (Fifth).U.S.A. Thomson,2002 [2] C. E. Housecroft and A. G. Sharpe, Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd edition, Pearson Education/ Prentice Hall [3] F. A. Cotton, G. Wilkinson, C. A. Murillo, and M. Bochmann, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, Six Edition, Willey Interscience, 1999 [4] M. S. Silberberg,Chemistry – The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change, 4th ed, , McGraw Hill, Boston, 2006 [5] G. Rayner-Canham, T. Overton, Descriptive Inorganic Chemistry, 4th ed, Freeman & Co., New York, 2006. 扩充性无机化学中文优秀教材 [1] 傅献彩主编. 大学化学(上、下册). 北京:高等教育出版 社,1999. [2] 吉林大学,武汉大学,南开大学等校编,宋天佑等,无 机化学,(上、下册),高等教育出版社,2005. [3] 唐有祺主编. 当代无机化学前沿. 北京:中国致公出版 社,1997. [4] 唐有祺,王 夔主编. 化学与社会. 北京:高等教育出版 社,1997. 二、 Targets of the course education 1.Aims of the course in view of moral character

Dialectic materialism theories will be utilized during the course to explain chemical basic principles and rules of elements and chemical reactions,in order to promote formation of Weltanschauung of dialectic materialism. Try to help students to understand some questions of wide interest in order to enrich their social responsibilities,strengthen their understanding about that science and technology is the first fertility,let them get to know the current status of the chemistry and chemical industries in the world,inspire their proper attitude towards study,love and get them to devote to chemistry and chemical technology relating career. 2.Aims in view of specialty knowledge and ability Teach student scientific thinking way,help them adapt study in university and improve their ability for self-study and self-solving chemistry questions. Combine new development of the chemical industries,reflect the developing trends of inorganic chemistry and its practical applications in high technologies, stimulate students'enthusiasm and consciousness,incubate their independence,activity and creativity The contents of the course is set up at three different levels,namely,(1)to master(learn),(2)to be familiar with (understand),and (3)to know. Contents and requirements on theory teaching(including time distribution) Chapter 1.Preface and introduction (1.5 hrs) $1.1 Chemistry---the central science full of practicability and creativity $1.2 Features of chemical changes $1.3 History,revival and development of inorganic chemistry $1.4 How to study easily but efficiently inorganic chemistry $1.5 Styles and forms of examination for the course This chapter mainly consists of brief introduction about the status of chemistry,features of chemical changes,the history,revival and development of inorganic chemistry,how to study effectively and efficiently inorganic chemistry,clarifying requirements,and course plan and styles of examinations Chapter 2 Thermochemistry(2.0 hrs) $2.1 Basic terms in thermodynamics $2.2 the First law of thermodynamics $2.3 Heat of a chemical reaction $2.4 the Hess's law aims of teaching:
Dialectic materialism theories will be utilized during the course to explain chemical basic principles and rules of elements and chemical reactions, in order to promote formation of Weltanschauung of dialectic materialism. Try to help students to understand some questions of wide interest in order to enrich their social responsibilities, strengthen their understanding about that science and technology is the first fertility, let them get to know the current status of the chemistry and chemical industries in the world, inspire their proper attitude towards study, love and get them to devote to chemistry and chemical technology relating career. 2.Aims in view of specialty knowledge and ability Teach student scientific thinking way, help them adapt study in university and improve their ability for self-study and self-solving chemistry questions. Combine new development of the chemical industries, reflect the developing trends of inorganic chemistry and its practical applications in high technologies, stimulate students’ enthusiasm and consciousness, incubate their independence, activity and creativity The contents of the course is set up at three different levels, namely, (1) to master (learn),(2) to be familiar with (understand), and (3) to know. 三、 Contents and requirements on theory teaching (including time distribution) Chapter 1. Preface and introduction (1.5 hrs) §1.1 Chemistry---the central science full of practicability and creativity §1.2 Features of chemical changes §1.3 History, revival and development of inorganic chemistry §1.4 How to study easily but efficiently inorganic chemistry §1.5 Styles and forms of examination for the course This chapter mainly consists of brief introduction about the status of chemistry, features of chemical changes, the history, revival and development of inorganic chemistry, how to study effectively and efficiently inorganic chemistry, clarifying requirements, and course plan and styles of examinations Chapter 2 Thermochemistry (2.0 hrs) §2.1 Basic terms in thermodynamics §2.2 the First law of thermodynamics §2.3 Heat of a chemical reaction §2.4 the Hess’s law aims of teaching:

To know the concepts of system,surrounding,phase etc,and to be familiar with the Law of conservation and conversion of energy in chemical reactions.To understand the concepts of state function,enthalpy,molar enthalpy change,standard molar enthalpy of formation and so on.To master thermochemical equation, enthalpy change of a reaction,Hess'law and related calculation. important and difficult points Law of conservation and conversion of energy in chemical reactions.Heat and work are two forms of energy transfer between systems and surroundings. Reaction enthalpy is dependent on composition,state and condition of the chemical reaction. Paying attention on how to write thermochemical equation.Calculation of standard molar enthalpy change of a reaction Afrom standard molar enthalpy of formation of substancesA The essential of Hess'law:enthalpy is a state function,the enthalpy change of a reaction is constant,whether the reaction is carried out directly in one step or indirectly through a number of steps Chapter 3 Chemical kinetics(self-study) $3.1 Brief introduction of chemical reaction rates $3.2 Brief introduction of effect of concentration of reactants on reaction rate-the rate expression $3.3 Brief introduction of effect of temperature on reaction rate-Arrhenius equation $3.4 Brief introduction of theory of reaction rate and reaction mechanisms $3.5 Brief introduction of catalyst and catalysis aims of study To understand the concepts of reaction rate,order of a reaction and reaction rate expression.To master the concepts of activity energy,activated molecule,and to explain essential of the influence of concentration,catalyst on rate of a particular chemical reaction.To master reaction rate expression. important and difficult points Concept of reaction rate under constant pressure and temperature.Reaction rate expression in the case of complex reaction has to be determined by experiments.Rate constant k,and the order of a reaction a.B.Collision theory,activated complex.The concepts of activation energy,activated molecule,the influence of concentration,temperature,catalyst on a particular chemical reaction. Chapter 4 Chemical equalibria,entropy,and Gibbs function (5.0 hrs)
To know the concepts of system, surrounding, phase etc, and to be familiar with the Law of conservation and conversion of energy in chemical reactions. To understand the concepts of state function, enthalpy, molar enthalpy change, standard molar enthalpy of formation and so on. To master thermochemical equation, enthalpy change of a reaction, Hess’ law and related calculation. important and difficult points Law of conservation and conversion of energy in chemical reactions. Heat and work are two forms of energy transfer between systems and surroundings. Reaction enthalpy is dependent on composition, state and condition of the chemical reaction. Paying attention on how to write thermochemical equation. Calculation of standard molar enthalpy change of a reaction ΔfHm Q from standard molar enthalpy of formation of substances ΔfHm Q. The essential of Hess’ law: enthalpy is a state function, the enthalpy change of a reaction is constant, whether the reaction is carried out directly in one step or indirectly through a number of steps. Chapter 3 Chemical kinetics (self-study) §3.1 Brief introduction of chemical reaction rates §3.2 Brief introduction of effect of concentration of reactants on reaction rate —the rate expression §3.3 Brief introduction of effect of temperature on reaction rate—Arrhenius equation §3.4 Brief introduction of theory of reaction rate and reaction mechanisms §3.5 Brief introduction of catalyst and catalysis aims of study To understand the concepts of reaction rate, order of a reaction and reaction rate expression. To master the concepts of activity energy, activated molecule, and to explain essential of the influence of concentration, catalyst on rate of a particular chemical reaction. To master reaction rate expression. important and difficult points Concept of reaction rate under constant pressure and temperature. Reaction rate expression in the case of complex reaction has to be determined by experiments. Rate constant k, and the order of a reaction α、β. Collision theory, activated complex. The concepts of activation energy, activated molecule, the influence of concentration, temperature, catalyst on a particular chemical reaction. Chapter 4 Chemical equalibria, entropy, and Gibbs function(5.0 hrs)

$4.1 The standard equilibrium constant $4.2 The application of the standard equilibrium constant $4.3 The shift of a chemical equilibrium $4.4 Spontaneous reactions and entropy $4.5 Gibbs function aims of teaching: To be familiar with the concept of shift of a chemical equilibrium,calculation of stand equilibrium constant and compositions of a reaction from thermodynamic functions or Van't Hoff equation equilibrium.To be familiar with reaction quotient criterion,Le Chatelier principle,to master how concentration,pressure, temperature influence a shift of chemical equilibrium and related calculation.To know the concepts of standard molar entropy Sstandard molar Gibbs function of formation AGm,simple calculation of standard molar entropy change ASand standard molar Gibbs function change of a reaction ArGm,the relationship amongandStojudge in principle the direction and extent of a chemical reaction based onandA important and difficult points: Calculation of stand equilibrium constant of a reaction from thermodynamic functions or Van't Hoff equation.Summarizing the parameters influencing chemical equilibrium shift and rules of chemical equilibrium shift,understanding on the Le Chatelier principle. Chapter 5 Acid-base equilibria (8.0 hrs) 5.1 The Brensted theory of acids and bases $5.2 Ionization equilibrium of water and the pH scale 5.3 Equilibria in solutions of weak acids and weak bases 5.4 Buffer solutions 5.5 Acid-bases indicators 5.6 Lewis acids and bases and coordination compounds 5.7 Complexation reaction and coordination equilibria aims of teaching:
§4.1 The standard equilibrium constant §4.2 The application of the standard equilibrium constant §4.3 The shift of a chemical equilibrium §4.4 Spontaneous reactions and entropy §4.5 Gibbs function aims of teaching: To be familiar with the concept of shift of a chemical equilibrium, calculation of stand equilibrium constant and compositions of a reaction from thermodynamic functions or Van’t Hoff equation equilibrium. To be familiar with reaction quotient criterion, Le Châtelier principle, to master how concentration, pressure, temperature influence a shift of chemical equilibrium and related calculation. To know the concepts of standard molar entropy Sm Q, standard molar Gibbs function of formation DfGm Q , simple calculation of standard molar entropy change DSm Q and standard molar Gibbs function change of a reaction DrGm Q, the relationship among DrGm Q , DrHm Q and DrSm Q , to judge in principle the direction and extent of a chemical reaction based on DrGm and DrGm Q. important and difficult points: Calculation of stand equilibrium constant of a reaction from thermodynamic functions or Van’t Hoff equation. Summarizing the parameters influencing chemical equilibrium shift and rules of chemical equilibrium shift, understanding on the Le Châtelier principle. Chapter 5 Acid-base equilibria(8.0 hrs) § 5.1 The Brønsted theory of acids and bases § 5.2 Ionization equilibrium of water and the pH scale § 5.3 Equilibria in solutions of weak acids and weak bases § 5.4 Buffer solutions § 5.5 Acid-bases indicators § 5.6 Lewis acids and bases and coordination compounds § 5.7 Complexation reaction and coordination equilibria aims of teaching: