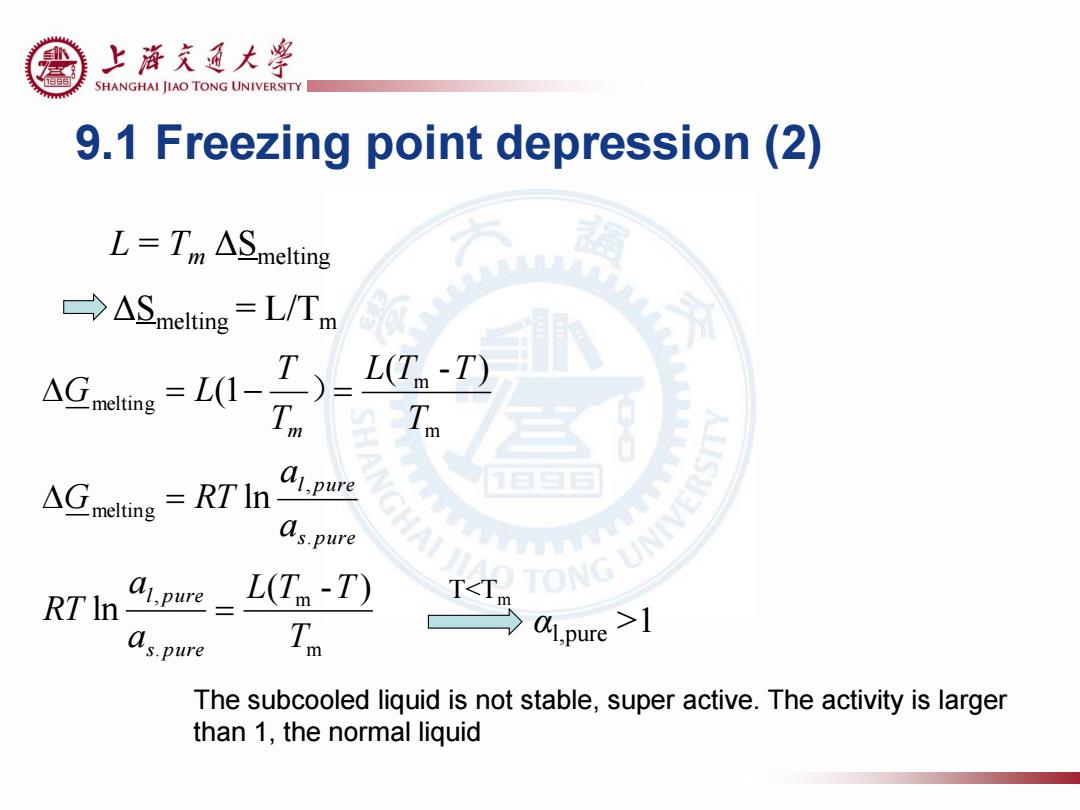
上浒充通大警 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 9.1 Freezing point depression(2) L=Tm ASmelting →ASmelting=L/Tm L(T-T) Tm △G RT In as.pure RT In- ai.pure L(T-T) T<Tm as.pure Zo a.pure >1 The subcooled liquid is not stable,super active.The activity is larger than 1,the normal liquid
9.1 Freezing point depression (2) L = Tm ΔSmelting ΔSmelting = L/Tm m m . , . , melting m m melting ( - ) ln ln ( - ) (1 T L T T a a RT a a G RT T L T T T T G L s pure l pure s pure l pure m ) T<Tm αl,pure >1 The subcooled liquid is not stable, super active. The activity is larger than 1, the normal liquid
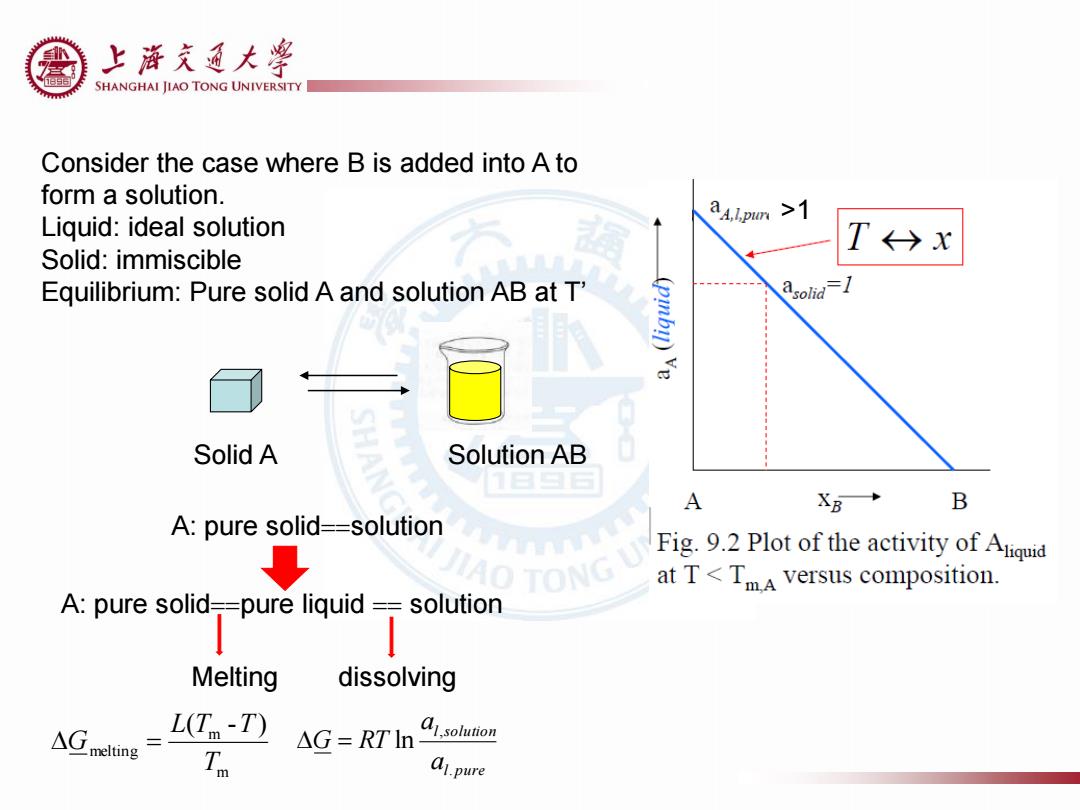
上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Consider the case where B is added into A to form a solution. Liquid:ideal solution Solid:immiscible T→x Equilibrium:Pure solid A and solution AB at T' Solid A Solution AB A XB→ B A:pure solid==solution ↓ Fig.9.2 Plot of the activity of Aqi AO TONG at T<TmA versus composition. A:pure solid-=pure liquid =solution 1 Melting dissolving △melting L(T-T) △G=RTln 4Isolution Tn a1.pure
>1 Consider the case where B is added into A to form a solution. Liquid: ideal solution Solid: immiscible Equilibrium: Pure solid A and solution AB at T’ l pure l solution a a G RT . , ln Solid A Solution AB A: pure solidsolution A: pure solidpure liquid solution Melting dissolving m m melting ( - ) T L T T G
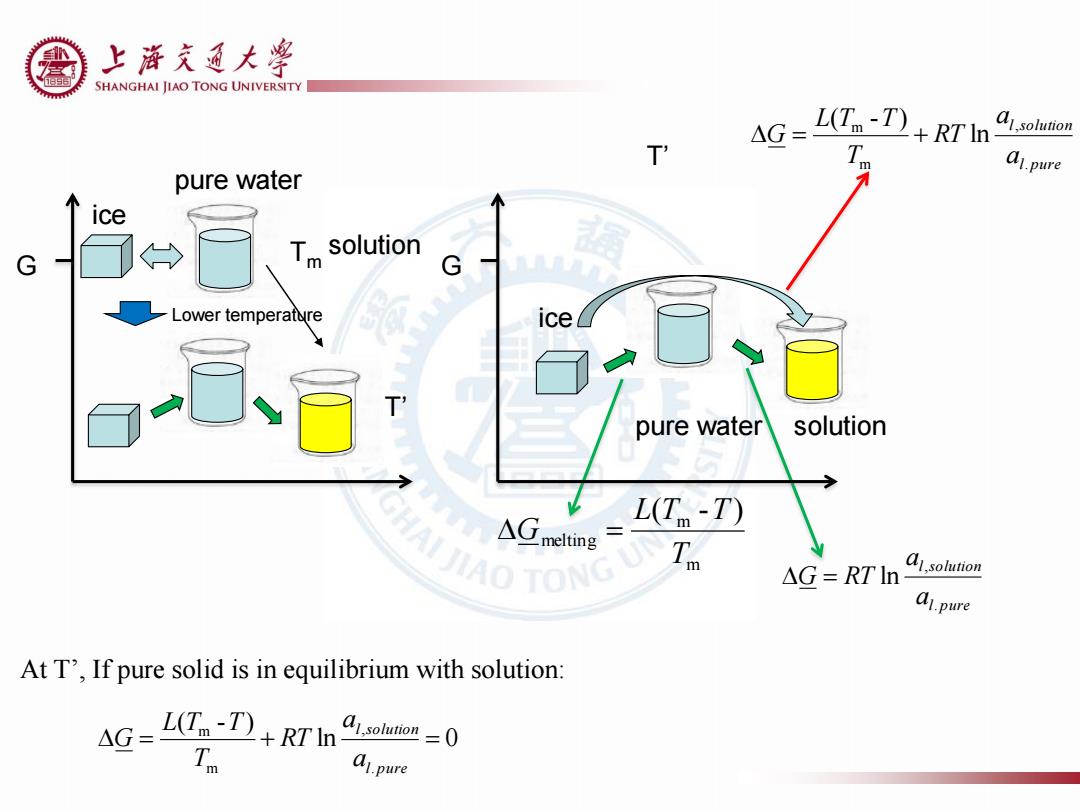
上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY L(T-T)RTI o T 4G= m A1.pure pure water ice > Tm solution G G Lower temperature ice pure water solution △melting L(T-T) A¥IAOTONG UN △G=RTln a1solution al.pure At T',If pure solid is in equilibrium with solution: AG-L(-T)+RT'In =0 A1.pure
T’ G ice ice pure water solution l pure l solution a a G RT . , ln m m melting ( - ) T L T T G G l pure l solution a a RT T L T T G . , m m ln ( - ) ln 0 ( - ) . , m m l pure l solution a a RT T L T T G At T’, If pure solid is in equilibrium with solution: Tm pure water solution T’ Lower temperature
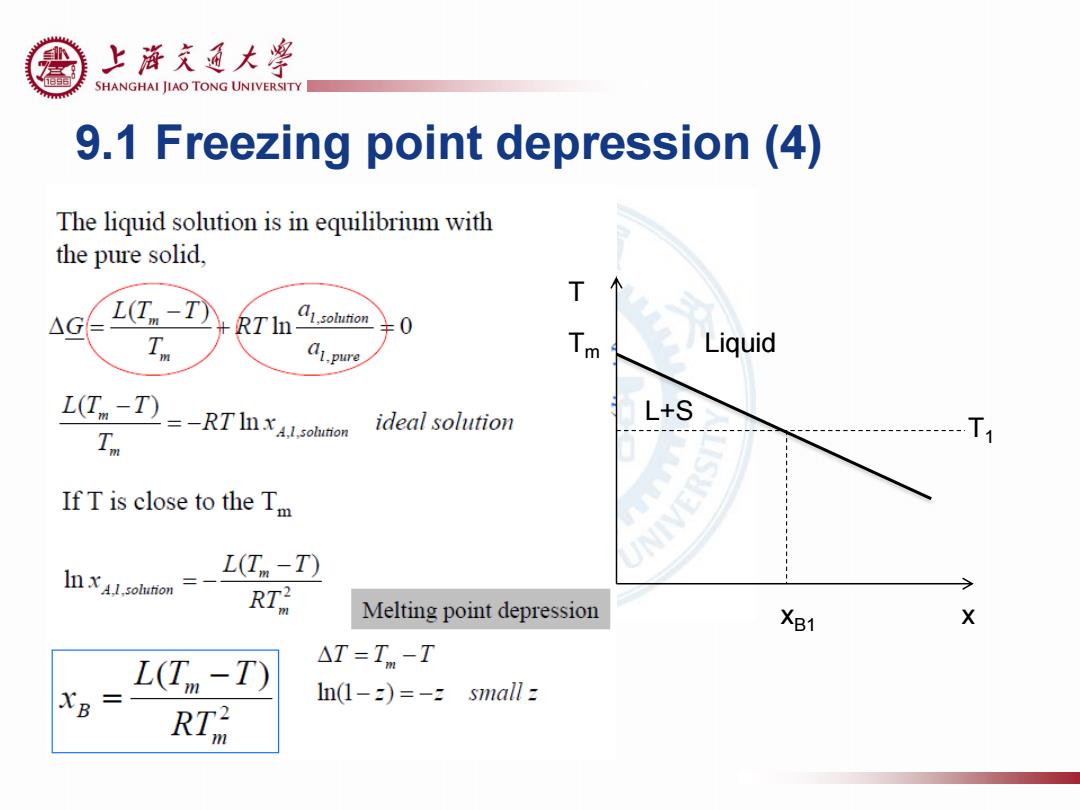
上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 9.1 Freezing point depression(4) The liquid solution is in equilibrium with the pure solid, T △G L(T-T) RTI 9ohnon T a1.pure 人 Liquid L(T-T ideal solution L+S Tm )=-RT I X41.hion If T is close to the Tm NIVE L(T-T) In x 1.solution RT Melting point depression XB1 X L(T -T) △T=Tm-T XB In(1-2=-z small z RT
9.1 Freezing point depression (4) Tm T Liquid L+S T1 xB1 x