27.2 Cycle progression depends on discrete control points Cyclins are proteins that accumulate continuously throughout the cell cycle and are then destroyed by proteolysis during mitosis.A cyclin is one of the two subunits of the M-phase kinase. Heterokaryon is a cell containing two (or more) nuclei in a common cytoplasm,generated by fusing somatic cells. 情華大当
Cyclins are proteins that accumulate continuously throughout the cell cycle and are then destroyed by proteolysis during mitosis. A cyclin is one of the two subunits of the M-phase kinase. Heterokaryon is a cell containing two (or more) nuclei in a common cytoplasm, generated by fusing somatic cells. 27.2 Cycle progression depends on discrete control points

27.2 Cycle progression depends on discrete control points GO phase reactivation GO phase indefinite Figure 27.1 Overview: withdrawa interphase is divided into the G1,S,and G2 G2 phase periods.One cell cycle 3-4 hrs 4n DNA G1 phase is separated from the 6-12hrs 2n DNA next by mitosis (M). S phase 6-8 hrs Cells may withdraw DNA synthesis 2-4n DNA from the cycle into G0 or reenter from it. 清菜大当
Figure 27.1 Overview: interphase is divided into the G1, S, and G2 periods. One cell cycle is separated from the next by mitosis (M). Cells may withdraw from the cycle into G0 or reenter from it. 27.2 Cycle progression depends on discrete control points
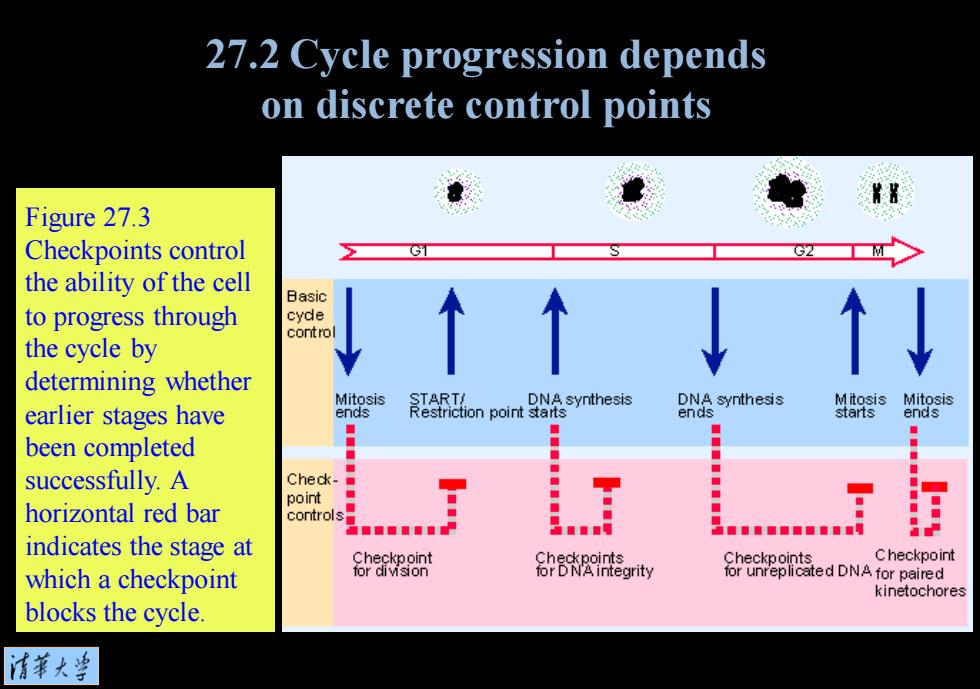
27.2 Cycle progression depends on discrete control points Figure 27.3 Checkpoints control the ability of the cell 日asic to progress through cyde contro the cycle by ↑↑ determining whether Mitosis cion point DNA synthesis DNA synthesis Mitosis Mitosis earlier stages have ends ends starts ends ■ been completed successfully.A ◆ Check- point horizontal red bar controls S. indicates the stage at Checkpoint Checkpoints C heckpoint which a checkpoint for division negrity for unreplicated DNA for paired kinetochores blocks the cycle. 清菜大当
Figure 27.3 Checkpoints control the ability of the cell to progress through the cycle by determining whether earlier stages have been completed successfully. A horizontal red bar indicates the stage at which a checkpoint blocks the cycle. 27.2 Cycle progression depends on discrete control points
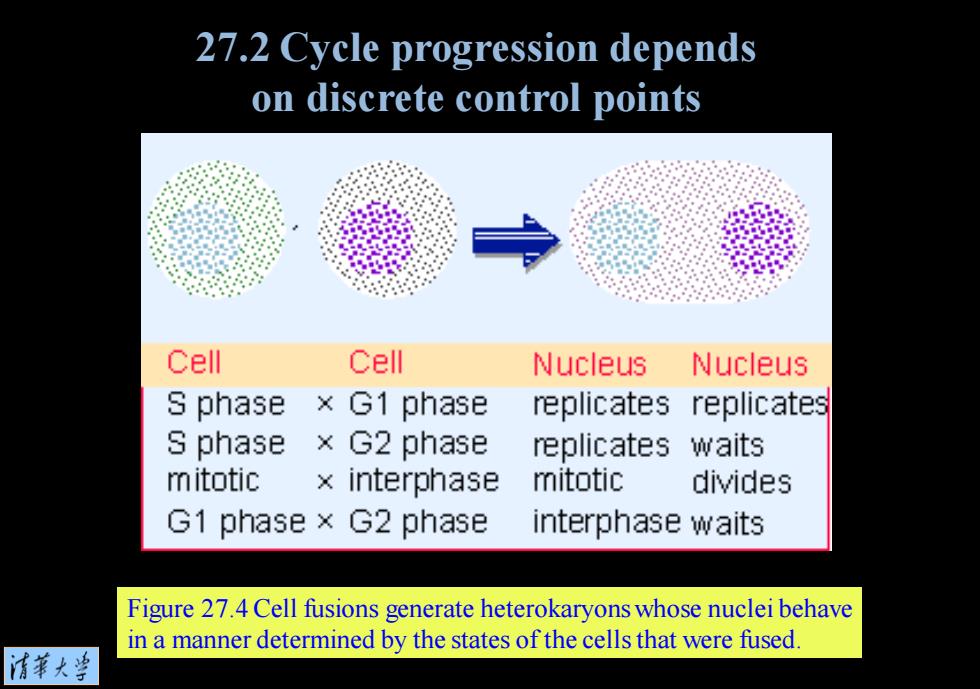
27.2 Cycle progression depends on discrete control points Cell Cell Nucleus Nucleus S phase ×G1 phase replicates replicates S phase × G2 phase replicates waits mitotic ×interphase mitotic divides G1 phase×G2 phase interphase waits Figure 27.4 Cell fusions generate heterokaryons whose nuclei behave in a manner determined by the states of the cells that were fused. 清苇大当
Figure 27.4 Cell fusions generate heterokaryons whose nuclei behave in a manner determined by the states of the cells that were fused. 27.2 Cycle progression depends on discrete control points
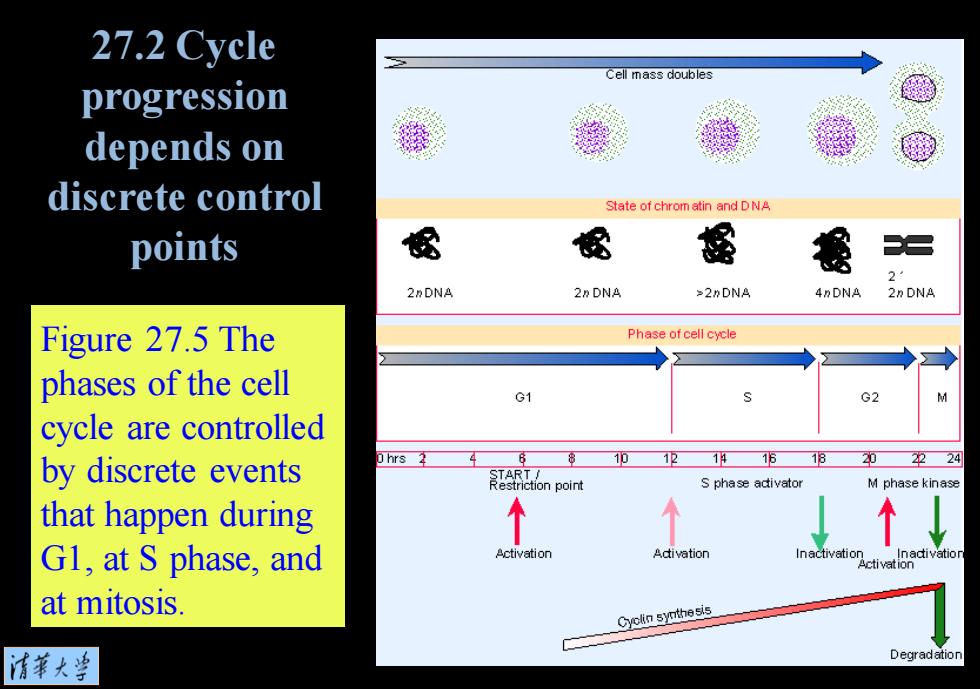
27.2 Cycle Cell mass doubles progression depends on discrete control State of chrom atin and DNA points 2 2nDNA 2n DNA >2DNA 4nDNA 2n DNA Figure 27.5 The Phase of cell cycle phases of the cell G1 G2 cycle are controlled by discrete events hrs 2 14 15 18 2224 ction point S phase adivator M phase kinase that happen during Gl,at S phase,and Activation Adivation at mitosis. Cyoin synthesis 清菜大当 Degradation
Figure 27.5 The phases of the cell cycle are controlled by discrete events that happen during G1, at S phase, and at mitosis. 27.2 Cycle progression depends on discrete control points