The kinetic properties of the various LDH isozymes differ in terms of their relative affinities for the various substrates and their sensitivity to inhibition by product.Different tissues express different isozyme forms,as appropriate to their particular metabolic needs. By regulating the relative amounts of a and B subunits they synthesize,the cells of various tissues control which isozymic forms are likely to assemble,and,thus,which kinetic parameters prevail
The kinetic properties of the various LDH isozymes differ in terms of their relative affinities for the various substrates and their sensitivity to inhibition by product. Different tissues express different isozyme forms, as appropriate to their particular metabolic needs. By regulating the relative amounts of A and B subunits they synthesize, the cells of various tissues control which isozymic forms are likely to assemble, and, thus, which kinetic parameters prevail

Example 2:Blood clotting Blood clotting results from a cascade of reactions. In a cascade,a signal initiates a series of steps,each of them catalyzed by an enzyme.At each step the signal is amplified. In blood clotting the activated form of one clotting factor catalyzes activation of the next. Very small amounts of the initial factors trigger the cascade, =rapid response to trauma(e.g.,damage to a blood vessel)
Example 2: Blood clotting Blood clotting results from a cascade of reactions. In a cascade, a signal initiates a series of steps, each of them catalyzed by an enzyme. At each step the signal is amplified. In blood clotting the activated form of one clotting factor catalyzes activation of the next. Very small amounts of the initial factors trigger the cascade, => rapid response to trauma (e.g., damage to a blood vessel)
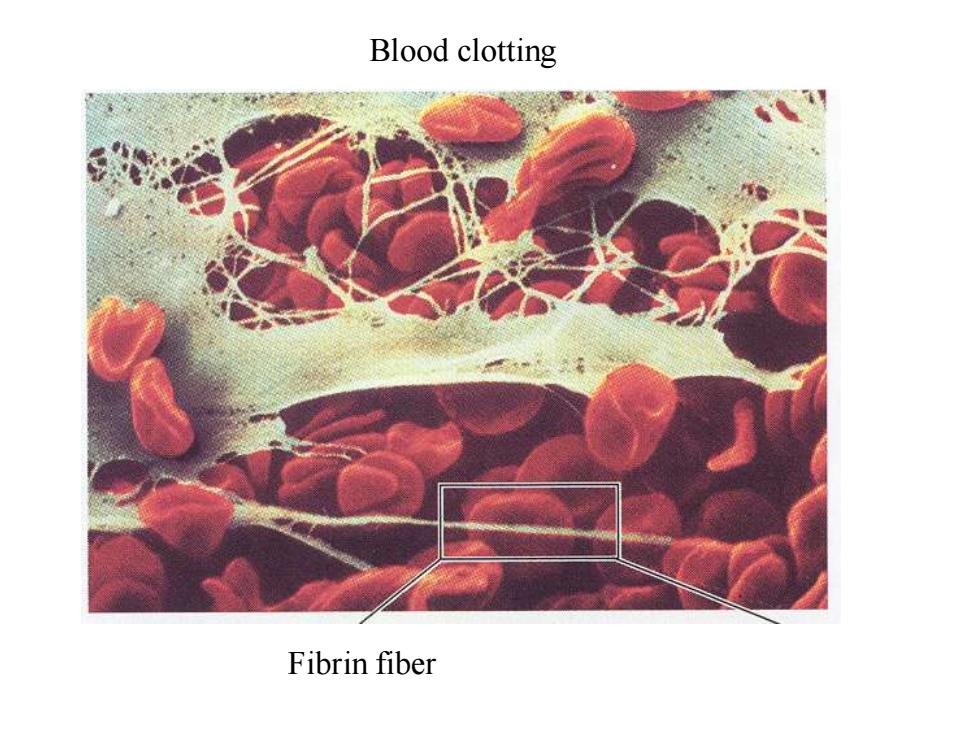
Blood clotting Fibrin fiber
Blood clotting Fibrin fiber
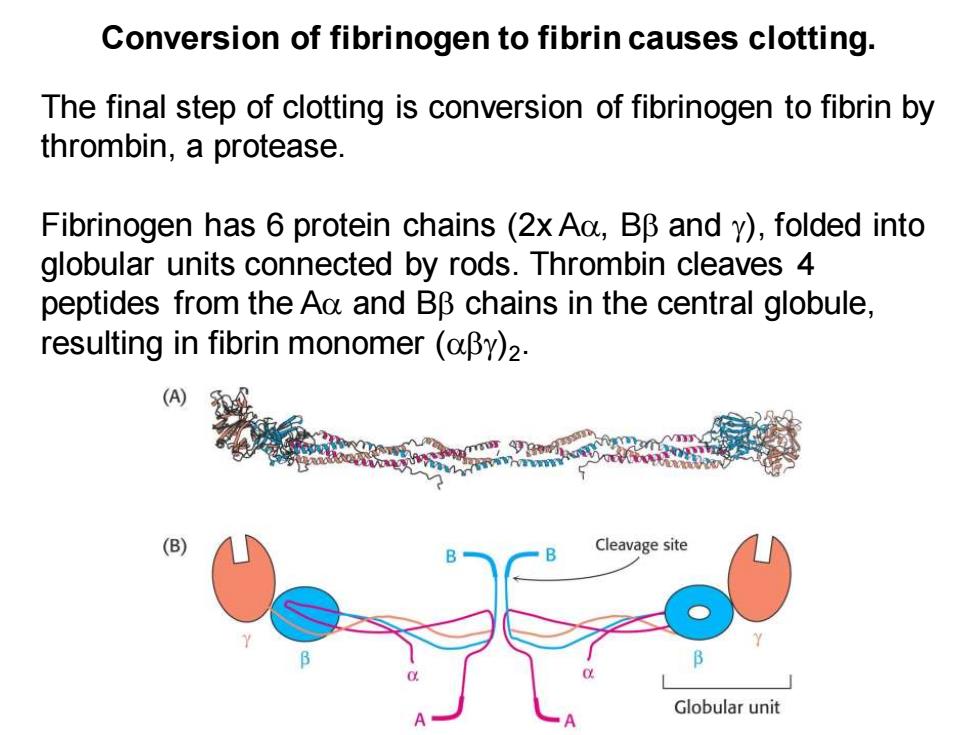
Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin causes clotting. The final step of clotting is conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin by thrombin,a protease. Fibrinogen has 6 protein chains(2x Aa,BB and y),folded into globular units connected by rods.Thrombin cleaves 4 peptides from the Aa and BB chains in the central globule, resulting in fibrin monomer(aBy)2. (A) (B) Cleavage site Globular unit
Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin causes clotting. The final step of clotting is conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin by thrombin, a protease. Fibrinogen has 6 protein chains (2x A, B and ), folded into globular units connected by rods. Thrombin cleaves 4 peptides from the A and B chains in the central globule, resulting in fibrin monomer ()2
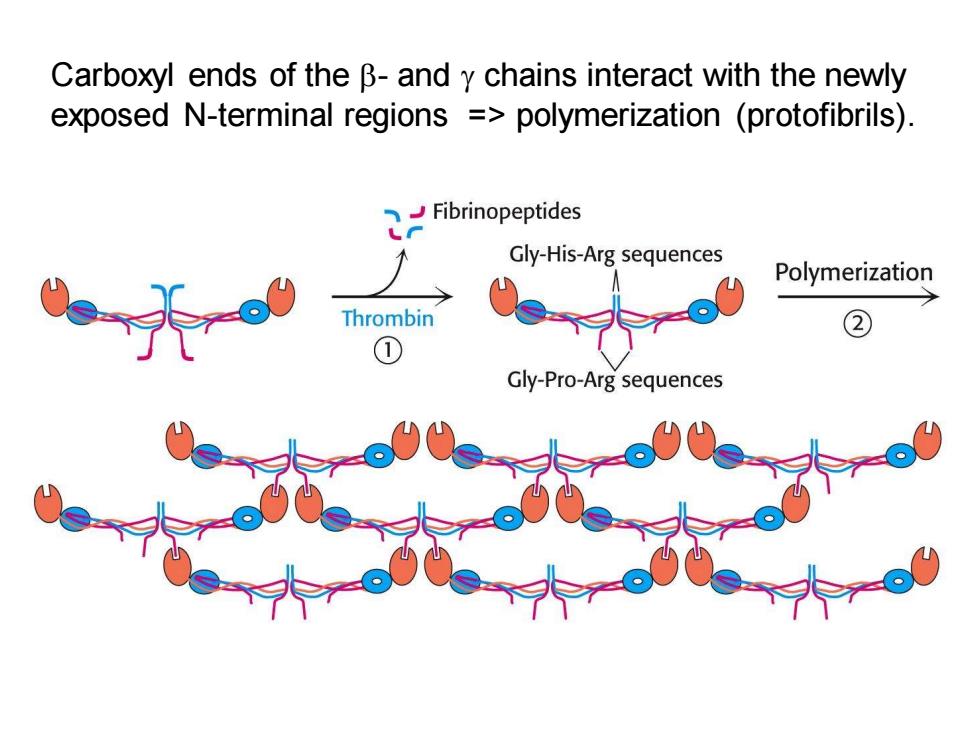
Carboxyl ends of the B-and y chains interact with the newly exposed N-terminal regions =polymerization (protofibrils). Fibrinopeptides Gly-His-Arg sequences Polymerization Thrombin ② ① Gly-Pro-Arg sequences
Carboxyl ends of the - and chains interact with the newly exposed N-terminal regions => polymerization (protofibrils)