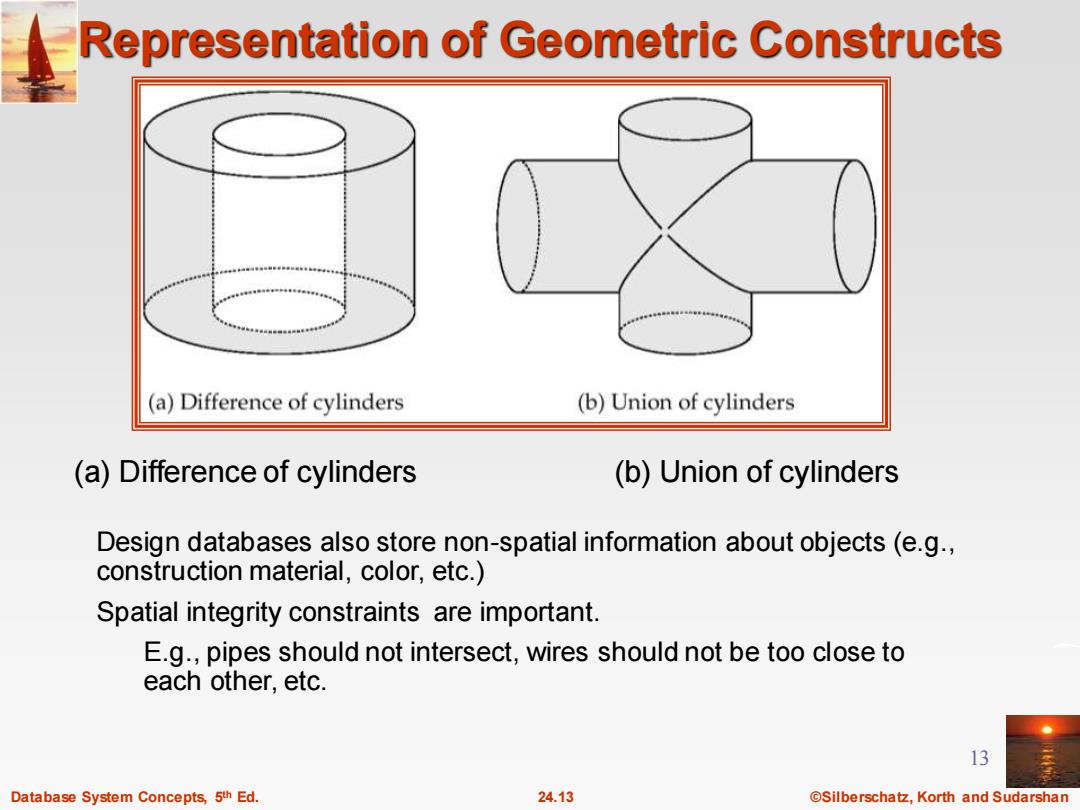
Representation of Geometric Constructs (a)Difference of cylinders (b)Union of cylinders (a)Difference of cylinders (b)Union of cylinders Design databases also store non-spatial information about objects(e.g., construction material,color,etc.) Spatial integrity constraints are important. E.g.,pipes should not intersect,wires should not be too close to each other.etc. 13 Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 24.13 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 24.13 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. 13 Representation of Geometric Constructs Design databases also store non-spatial information about objects (e.g., construction material, color, etc.) Spatial integrity constraints are important. E.g., pipes should not intersect, wires should not be too close to each other, etc. (a) Difference of cylinders (b) Union of cylinders

Geographic Data Raster data consist of bit maps or pixel maps,in two or more dimensions. Example 2-D raster image:satellite image of cloud cover, where each pixel stores the cloud visibility in a particular area. Additional dimensions might include the temperature at different altitudes at different regions,or measurements taken at different points in time. Design databases generally do not store raster data. 14 Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 24.14 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 24.14 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. 14 Geographic Data Raster data consist of bit maps or pixel maps, in two or more dimensions. Example 2-D raster image: satellite image of cloud cover, where each pixel stores the cloud visibility in a particular area. Additional dimensions might include the temperature at different altitudes at different regions, or measurements taken at different points in time. Design databases generally do not store raster data
Geographic Data (Cont.) Vector data are constructed from basic geometric objects:points, line segments,triangles,and other polygons in two dimensions,and cylinders,speheres,cuboids,and other polyhedrons in three dimensions. Vector format often used to represent map data. Roads can be considered as two-dimensional and represented by lines and curves. Some features,such as rivers,may be represented either as complex curves or as complex polygons,depending on whether their width is relevant. Features such as regions and lakes can be depicted as polygons. 15 Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 24.15 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 24.15 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. 15 Geographic Data (Cont.) Vector data are constructed from basic geometric objects: points, line segments, triangles, and other polygons in two dimensions, and cylinders, speheres, cuboids, and other polyhedrons in three dimensions. Vector format often used to represent map data. Roads can be considered as two-dimensional and represented by lines and curves. Some features, such as rivers, may be represented either as complex curves or as complex polygons, depending on whether their width is relevant. Features such as regions and lakes can be depicted as polygons

Applications of Geographic Data Examples of geographic data map data for vehicle navigation distribution network information for power,telephones,water supply,and sewage Vehicle navigation systems store information about roads and services for the use of drivers: Spatial data:e.g,road/restaurant/gas-station coordinates Non-spatial data:e.g.,one-way streets,speed limits,traffic congestion Global Positioning System(GPS)unit-utilizes information broadcast from GPS satellites to find the current location of user with an accuracy of tens of meters. increasingly used in vehicle navigation systems as well as utility maintenance applications. 16 Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 24.16 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 24.16 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. 16 Applications of Geographic Data Examples of geographic data map data for vehicle navigation distribution network information for power, telephones, water supply, and sewage Vehicle navigation systems store information about roads and services for the use of drivers: Spatial data: e.g, road/restaurant/gas-station coordinates Non-spatial data: e.g., one-way streets, speed limits, traffic congestion Global Positioning System (GPS) unit - utilizes information broadcast from GPS satellites to find the current location of user with an accuracy of tens of meters. increasingly used in vehicle navigation systems as well as utility maintenance applications

Spatial Queries Nearness queries request objects that lie near a specified location. Nearest neighbor queries,given a point or an object,find the nearest object that satisfies given conditions. Region queries deal with spatial regions.e.g.,ask for objects that lie partially or fully inside a specified region. Queries that compute intersections or unions of regions. Spatial join of two spatial relations with the location playing the role of join attribute. 17 Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 24.17 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 24.17 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. 17 Spatial Queries Nearness queries request objects that lie near a specified location. Nearest neighbor queries, given a point or an object, find the nearest object that satisfies given conditions. Region queries deal with spatial regions. e.g., ask for objects that lie partially or fully inside a specified region. Queries that compute intersections or unions of regions. Spatial join of two spatial relations with the location playing the role of join attribute