
Chapter 18:Data Analysis and Mining Decision Support Systems Data Analysis and OLAP Data Warehousing Data Mining Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Aug 26,2005 18.2 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 18.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Aug 26, 2005 Chapter 18: Data Analysis and Mining Decision Support Systems Data Analysis and OLAP Data Warehousing Data Mining

Decision Support Systems Decision-support systems are used to make business decisions,often based on data collected by on-line transaction-processing systems. Examples of business decisions: What items to stock? What insurance premium to change? To whom to send advertisements? Examples of data used for making decisions Retail sales transaction details Customer profiles(income,age,gender,etc.) Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Aug 26,2005 18.3 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 18.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Aug 26, 2005 Decision Support Systems Decision-support systems are used to make business decisions, often based on data collected by on-line transaction-processing systems. Examples of business decisions: What items to stock? What insurance premium to change? To whom to send advertisements? Examples of data used for making decisions Retail sales transaction details Customer profiles (income, age, gender, etc.)
Decision-Support Systems:Overview Data analysis tasks are simplified by specialized tools and SQL extensions Example tasks For each product category and each region,what were the total sales in the last quarter and how do they compare with the same quarter last year As above,for each product category and each customer category Statistical analysis packages (e.g.,S++)can be interfaced with databases Statistical analysis is a large field,but not covered here Data mining seeks to discover knowledge automatically in the form of statistical rules and patterns from large databases. A data warehouse archives information gathered from multiple sources, and stores it under a unified schema,at a single site. Important for large businesses that generate data from multiple divisions,possibly at multiple sites Data may also be purchased externally Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Aug 26,2005 18.4 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 18.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Aug 26, 2005 Decision-Support Systems: Overview Data analysis tasks are simplified by specialized tools and SQL extensions Example tasks For each product category and each region, what were the total sales in the last quarter and how do they compare with the same quarter last year As above, for each product category and each customer category Statistical analysis packages (e.g., : S++) can be interfaced with databases Statistical analysis is a large field, but not covered here Data mining seeks to discover knowledge automatically in the form of statistical rules and patterns from large databases. A data warehouse archives information gathered from multiple sources, and stores it under a unified schema, at a single site. Important for large businesses that generate data from multiple divisions, possibly at multiple sites Data may also be purchased externally

Data Analysis and OLAP Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) Interactive analysis of data,allowing data to be summarized and viewed in different ways in an online fashion(with negligible delay) Data that can be modeled as dimension attributes and measure attributes are called multidimensional data. Measure attributes measure some value can be aggregated upon e.g.the attribute number of the sales relation Dimension attributes define the dimensions on which measure attributes (or aggregates thereof)are viewed e.g.the attributes item name,color,and size of the sales relation Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Aug 26,2005 18.5 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 18.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Aug 26, 2005 Data Analysis and OLAP Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) Interactive analysis of data, allowing data to be summarized and viewed in different ways in an online fashion (with negligible delay) Data that can be modeled as dimension attributes and measure attributes are called multidimensional data. Measure attributes measure some value can be aggregated upon e.g. the attribute number of the sales relation Dimension attributes define the dimensions on which measure attributes (or aggregates thereof) are viewed e.g. the attributes item_name, color, and size of the sales relation
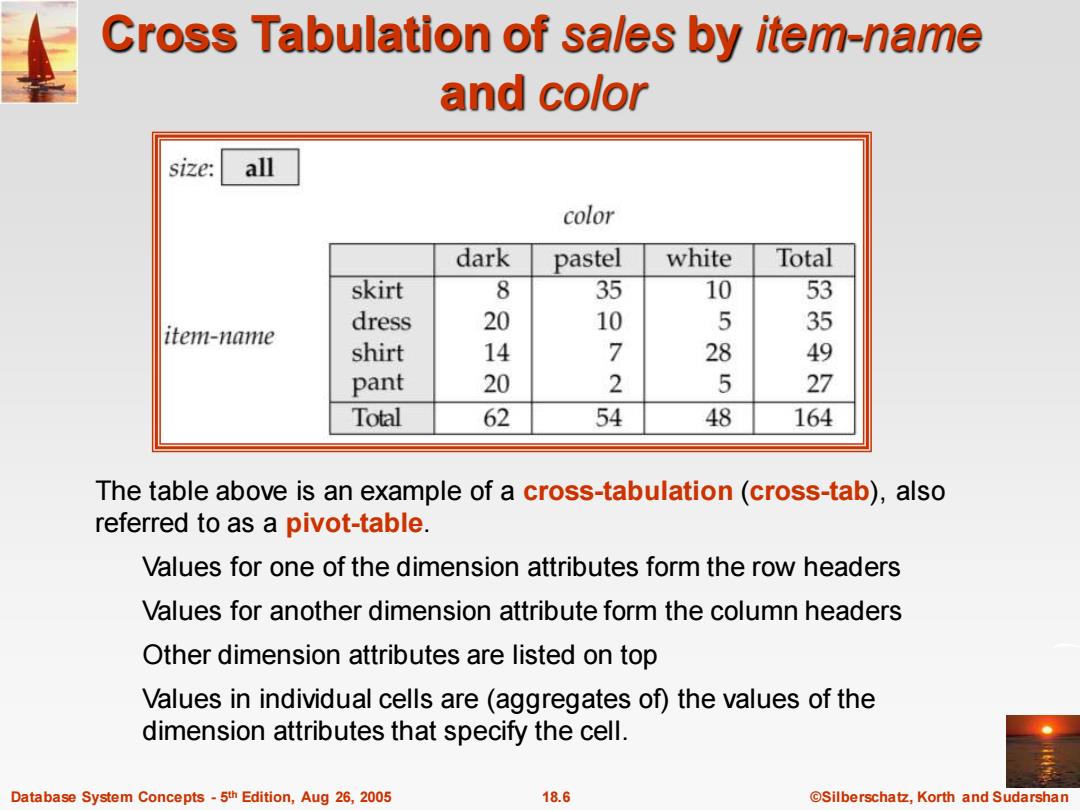
Cross Tabulation of sales by item-name and color size: all color dark pastel white Total skirt 8 35 10 53 dress 20 10 5 35 item-name shirt 14 7 28 49 pant 20 2 5 27 Total 62 54 48 164 The table above is an example of a cross-tabulation(cross-tab),also referred to as a pivot-table. Values for one of the dimension attributes form the row headers Values for another dimension attribute form the column headers Other dimension attributes are listed on top Values in individual cells are (aggregates of)the values of the dimension attributes that specify the cell. Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Aug 26,2005 18.6 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 18.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Aug 26, 2005 Cross Tabulation of sales by item-name and color The table above is an example of a cross-tabulation (cross-tab), also referred to as a pivot-table. Values for one of the dimension attributes form the row headers Values for another dimension attribute form the column headers Other dimension attributes are listed on top Values in individual cells are (aggregates of) the values of the dimension attributes that specify the cell