
Spatial and Geographic Databases Spatial databases store information related to spatial locations,and support efficient storage,indexing and querying of spatial data. Special purpose index structures are important for accessing spatial data,and for processing spatial join queries. Computer Aided Design(CAD)databases store design information about how objects are constructed E.g.:designs of buildings,aircraft, layouts of integrated-circuits Geographic databases store geographic information(e.g.,maps): often called geographic information systems or GIS 8 Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 24.8 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 24.8 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. 8 Spatial and Geographic Databases Spatial databases store information related to spatial locations, and support efficient storage, indexing and querying of spatial data. Special purpose index structures are important for accessing spatial data, and for processing spatial join queries. Computer Aided Design (CAD) databases store design information about how objects are constructed E.g.: designs of buildings, aircraft, layouts of integrated-circuits Geographic databases store geographic information (e.g., maps): often called geographic information systems or GIS
Represented of Geometric Information Various geometric constructs can be represented in a database in a normalized fashion. Represent a line segment by the coordinates of its endpoints. Approximate a curve by partitioning it into a sequence of segments Create a list of vertices in order,or Represent each segment as a separate tuple that also carries with it the identifier of the curve(2D features such as roads) Closed polygons List of vertices in order,starting vertex is the same as the ending vertex,or Represent boundary edges as separate tuples,with each containing identifier of the polygon,or Use triangulation-divide polygon into triangles Note the polygon identifier with each of its triangles. Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 24.9 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 24.9 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. 9 Represented of Geometric Information Various geometric constructs can be represented in a database in a normalized fashion. Represent a line segment by the coordinates of its endpoints. Approximate a curve by partitioning it into a sequence of segments Create a list of vertices in order, or Represent each segment as a separate tuple that also carries with it the identifier of the curve (2D features such as roads). Closed polygons List of vertices in order, starting vertex is the same as the ending vertex, or Represent boundary edges as separate tuples, with each containing identifier of the polygon, or Use triangulation — divide polygon into triangles Note the polygon identifier with each of its triangles
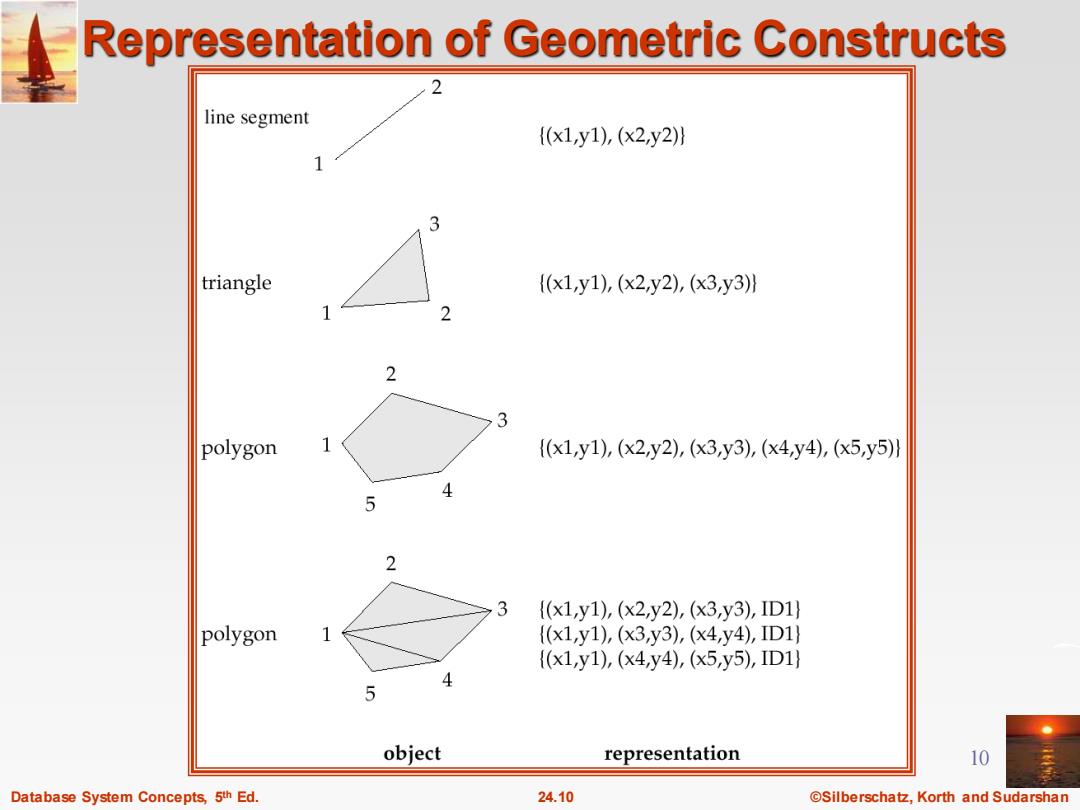
Representation of Geometric Constructs line segment {(x1,y1),(x2,y2)》 3 triangle {(x1,y1),(x2y2),(x3,y3)} 2 2 3 polygon {(x1,y1),(x2,y2),(x3,y3),(x4,y4),(x5,y5)} 4 5 2 3 {(x1y1),(x2,y2),(x3,y3),ID1 polygon {(x1,y1),(x3,y3),(x4,y4),ID1 {(x1,y1),(x4y4),(x5,y5),ID1} 4 5 object representation 10 Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 24.10 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 24.10 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. 10 Representation of Geometric Constructs
Representation of Geometric Information (Cont.) Representation of points and line segment in 3-D similar to 2-D,except that points have an extra z component Represent arbitrary polyhedra by dividing them into tetrahedrons,like triangulating polygons. Alternative:List their faces,each of which is a polygon,along with an indication of which side of the face is inside the polyhedron. 11 Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 24.11 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 24.11 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. 11 Representation of Geometric Information (Cont.) Representation of points and line segment in 3-D similar to 2-D, except that points have an extra z component Represent arbitrary polyhedra by dividing them into tetrahedrons, like triangulating polygons. Alternative: List their faces, each of which is a polygon, along with an indication of which side of the face is inside the polyhedron

Design Databases Represent design components as objects(generally geometric objects);the connections between the objects indicate how the design is structured. Simple two-dimensional objects:points,lines,triangles, rectangles,polygons. Complex two-dimensional objects:formed from simple objects via union,intersection,and difference operations. Complex three-dimensional objects:formed from simpler objects such as spheres,cylinders,and cuboids,by union,intersection, and difference operations. Wireframe models represent three-dimensional surfaces as a set of simpler objects. 12 Database System Concepts,5th Ed. 24.12 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts, 5 24.12 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Ed. 12 Design Databases Represent design components as objects (generally geometric objects); the connections between the objects indicate how the design is structured. Simple two-dimensional objects: points, lines, triangles, rectangles, polygons. Complex two-dimensional objects: formed from simple objects via union, intersection, and difference operations. Complex three-dimensional objects: formed from simpler objects such as spheres, cylinders, and cuboids, by union, intersection, and difference operations. Wireframe models represent three-dimensional surfaces as a set of simpler objects