
Chapter 2:Relational Model Structure of Relational Databases Fundamental Relational-Algebra-Operations Additional Relational-Algebra-Operations Extended Relational-Algebra-Operations Null Values Modification of the Database Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 2.2 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 2.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Chapter 2: Relational Model Structure of Relational Databases Fundamental Relational-Algebra-Operations Additional Relational-Algebra-Operations Extended Relational-Algebra-Operations Null Values Modification of the Database

Example of a Relation account_number branch_name balance A-101 Downtown 500 A-102 Perryridge 400 A-201 Brighton 900 A-215 Mianus 700 A-217 Brighton 750 A-222 Redwood 700 A-305 Round Hill 350 Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 23 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 2.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Example of a Relation
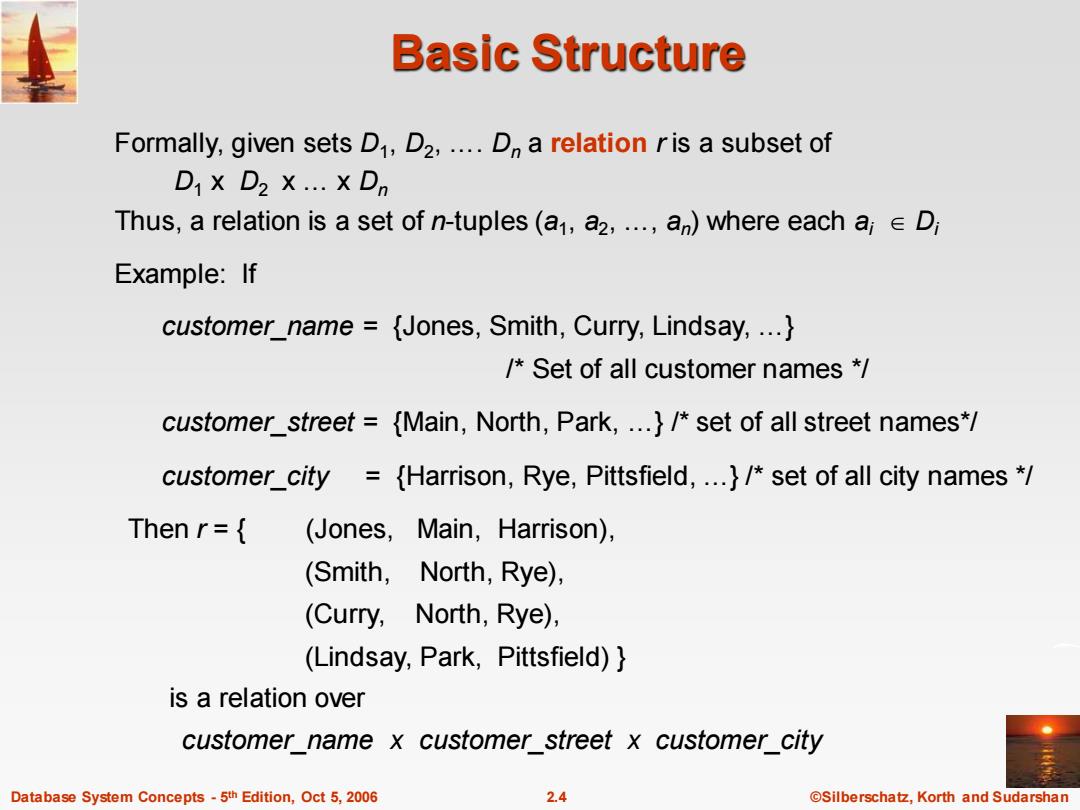
Basic Structure Formally,given sets D,D2,...D a relation ris a subset of D x D2 X ..X Dn Thus,a relation is a set of n-tuples(a,a2,...a)where each aie D Example:If customer_name {Jones,Smith,Curry,Lindsay,...} /Set of all customer names * customer street {Main,North,Park,...}/set of all street names*/ customer_city ={Harrison,Rye,Pittsfield,...}/set of all city names * Then r={ (Jones,Main,Harrison), (Smith,North,Rye), (Curry,North,Rye), (Lindsay,Park,Pittsfield)} is a relation over customer name x customer street x customer_city Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 2.4 ©Silberschat乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 2.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Basic Structure Formally, given sets D1 , D2 , …. Dn a relation r is a subset of D1 x D2 x … x Dn Thus, a relation is a set of n-tuples (a1 , a2 , …, an ) where each ai Di Example: If customer_name = {Jones, Smith, Curry, Lindsay, …} /* Set of all customer names */ customer_street = {Main, North, Park, …} /* set of all street names*/ customer_city = {Harrison, Rye, Pittsfield, …} /* set of all city names */ Then r = { (Jones, Main, Harrison), (Smith, North, Rye), (Curry, North, Rye), (Lindsay, Park, Pittsfield) } is a relation over customer_name x customer_street x customer_city
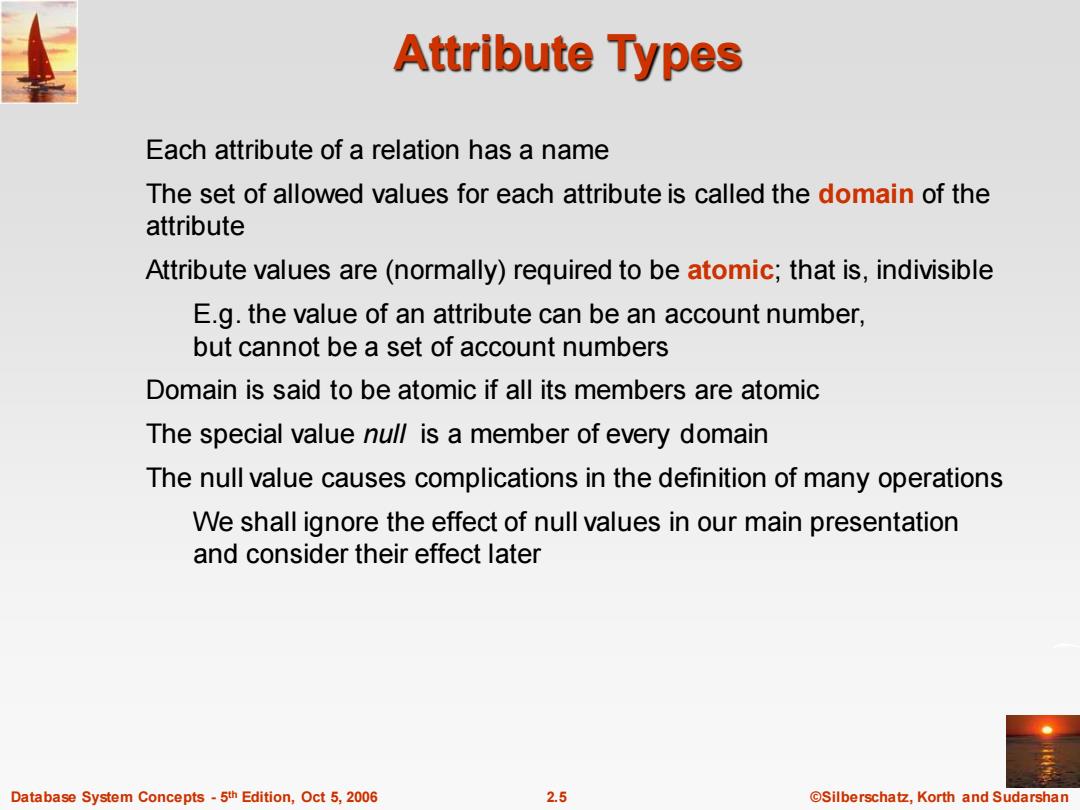
Attribute Types Each attribute of a relation has a name The set of allowed values for each attribute is called the domain of the attribute Attribute values are(normally)required to be atomic;that is,indivisible E.g.the value of an attribute can be an account number, but cannot be a set of account numbers Domain is said to be atomic if all its members are atomic The special value null is a member of every domain The null value causes complications in the definition of many operations We shall ignore the effect of null values in our main presentation and consider their effect later Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 2.5 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 2.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Attribute Types Each attribute of a relation has a name The set of allowed values for each attribute is called the domain of the attribute Attribute values are (normally) required to be atomic; that is, indivisible E.g. the value of an attribute can be an account number, but cannot be a set of account numbers Domain is said to be atomic if all its members are atomic The special value null is a member of every domain The null value causes complications in the definition of many operations We shall ignore the effect of null values in our main presentation and consider their effect later
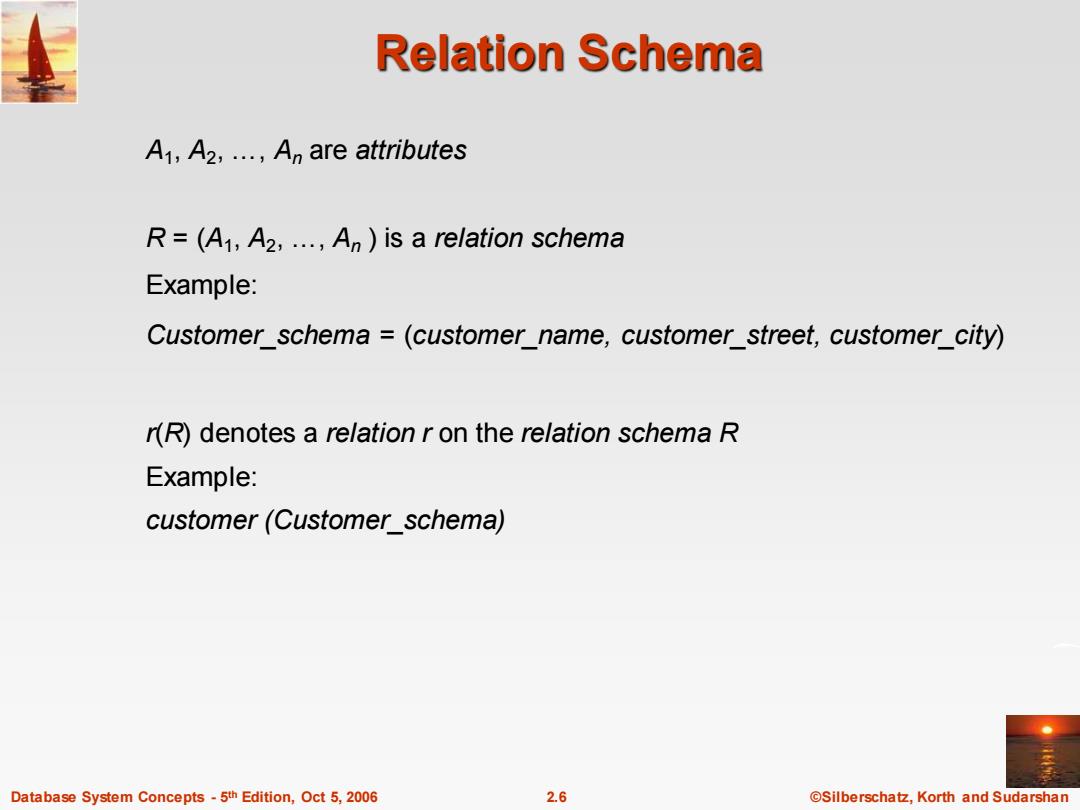
Relation Schema A1,A2,...,An are attributes R=(A1,A2,...,An)is a relation schema Example: Customer schema =(customer_name,customer_street,customer_city) r(R)denotes a relation r on the relation schema R Example: customer(Customer_schema) Database System Concepts-5th Edition,Oct 5,2006 2.6 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 5 2.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition, Oct 5, 2006 Relation Schema A1 , A2 , …, An are attributes R = (A1 , A2 , …, An ) is a relation schema Example: Customer_schema = (customer_name, customer_street, customer_city) r(R) denotes a relation r on the relation schema R Example: customer (Customer_schema)