Classification of Physical Storage Media Can differentiate storage into: volatile storage:loses contents when power is switched off non-volatile storage: Contents persist even when power is switched off. Includes secondary and tertiary storage,as well as batter-backed up main-memory. Factors affecting choice of storage media include Speed with which data can be accessed ·Cost per unit of data ·Reliability Database System Concepts-7th Edition 12.2 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 12.2 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Classification of Physical Storage Media ▪ Can differentiate storage into: • volatile storage: loses contents when power is switched off • non-volatile storage: ▪ Contents persist even when power is switched off. ▪ Includes secondary and tertiary storage, as well as batter-backed up main-memory. ▪ Factors affecting choice of storage media include • Speed with which data can be accessed • Cost per unit of data • Reliability
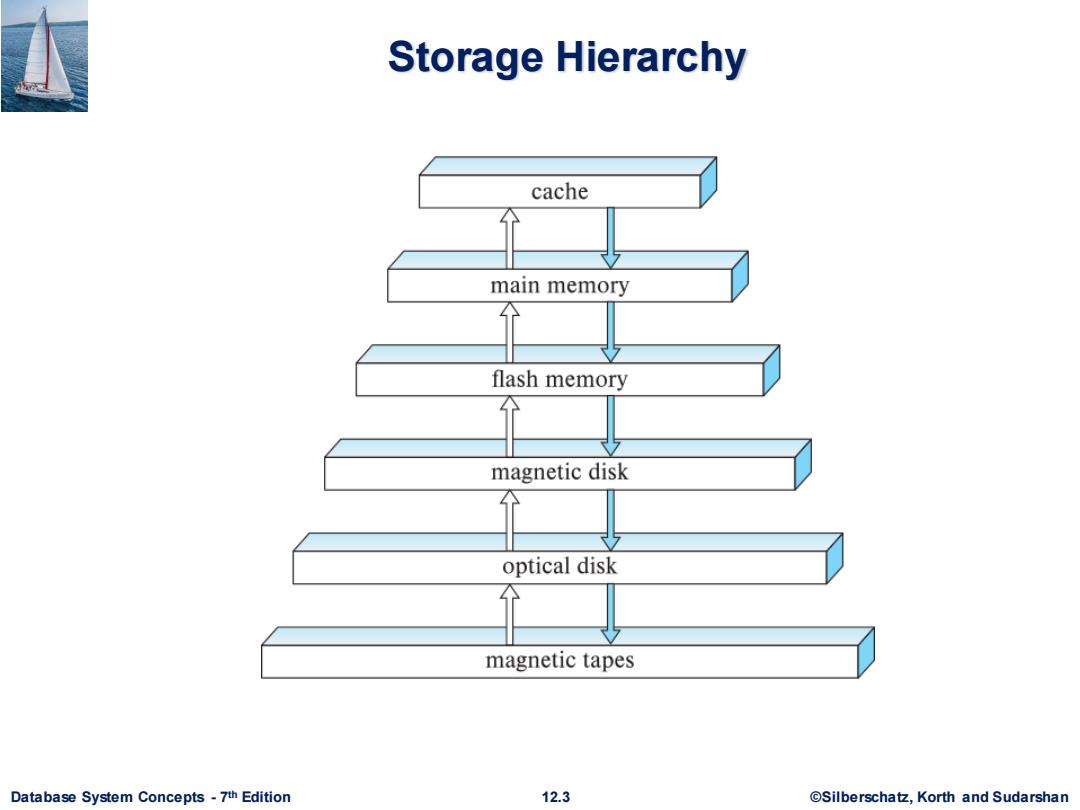
Storage Hierarchy cache main memory flash memory magnetic disk optical disk magnetic tapes Database System Concepts-7th Edition 12.3 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 12.3 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Storage Hierarchy
Storage Hierarchy (Cont.) primary storage:Fastest media but volatile(cache,main memory). ■ secondary storage:next level in hierarchy,non-volatile,moderately fast access time Also called on-line storage E.g.,flash memory,magnetic disks tertiary storage:lowest level in hierarchy,non-volatile,slow access time also called off-line storage and used for archival storage e.g.,magnetic tape,optical storage ·Magnetic tape Sequential access,1 to 12 TB capacity A few drives with many tapes Juke boxes with petabytes (1000's of TB)of storage Database System Concepts-7th Edition 12.4 ©Silberscha乜,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 12.4 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Storage Hierarchy (Cont.) ▪ primary storage: Fastest media but volatile (cache, main memory). ▪ secondary storage: next level in hierarchy, non-volatile, moderately fast access time • Also called on-line storage • E.g., flash memory, magnetic disks ▪ tertiary storage: lowest level in hierarchy, non-volatile, slow access time • also called off-line storage and used for archival storage • e.g., magnetic tape, optical storage • Magnetic tape ▪ Sequential access, 1 to 12 TB capacity ▪ A few drives with many tapes ▪ Juke boxes with petabytes (1000’s of TB) of storage
Storage Interfaces Disk interface standards families ·SATA(Serial ATA) SATA 3 supports data transfer speeds of up to 6 gigabits/sec SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) SAS Version 3 supports 12 gigabits/sec NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express)interface Works with PCle connectors to support lower latency and higher transfer rates Supports data transfer rates of up to 24 gigabits/sec Disks usually connected directly to computer system In Storage Area Networks(SAN),a large number of disks are connected by a high-speed network to a number of servers In Network Attached Storage(NAS)networked storage provides a file system interface using networked file system protocol,instead of providing a disk system interface Database System Concepts-7th Edition 12.5 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 12.5 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Storage Interfaces ▪ Disk interface standards families • SATA (Serial ATA) ▪ SATA 3 supports data transfer speeds of up to 6 gigabits/sec • SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) ▪ SAS Version 3 supports 12 gigabits/sec • NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) interface ▪ Works with PCIe connectors to support lower latency and higher transfer rates ▪ Supports data transfer rates of up to 24 gigabits/sec ▪ Disks usually connected directly to computer system ▪ In Storage Area Networks (SAN), a large number of disks are connected by a high-speed network to a number of servers ▪ In Network Attached Storage (NAS) networked storage provides a file system interface using networked file system protocol, instead of providing a disk system interface
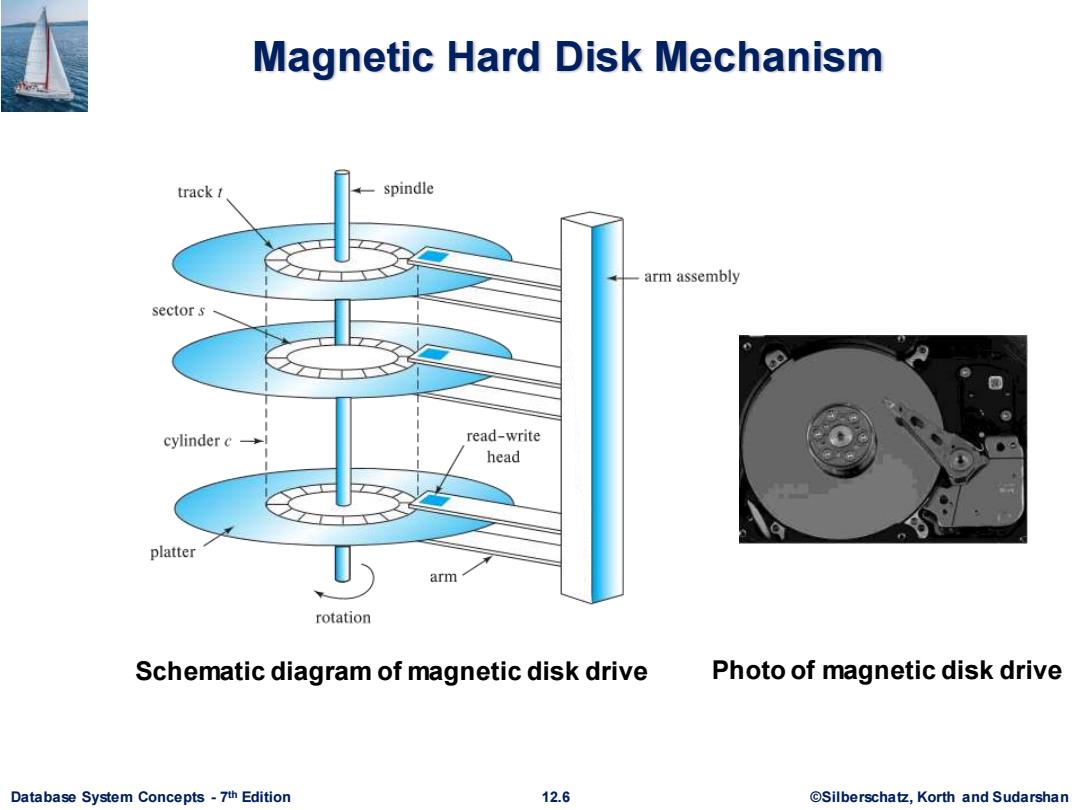
Magnetic Hard Disk Mechanism track t spindle arm assembly sector s cylinder c→ read-write head platter arm rotation Schematic diagram of magnetic disk drive Photo of magnetic disk drive Database System Concepts-7th Edition 12.6 @Silberschatz,Korth and Sudarshan
Database System Concepts - 7 12.6 ©Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan th Edition Magnetic Hard Disk Mechanism Schematic diagram of magnetic disk drive Photo of magnetic disk drive