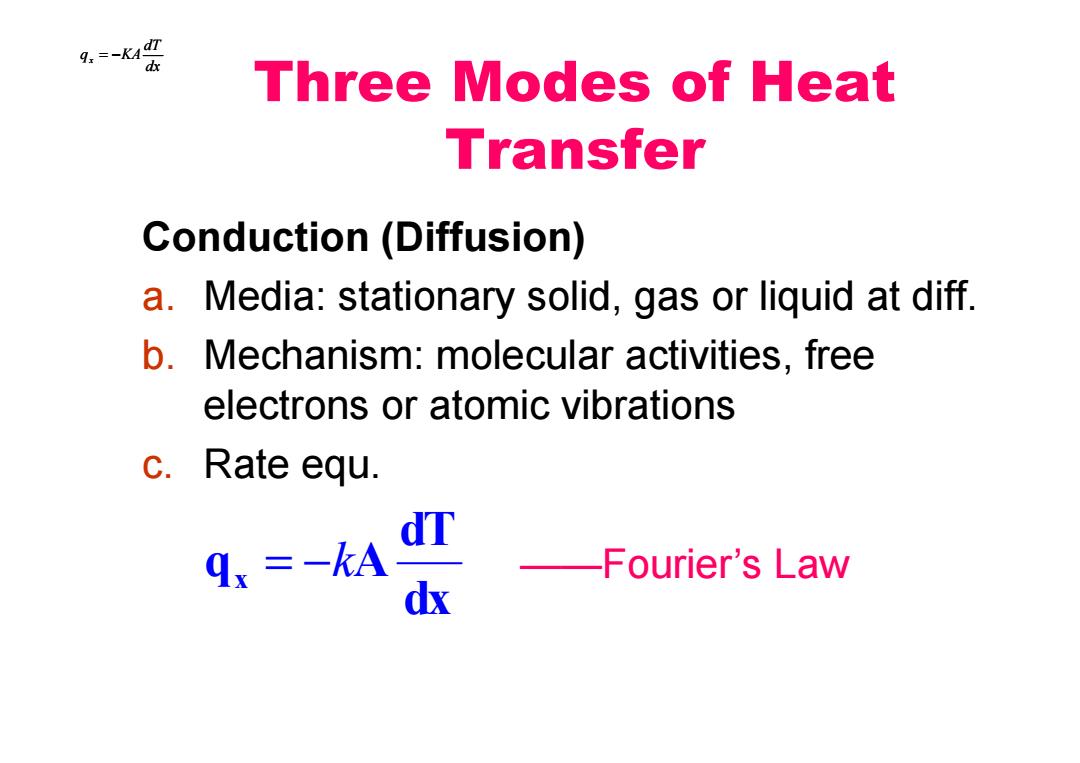
9.=-K40 Three Modes of Heat Transfer Conduction(Diffusion) a.Media:stationary solid,gas or liquid at diff b.Mechanism:molecular activities,free electrons or atomic vibrations c.Rate equ. d.=-kA E -Fourier's Law dx
Three Modes of Heat Transfer Conduction (Diffusion) a. Media: stationary solid, gas or liquid at diff. b. Mechanism: molecular activities, free electrons or atomic vibrations c. Rate equ. dx dT qx = −KA dx dT qx = −KA ——Fourier’s Law dx dT q x = − kA
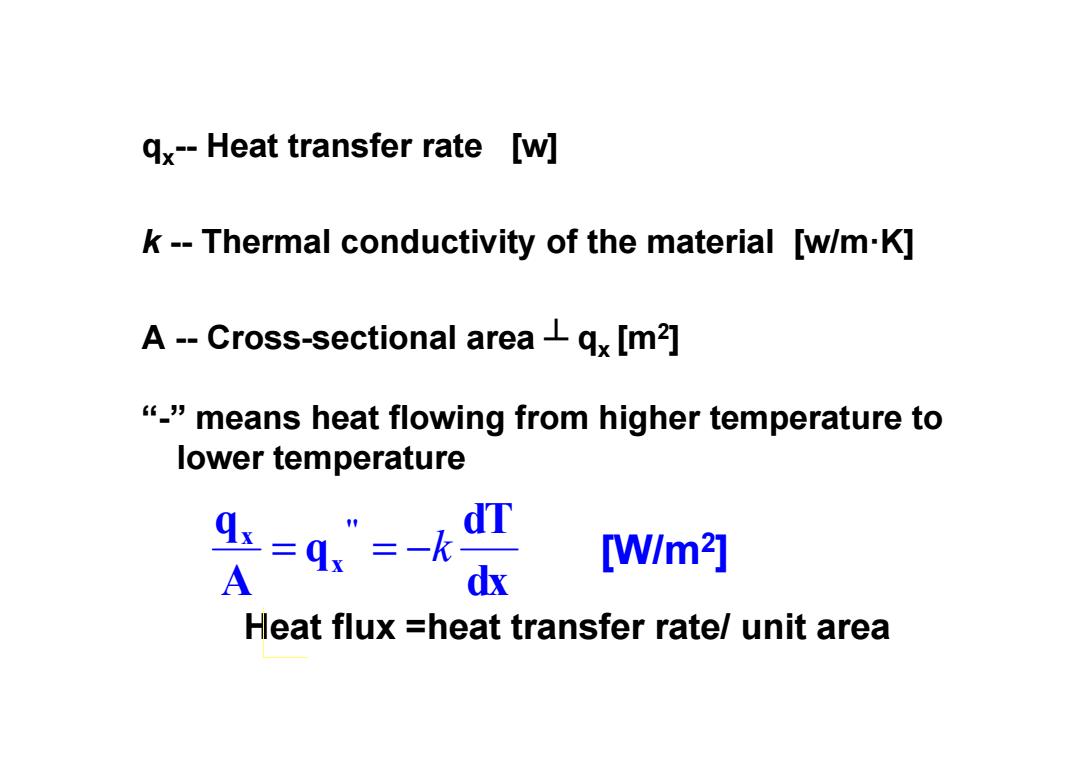
qx--Heat transfer rate [w] k--Thermal conductivity of the material [w/m-K] A--Cross-sectional areaqx [m2] "means heat flowing from higher temperature to lower temperature dT =q”=-k [W/m2] A dx Heat flux =heat transfer rate/unit area
qx-- Heat transfer rate [w] k -- Thermal conductivity of the material [w/m·K] A -- Cross-sectional area ┴ qx [m2] “-” means heat flowing from higher temperature to lower temperature dx dT q Aq '' x x = = −k [W/m2] Heat flux =heat transfer rate/ unit area
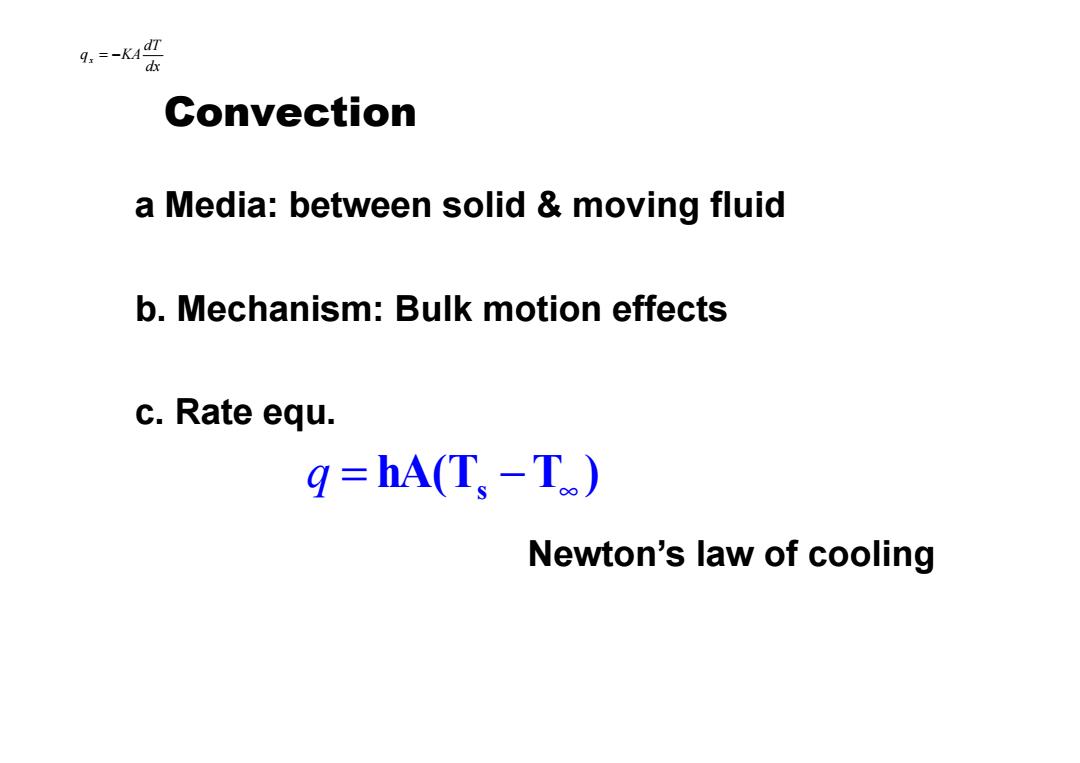
9.=-K4 4 Convection a Media:between solid moving fluid b.Mechanism:Bulk motion effects c.Rate equ. g=hA(T-T) Newton's law of cooling
Convection a Media: between solid & moving fluid b. Mechanism: Bulk motion effects c. Rate equ. dx dT qx = −KA Newton’s law of cooling hA(T T ) = s − ∞ q