
Chapter 1 Marketing -Creating and Capturing Customer Value 教学目的:本章从市场营销学对“市场”一词的理解出发,使学生了解市场的功能、作用, 并建立起市场营销的基本概念,明确认识市场营销的重要性和企业市场营销活动应树立 的指导思想即市场营销观念。 教学重点:市场的含义、类型:市场营销的含义及有关的概念:市场营销管理及其哲学 观念。 教学难点:区分市场营销与推销 学时分配: 教学内容 导入案例一一泰国东方饭店(通过此案例,了解市场营销的概念及市场营销的核心一 建立关系) 一、What is Marketing 1.Marketing defined:The process by which companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships in order to capture value from customers in return. 6R"定义法-Right:product.price place.promotion,time customer 2.The Marketing Process Understand the marketplace and customer needs and wants Design a customer-driven marketing strategy Construct an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value Construct an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value Build profitable relationships and create customer delight Capture value from customers to create profits and customer equity Understanding the Marketplace and Customer Needs 1.Customer Needs.Wants and Demands
Chapter 1 Marketing -Creating and Capturing Customer Value 教学目的:本章从市场营销学对“市场”一词的理解出发,使学生了解市场的功能、作用, 并建立起市场营销的基本概念,明确认识市场营销的重要性和企业市场营销活动应树立 的指导思想即市场营销观念。 教学重点:市场的含义、类型;市场营销的含义及有关的概念;市场营销管理及其哲学 观念。 教学难点:区分市场营销与推销 学时分配: 教学内容: 导入案例——泰国东方饭店(通过此案例,了解市场营销的概念及市场营销的核心—— 建立关系) 一、 What is Marketing 1. Marketing defined: The process by which companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships in order to capture value from customers in return. 6”R”定义法——Right: product, price, place, promotion, time, customer 2. The Marketing Process ⚫ Understand the marketplace and customer needs and wants ⚫ Design a customer-driven marketing strategy ⚫ Construct an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value ⚫ Construct an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value ⚫ Build profitable relationships and create customer delight ⚫ Capture value from customers to create profits and customer equity 二、 Understanding the Marketplace and Customer Needs 1. Customer Needs, Wants and Demands

(1)Needs-state of felt deprivation for basic items such as food and clothing and complex needs such as for belonging.ie.I am hungry (2)Wants-form that a human need takes as shaped by culture and individual personality.i.e.I want a hamburger,and a soft drink (3)Demands-human wants backed by buying power.i.e.I have money to buy this meal. 2.Marketingofferings-products,services and experiences (1)Products:Anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a need or want (2)Services:Activities or benefits offered for sale that are essentially intangible and don't result in the ownership of anything. 3.Value and satisfaction Value=benefit-cost=(physical+emotional)benefit-(money+time+energy)cost Satisfaction=result-expectation 4.Exchange,transactions and relationships (1)Relationships:Building a marketing network consisting of the company and all its supporting stakeholders-Parties with an interest in a firm's decision-making. ie.employees,customers,suppliers,competitors,shareholders,etc. 5.Markets:the set of all actual and potential buyers of a product or service Markets=actural+potential buyers ◆Needs resources for exchange willingness to exchange 3.Modern marketingsystem(P32) 三、 Designing a Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy Marketing management:The art science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them. (-)Selecting Customersto Serve ()Choosinga Value Proposition (三) Marketing management orientations
(1) Needs - state of felt deprivation for basic items such as food and clothing and complex needs such as for belonging. i.e. I am hungry. (2) Wants - form that a human need takes as shaped by culture and individual personality. i.e. I want a hamburger, and a soft drink. (3) Demands - human wants backed by buying power. i.e. I have money to buy this meal. 2. Marketing offerings-products, services and experiences (1) Products: Anything that can be offered to a market to satisfy a need or want (2) Services: Activities or benefits offered for sale that are essentially intangible and don’t result in the ownership of anything. 3. Value and satisfaction ⚫ Value=benefit-cost=(physical+emotional)benefit-(money+time+energy)cost ⚫ Satisfaction=result-expectation 4. Exchange, transactions and relationships (1) Relationships: Building a marketing network consisting of the company and all its supporting stakeholders-Parties with an interest in a firm’s decision-making. i.e. employees, customers, suppliers, competitors, shareholders, etc. 5. Markets: the set of all actual and potential buyers of a product or service. ⚫ Markets=actural+potential buyers Needs resources for exchange willingness to exchange 3. Modern marketing system (P32) 三、 Designing a Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy Marketing management: The art & science of choosing target markets and building profitable relationships with them. (一) Selecting Customers to Serve (二) Choosing a Value Proposition (三) Marketing management orientations
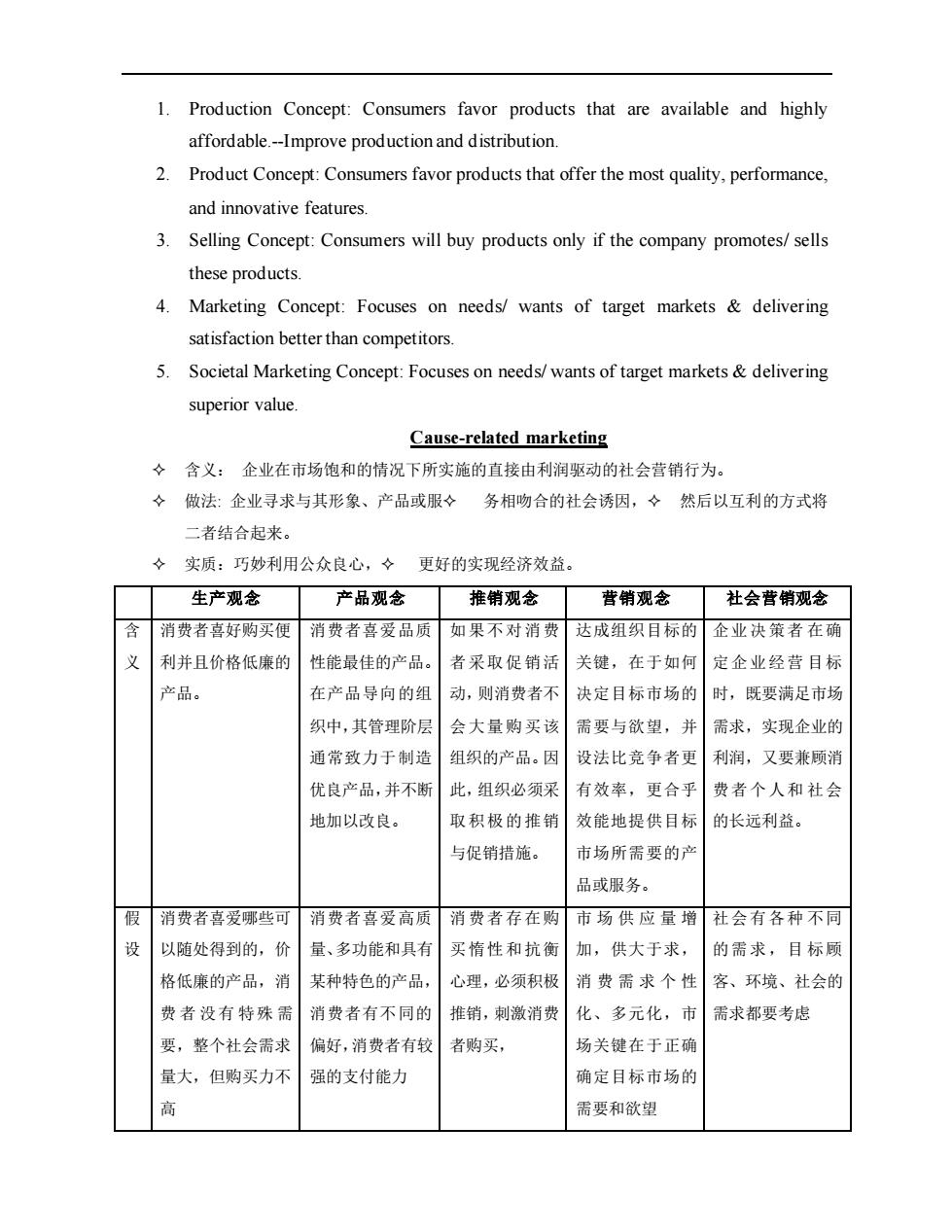
1. Production Concept:Consumers favor products that are available and highly affordable-Improve production and distribution 2.Product Concept:Consumers favor products that offer the most quality.performance, and innovative features. 3.Selling Concept:Consumers will buy products only if the company promotes/sells these products. 4.Marketing Concept:Focuses on needs/wants of target markets delivering satisfaction better than competitors 5. Societal Marketing Concept:Focuses on needs/wants of target markets&delivering superior value. Cause-related marketing 令含义:企业在市场饱和的情况下所实施的直接由利润驱动的社会营销行为。 ◇做法:企业寻求与其形象、产品或服◇务相吻合的社会诱因,◆然后以互利的方式将 二者结合起来。 令实质:巧妙利用公众良心,夕更好的实现经济效益。 生产观念 产品观念 推销观念 营销观念 社会营销观念 消费者喜好购买使消费者喜爱品质 如果不对消费达成组织目标的企业决策者在确 利并且价格低廉的 性能最佳的产品 者采取促销活 关键,在于如何 定企业经营目标 产品。 在产品导向的组 动,则消费者不 决定目标市场的 时,既要满足市场 织中,其管理阶层 会大量购买该 需要与欲望,并 需求,实现企业的 通常致力于制造 组织的产品。因 设法比竞争者更 利润,又要兼顾消 优良产品,并不断 此,组织必须采 有效率,更合乎 费者个人和社会 地加以改良。 取积极的推销 效能地提供目标 的长远利益。 与促销措施。 市场所需要的 品或服务。 假消费者喜爱哪些可消费者喜爱高质 消费者存在购市场供应量增社会有各种不同 设 以随处得到的,价量、多功能和具有 买惰性和抗衡加,供大于求, 的需求,目标顾 格低廉的产品,消 某种特色的产品, 心理,必须积极消费需求个性客、环境、社会的 费者没有特殊需 消费者有不同的 推销,刺激消费化、多元化,市需求都要考虑 要,整个社会需求 偏好,消费者有较 者购买, 场关键在于正确 量大,但购买力不 强的支付能力 确定目标市场的 需要和欲望
1. Production Concept: Consumers favor products that are available and highly affordable.-Improve production and distribution. 2. Product Concept: Consumers favor products that offer the most quality, performance, and innovative features. 3. Selling Concept: Consumers will buy products only if the company promotes/ sells these products. 4. Marketing Concept: Focuses on needs/ wants of target markets & delivering satisfaction better than competitors. 5. Societal Marketing Concept: Focuses on needs/ wants of target markets & delivering superior value. Cause-related marketing 含义: 企业在市场饱和的情况下所实施的直接由利润驱动的社会营销行为。 做法: 企业寻求与其形象、产品或服 务相吻合的社会诱因, 然后以互利的方式将 二者结合起来。 实质:巧妙利用公众良心, 更好的实现经济效益。 生产观念 产品观念 推销观念 营销观念 社会营销观念 含 义 消费者喜好购买便 利并且价格低廉的 产品。 消费者喜爱品质 性能最佳的产品。 在产品导向的组 织中,其管理阶层 通常致力于制造 优良产品,并不断 地加以改良。 如果不对消费 者采取促销活 动,则消费者不 会大量购买该 组织的产品。因 此,组织必须采 取积极的推销 与促销措施。 达成组织目标的 关键,在于如何 决定目标市场的 需要与欲望,并 设法比竞争者更 有效率,更合乎 效能地提供目标 市场所需要的产 品或服务。 企业决策者 在确 定企业经营 目标 时,既要满足市场 需求,实现企业的 利润,又要兼顾消 费者个人和 社会 的长远利益。 假 设 消费者喜爱哪些可 以随处得到的,价 格低廉的产品,消 费 者 没有 特殊 需 要,整个社会需求 量大,但购买力不 高 消费者喜爱高质 量、多功能和具有 某种特色的产品, 消费者有不同的 偏好,消费者有较 强的支付能力 消费者存在购 买惰性和抗衡 心理,必须积极 推销,刺激消费 者购买, 市场供应量增 加,供大于求, 消费需求个性 化、多元化,市 场关键在于正确 确定目标市场的 需要和欲望 社会有各种 不同 的需求,目 标顾 客、环境、社会的 需求都要考虑
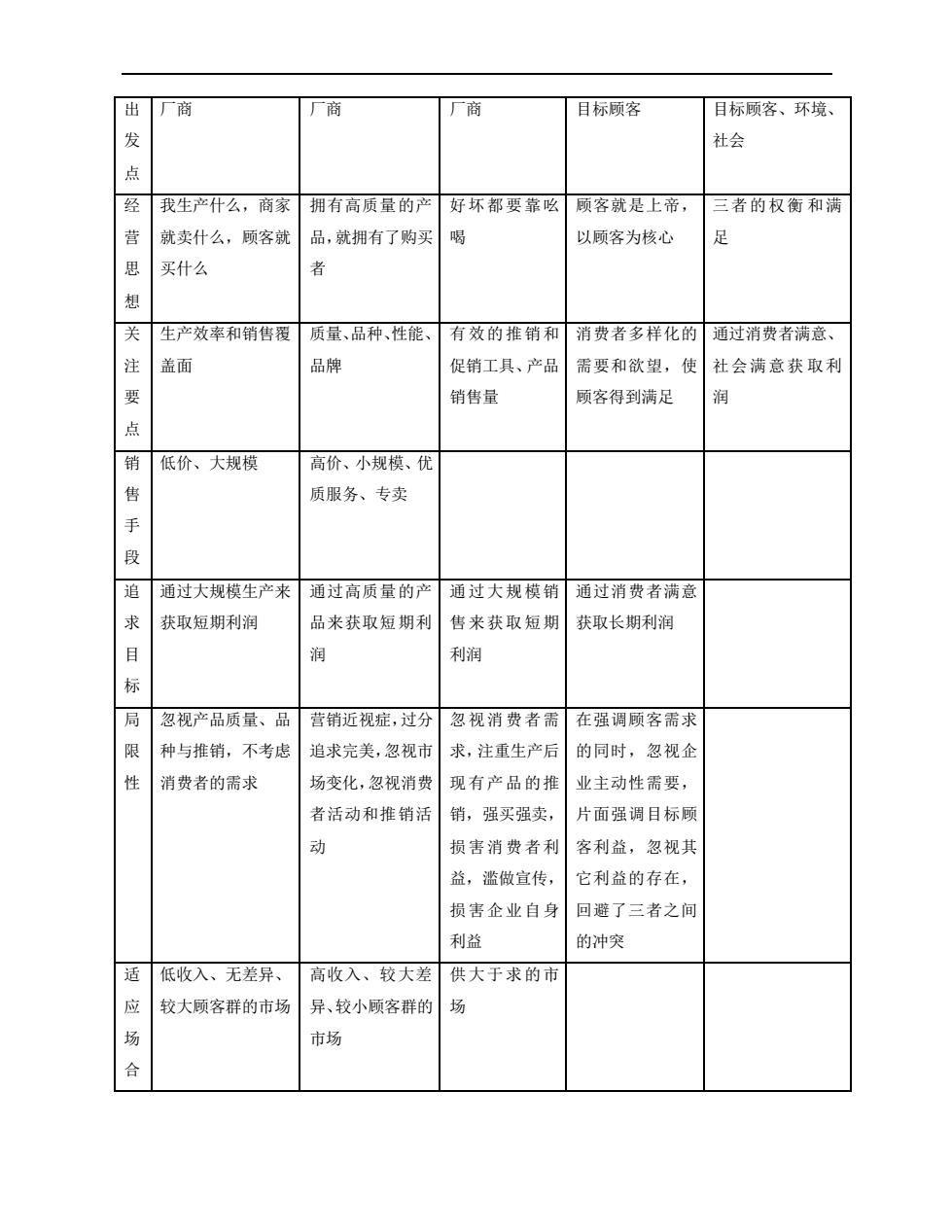
出厂商 厂商 一商 目标顾客 目标顾客、环境、 社会 点 我生产什么,商家 拥有高质量的产 好坏都要靠吆 顾客就是上帝 三者的权衡和满 营 就卖什么,顾客就 品,就拥有了购买 喝 以顾客为核心 足 思 买什么 者 关生产效率和销售覆质量、品种、性能、 有效的推销和消费者多样化的通过消费者满意、 注盖面 品牌 促销工具、产品需要和欲望,使 社会满意获取利 销售量 顾客得到满足 润 销低价、大规模 高价、小规模、优 售 质服务、专卖 追通过大规模生产来 通过高质量的 通过大规模销 通过消费者满意 求 获取短期利润 品来获取短期利 售来获取短期获取长期利润 润 利润 标 局忽视产品质量、品 营销近视症,过分 忽视消费者需在强调顾客需求 限 种与推销,不考虑 追求完美,忽视市 求,注重生产后的同时,忽视企 性 消费者的需求 场变化,忽视消费 现有产品的推业主动性需要, 者活动和推销活 销,强买强卖, 片面强调目标顾 损害消费者利客利益,忽视其 益,滥做宜传, 它利益的存在, 损苦企业自身回避了三者之间 利益 的冲突 适低收入、无差异、 高收入、较大差 供大于求的市 较大顾客群的市场异、较小顾客群的 市场
出 发 点 厂商 厂商 厂商 目标顾客 目标顾客、环境、 社会 经 营 思 想 我生产什么,商家 就卖什么,顾客就 买什么 拥有高质量的产 品,就拥有了购买 者 好坏都要靠吆 喝 顾客就是上帝, 以顾客为核心 三者的权衡 和满 足 关 注 要 点 生产效率和销售覆 盖面 质量、品种、性能、 品牌 有效的推销和 促销工具、产品 销售量 消费者多样化的 需要和欲望,使 顾客得到满足 通过消费者满意、 社会满意获 取利 润 销 售 手 段 低价、大规模 高价、小规模、优 质服务、专卖 追 求 目 标 通过大规模生产来 获取短期利润 通过高质量的产 品来获取短期利 润 通过大规模销 售来获取短期 利润 通过消费者满意 获取长期利润 局 限 性 忽视产品质量、品 种与推销,不考虑 消费者的需求 营销近视症,过分 追求完美,忽视市 场变化,忽视消费 者活动和推销活 动 忽视消费者需 求,注重生产后 现有产品的推 销,强买强卖, 损害消费者利 益,滥做宣传, 损害企业自身 利益 在强调顾客需求 的同时,忽视企 业主动性需要, 片面强调目标顾 客利益,忽视其 它利益的存在, 回避了三者之间 的冲突 适 应 场 合 低收入、无差异、 较大顾客群的市场 高收入、较大差 异、较小顾客群的 市场 供大于求的市 场

四、 Preparing an Integrated Marketing Plan and Program (一) Building Customer Relationships 1.Customer Relationship Management The overall process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction (1)Relationship building blocks:customer value and satisfaction ●Customer value Total customer value Product value:dependability,durability,security Service value:delivery,training.repair Personnel value:knowledge.experience,responsibility Image value:brand,Corporate image,goodwill ◇Total customer cost √Monetary cost √Time cost √Energy cost √Physical cost Customer satisfaction Today's most successful companies are raising expectations-and delivering performance to match These companies embrace total customer satisfaction. Firm that seeks total customer satisfaction doesn't have to attempt maximum customer satisfaction. Purpose of marketing is to generate customer value profitably-offer customer satisfaction without sacrificing profits. (2)Customer relationship levels and tools ●Levels 令basic relationships ◇full partnerships ·Tools: Frequency marketing programs
四、 Preparing an Integrated Marketing Plan and Program (一) Building Customer Relationships 1. Customer Relationship Management The overall process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction. (1) Relationship building blocks: customer value and satisfaction ⚫ Customer value Total customer value: ✓ Product value: dependability, durability, security ✓ Service value: delivery, training, repair ✓ Personnel value: knowledge, experience, responsibility ✓ Image value: brand, Corporate image, goodwill Total customer cost ✓ Monetary cost ✓ Time cost ✓ Energy cost ✓ Physical cost ⚫ Customer satisfaction Today’s most successful companies are raising expectations – and delivering performance to match. These companies embrace total customer satisfaction. Firm that seeks total customer satisfaction doesn’t have to attempt maximum customer satisfaction. Purpose of marketing is to generate customer value profitably – offer customer satisfaction without sacrificing profits. (2) Customer relationship levels and tools ⚫ Levels basic relationships full partnerships ⚫ Tools: Frequency marketing programs