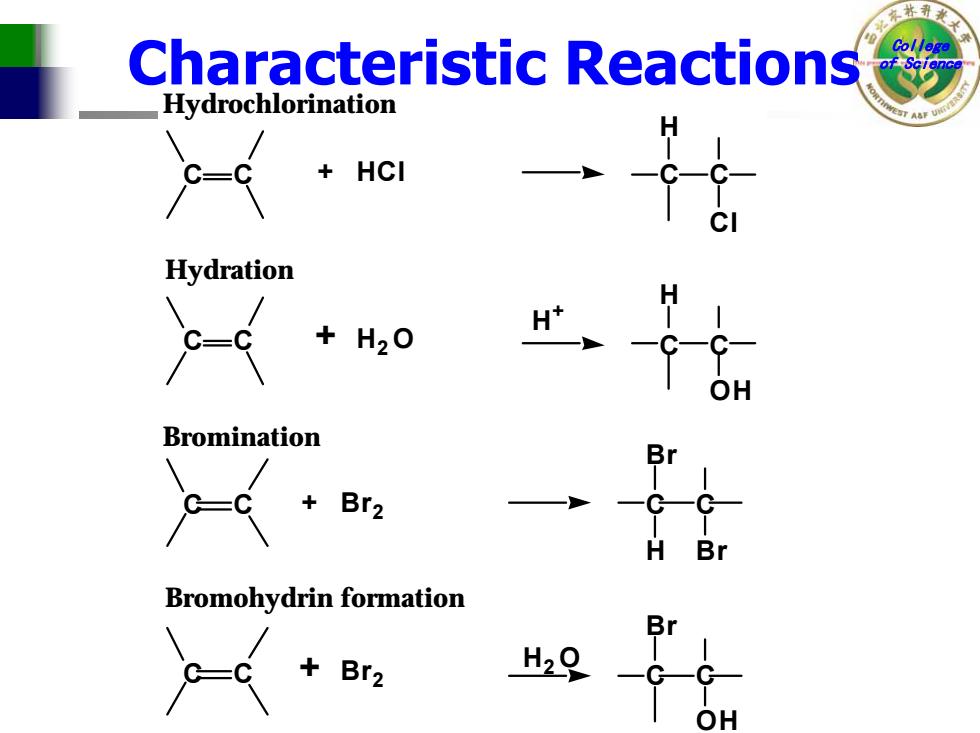
Characteristic Reactions Hydrochlorination C- HCI Hydration C-c +H20 Bromination + B Bromohydrin formation Br2 H29
College Characteristic Reactions of Science + H 2 O Hydration + Hydrochlorination C C C C Cl H HCl C C C C OH H H + Br + 2 Bromohydrin formation + Bromination C C C C H Br Br Br 2 C C C C OH Br H 2 O

林 Characteristic Reactions Oxymercuration OH C- +Hg(OAc2H0--g H HgOAc Hydroboration C=( BH2 Diol formation(oxidation) +0s04— OH OH Hydrogenation(reduction) +H2 -c HH
College Characteristic Reactions of Science + Oxymercuration C C Hg ( OAc ) 2 C C H Hg O A c OH H 2 O + Os O 4 Diol formation (oxidation) + Hydrogenation (reduction) C C H 2 + Hydroboration C C C C H BH 2 BH 3 C C C C OH OH C C H H
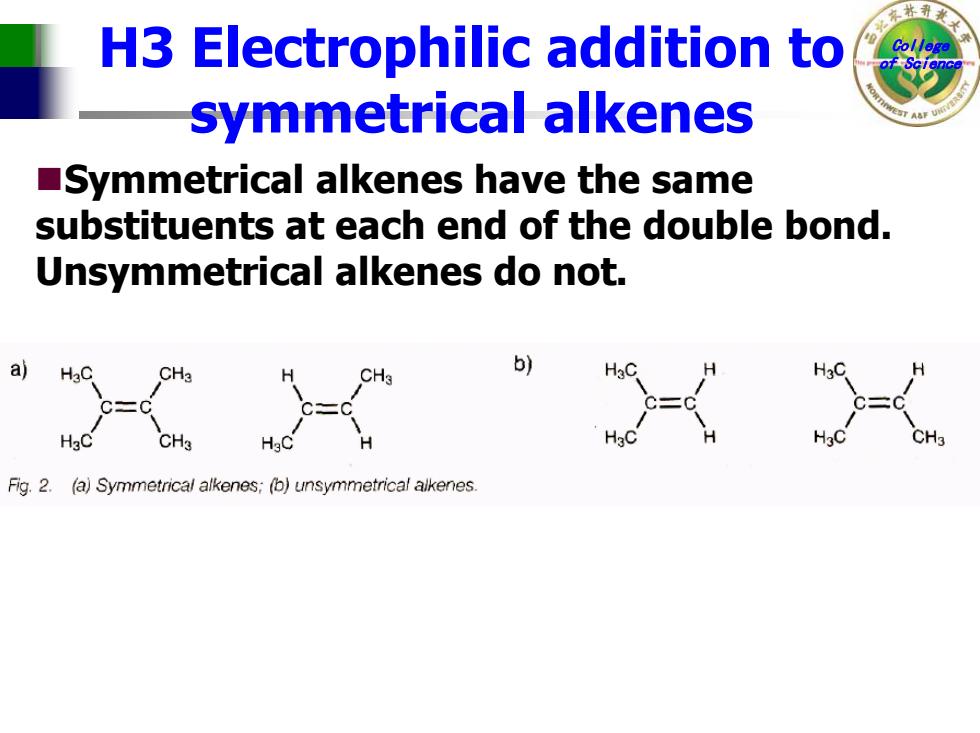
林 H3 Electrophilic addition to symmetrical alkenes Symmetrical alkenes have the same substituents at each end of the double bond. Unsymmetrical alkenes do not. a) HaC b) Fig.2.(a)Symmetrical alkenes;(b)unsymmetrical alkenes
College H3 Electrophilic addition to of Science symmetrical alkenes Symmetrical alkenes have the same substituents at each end of the double bond. Unsymmetrical alkenes do not

H3 Electrophilic addition t0 College symmetrical alkenes Electrophilic addition Hydrogen halide addition:Alkenes react with hydrogen halides (HCl,HBr,and HI)to give an alkyl halide. ●Halogen addition ●Alkenes to alcohols ●Alkenes to ethers Alkenes to arylalkanes
College of Science H3 Electrophilic addition to symmetrical alkenes Electrophilic addition zHydrogen halide addition:Alkenes react with hydrogen halides (HCl, HBr, and HI) to give an alkyl halide. zHalogen addition zAlkenes to alcohols zAlkenes to ethers zAlkenes to arylalkanes
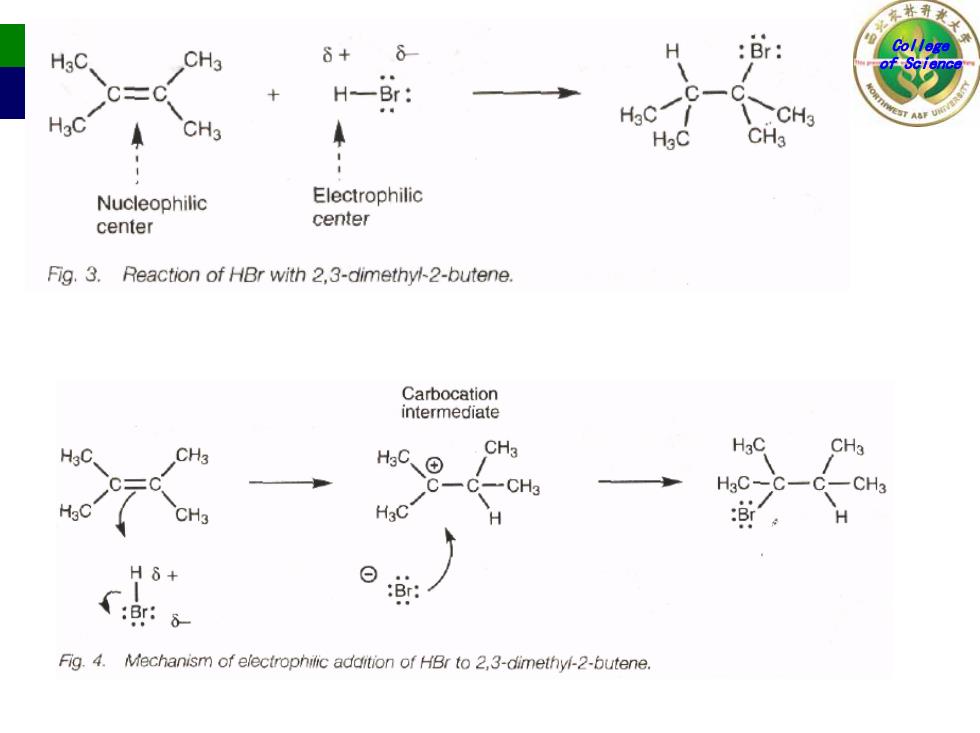
HgC CH3 6+ H :Br: H-Br: CH3 HgC Nucleophilic Electrophilic center center Fig.3.Reaction of HBr with 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene. Carbocation intermediate CH3 HC、 CH3 H3C CH3 DE CH3 HaC H6+ :Br: :Br:8 Fig.4.Mechanism of electrophilic addition of HBr to 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
College of Science