
a Halogenation Base-promoted halogenation of ketone. ■Base is consumed. Other products are water and chloride ion. OH
Halogenation ◼Base-promoted halogenation of ketone. ◼Base is consumed. ◼Other products are water and chloride ion. OH _ O H H O H _ O H Cl Cl Cl
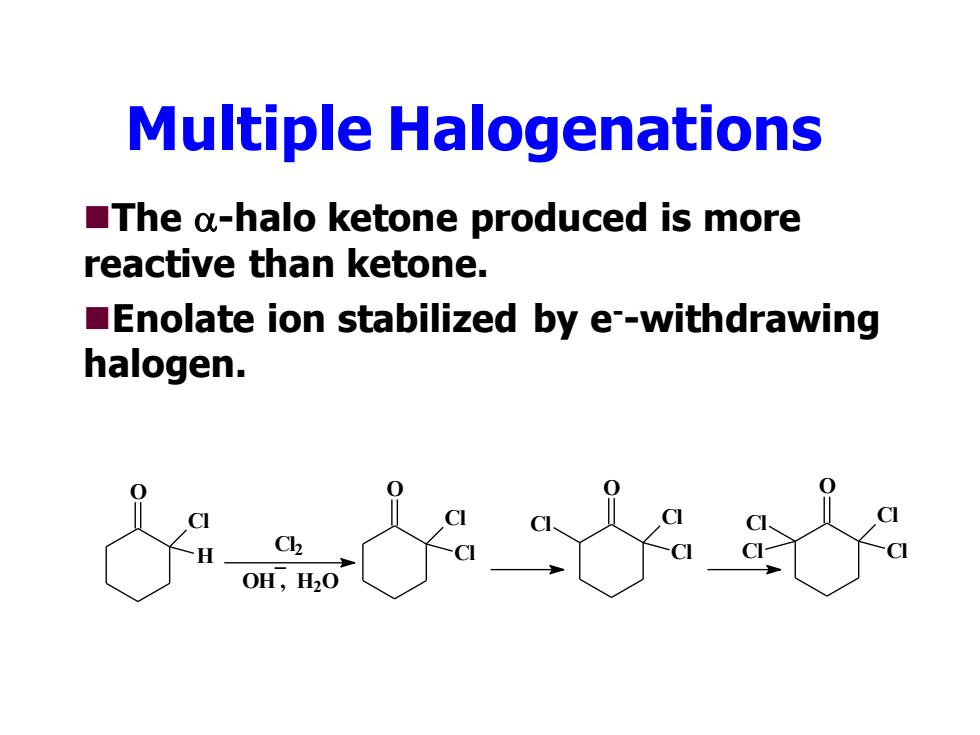
Multiple Halogenations The a-halo ketone produced is more reactive than ketone. Enolate ion stabilized by e--withdrawing halogen. 0 0H,H20
Multiple Halogenations ◼The -halo ketone produced is more reactive than ketone. ◼Enolate ion stabilized by e--withdrawing halogen. O H Cl Cl2 OH , H2O _ O Cl Cl O Cl C Cl l O Cl C Cl l Cl

Haloform Reaction Methyl ketones replace all three H's with halogen. The trihalo ketone then reacts with hydroxide ion to give carboxylic acid. OH CI3 HCI3 lodoform, yellow ppt
Haloform Reaction ◼Methyl ketones replace all three H’s with halogen. ◼The trihalo ketone then reacts with hydroxide ion to give carboxylic acid. Iodoform, yellow ppt. C O CH3 excess I2 OH - C O CI3 OH - C O OH CI3 - C O O - HCI3

Positive Iodoform for Alcohols If the iodine oxidizes the alcohol to a methyl ketone,the alcohol will give a positive iodoform test. R--aH,+一 R-C-CH +2HI -OH R-C-0-+HCI (one less carbon) Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Positive Iodoform for Alcohols If the iodine oxidizes the alcohol to a methyl ketone, the alcohol will give a positive iodoform test