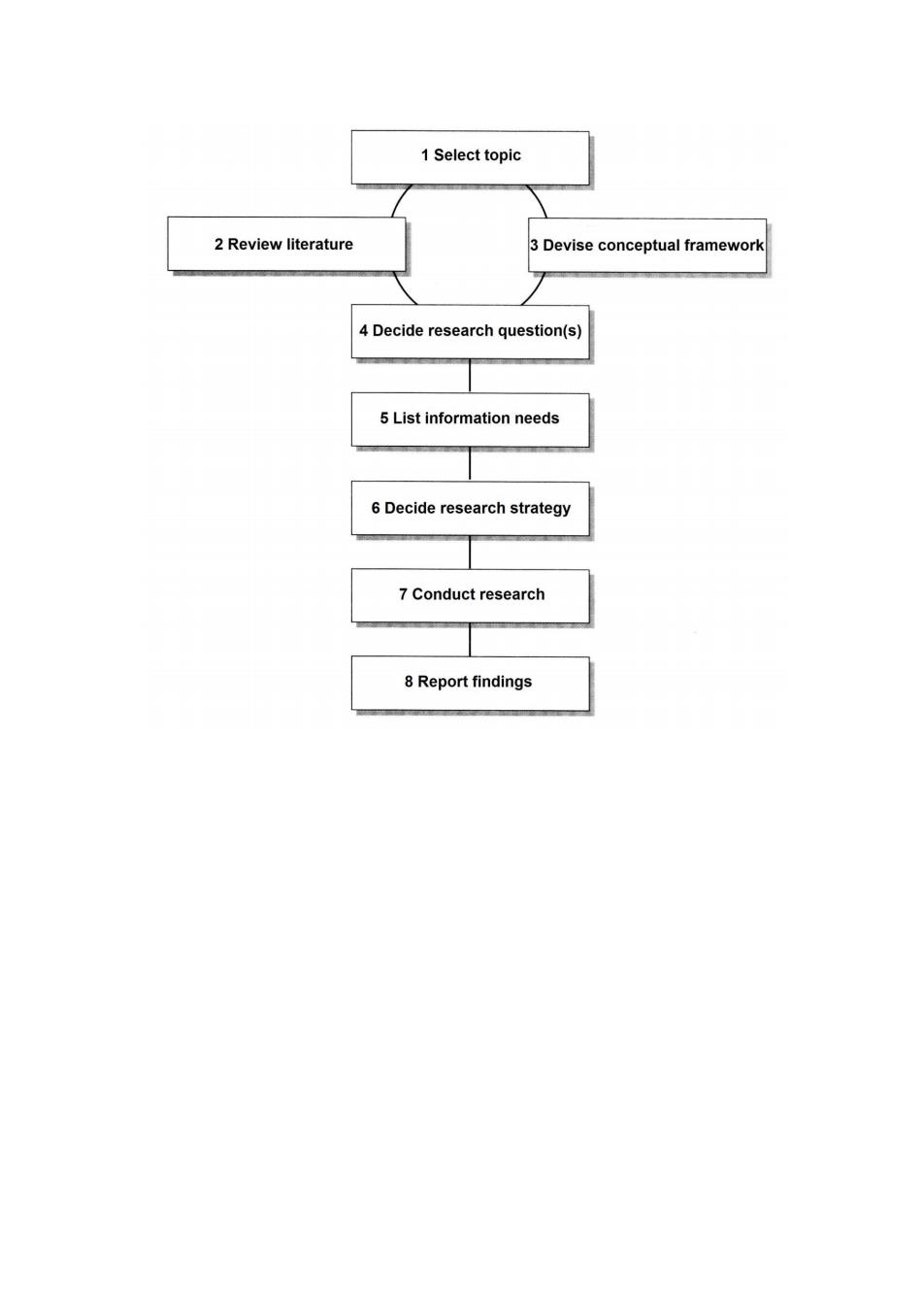
1Select topic 2 Review literature 3 Devise conceptual framework 4 Decide research question(s) 5 List information needs 6 Decide research strategy 7Conduct research 8 Report findings
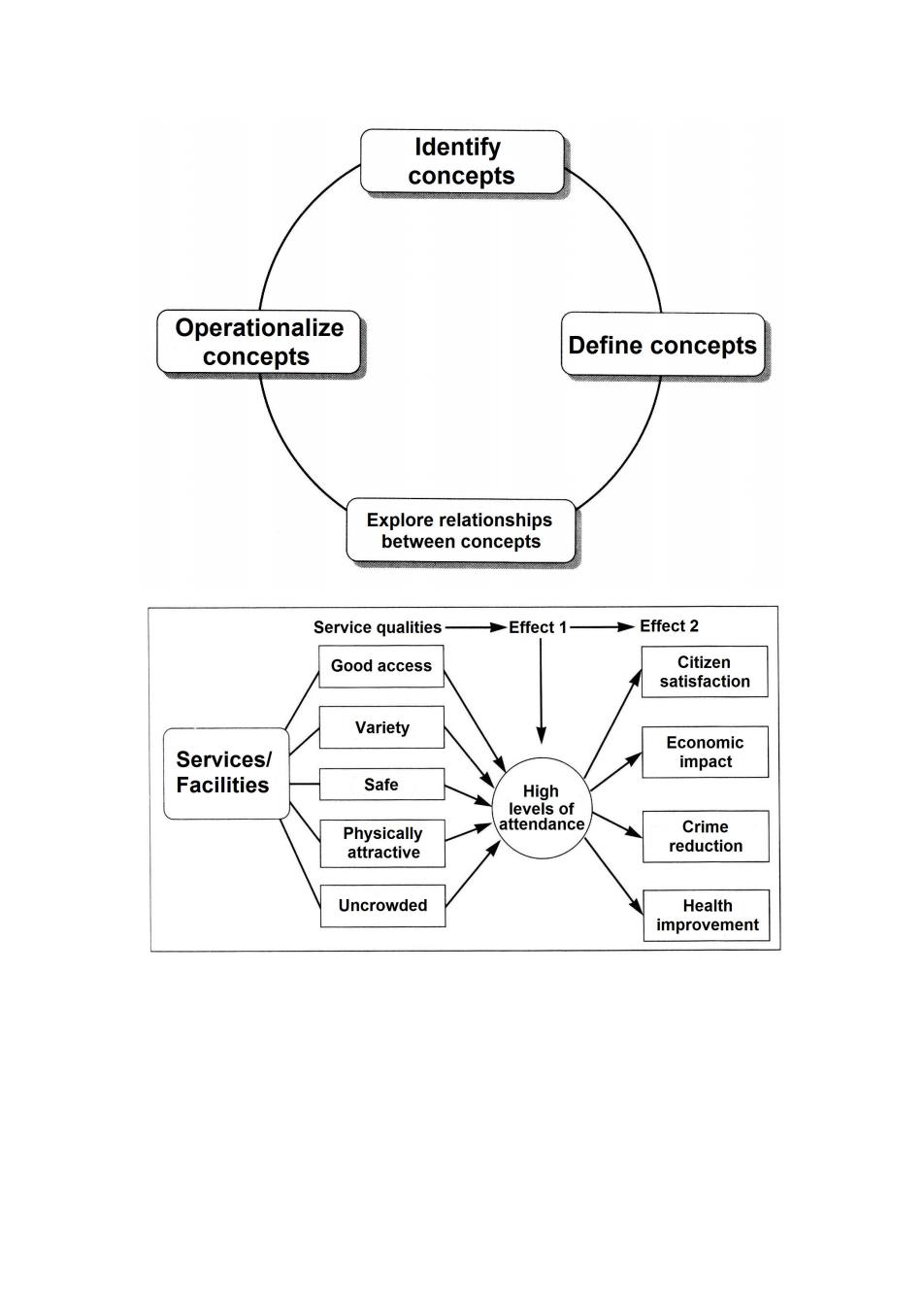
Identify concepts Operationalize concepts Define concepts Explore relationships between concepts Service qualities Effect 1 Effect 2 Good access Variety Services/ EcapacS Facilities Safe Physically attractive reducton Uncrowded ment
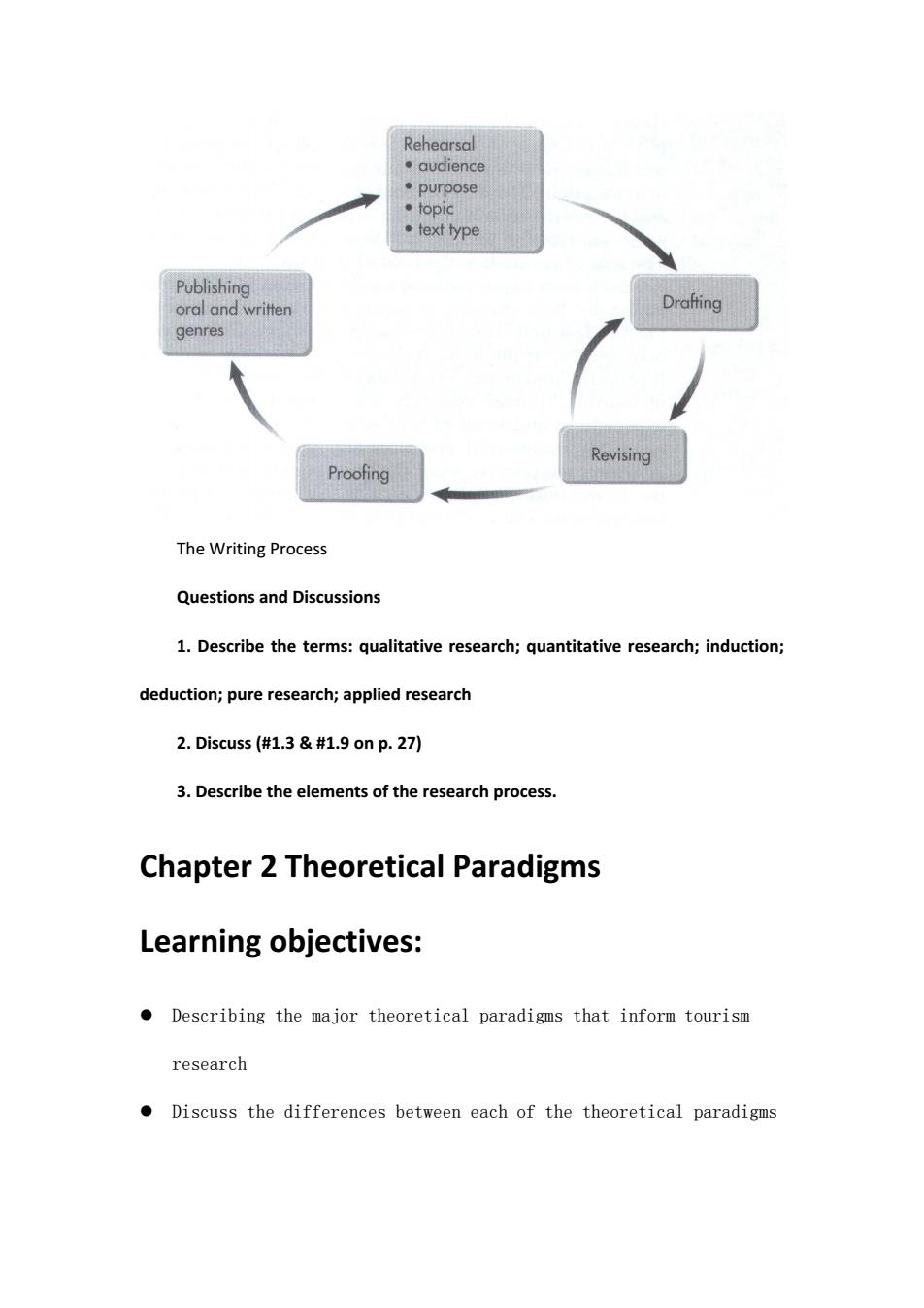
Rehearsal ·audience ·purpose 。topic ·text type Publishing oral and written genres Revising Proofing The Writing Process Questions and Discussions 1.Describe the terms:qualitative research;quantitative research;induction; deduction;pure research;applied research 2.Discuss(#1.3.9onp.27) 3.Describe the elements of the research process. Chapter 2 Theoretical Paradigms Learning objectives: Describing the major theoretical paradigms that inform tourism research Discuss the differences between each of the theoretical paradigms
The Writing Process Questions and Discussions 1. Describe the terms: qualitative research; quantitative research; induction; deduction; pure research; applied research 2. Discuss (#1.3 & #1.9 on p. 27) 3. Describe the elements of the research process. Chapter 2 Theoretical Paradigms Learning objectives: Describing the major theoretical paradigms that inform tourism research Discuss the differences between each of the theoretical paradigms

Explain the consequences of these differences for the conduct of tourism research Key knowledge:the consequences of these differences for the conduct of tourism research Difficult knowledge:the major theoretical paradigms that inform tourism research What is a paradigm? A paradigm can be defined as the entire constellation of beliefs, assumptions and values that underlie the way in which a society interprets reality at a given point in time.In this sense,a paradigm can also be described as a“world view'”or“cosmology”.In this textbook,a paradigm is defined as a basic set of beliefs that guides action. Theoretical Paradigms Term Definition Paradigm Theoretical Paradigms A set of beliefs Ontology The nature of reality
Explain the consequences of these differences for the conduct of tourism research Key knowledge: the consequences of these differences for the conduct of tourism research Difficult knowledge: the major theoretical paradigms that inform tourism research What is a paradigm? A paradigm can be defined as the entire constellation of beliefs, assumptions and values that underlie the way in which a society interprets reality at a given point in time. In this sense, a paradigm can also be described as a “world view” or “cosmology”. In this textbook, a paradigm is defined as a basic set of beliefs that guides action. Theoretical Paradigms Term Definition Paradigm Theoretical Paradigms A set of beliefs Ontology The nature of reality

Epistemology The relationship between the researcher and the subjects/objects Methodology The set of guidelines for conducting research Method The tools for data collection and analysis Questions used to organize the description of each paradigm ★How is the world perceived?(Ontological basis,,本体论) *What is the relationship between the researcher and the subjects or objects of research?(Epistemological basis,.认识论) How will the researcher gather data/information? (Methodological basis,方法论) Positivism embraces a view of the world as being guided by scientific rules that explain the behavior of phenomena through causal relationships. How is the world perceived?(Ontological basis) The natural world is perceived as being organized by universal laws and truths,the social world is also perceived by universal laws and truths.Human behavior is predictable and can be shaped and controlled What is the relationship between the researcher and the subjects or objects of research?(Epistemological basis)
Epistemology The relationship between the researcher and the subjects/objects Methodology The set of guidelines for conducting research Method The tools for data collection and analysis Questions used to organize the description of each paradigm ★ How is the world perceived? (Ontological basis,本体论) ★ What is the relationship between the researcher and the subjects or objects of research? (Epistemological basis, 认识论) ★ How will the researcher gather data/information? (Methodological basis, 方法论) Positivism embraces a view of the world as being guided by scientific rules that explain the behavior of phenomena through causal relationships. ★ How is the world perceived? (Ontological basis) The natural world is perceived as being organized by universal laws and truths, the social world is also perceived by universal laws and truths. Human behavior is predictable and can be shaped and controlled. ★ What is the relationship between the researcher and the subjects or objects of research? (Epistemological basis)