
Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2006,Prentice Hall
Chapter 13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2006, Prentice Hall Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr
circulution Introduction NMR is the most powerful tool available for organic structure determination. It is used to study a wide variety of nuclei: >1H >13C >15N >19F >31P => Chapter 13
Chapter 13 2 Introduction • NMR is the most powerful tool available for organic structure determination. • It is used to study a wide variety of nuclei: ➢1H ➢13C ➢15N ➢19F ➢31P =>
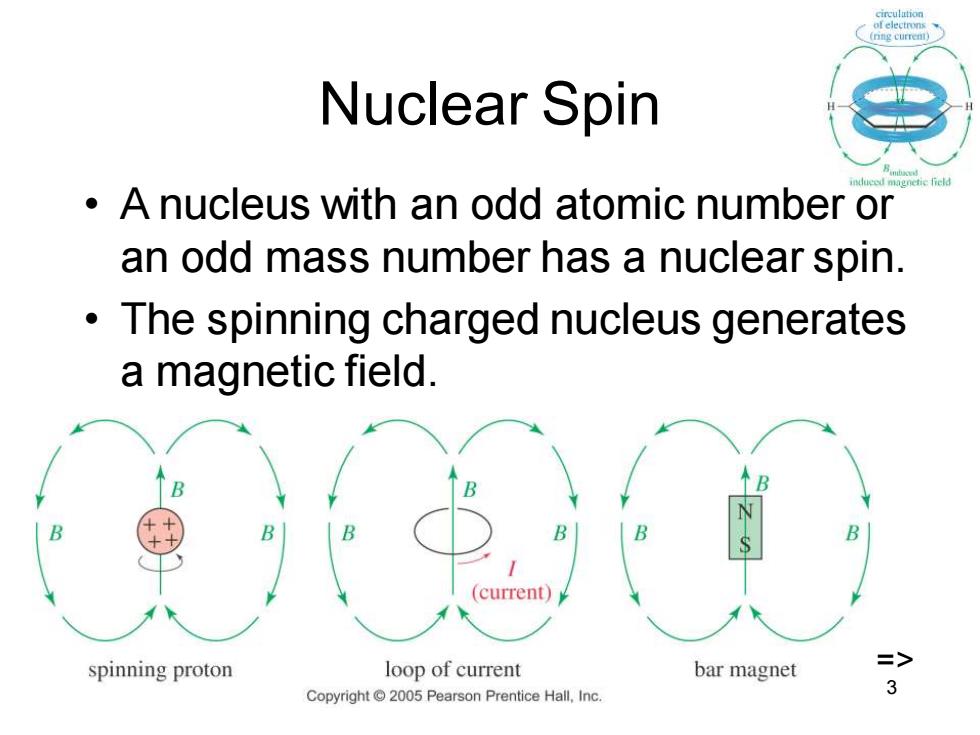
Nuclear Spin A nucleus with an odd atomic number or an odd mass number has a nuclear spin. The spinning charged nucleus generates a magnetic field. (current) spinning proton loop of current bar magnet Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Chapter 13 3 Nuclear Spin • A nucleus with an odd atomic number or an odd mass number has a nuclear spin. • The spinning charged nucleus generates a magnetic field. =>
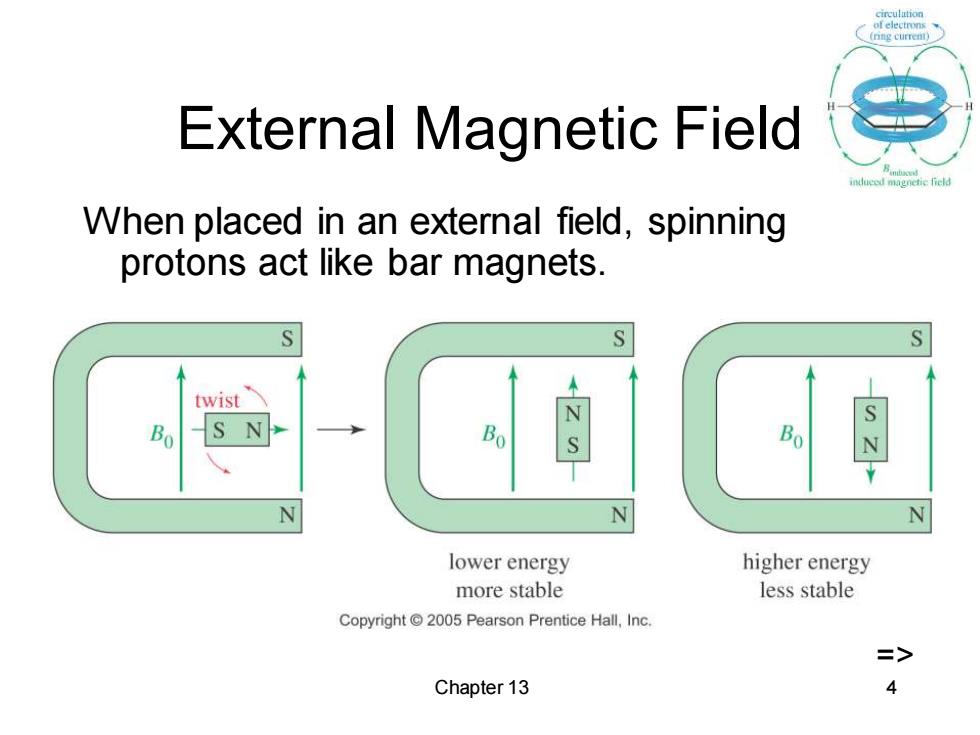
circulution External Magnetic Field When placed in an external field,spinning protons act like bar magnets. twist N S N lower energy higher energy more stable less stable Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. => Chapter 13 4
Chapter 13 4 External Magnetic Field When placed in an external field, spinning protons act like bar magnets. =>

Two Energy States The magnetic fields of the spinning nuclei will align either with B state the external field,or against the field. A photon with the right Bo hv=△E amount of energy can be absorbed and cause the a state spinning proton to flip. => Copyright2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc Chapter 13 5
Chapter 13 5 Two Energy States The magnetic fields of the spinning nuclei will align either with the external field, or against the field. A photon with the right amount of energy can be absorbed and cause the spinning proton to flip. =>