
Cons of propositional logic Propositional logic has very limited expressive power unlike natural language E.g.,cannot say "pits cause breezes in adjacent squares" except by writing one sentence for each square B1,1台(P1,2VP2,1) 口卡4三4色进分QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cons of propositional logic ▶ Propositional logic has very limited expressive power ▶ unlike natural language ▶ E.g., cannot say “pits cause breezes in adjacent squares” except by writing one sentence for each square B1,1 ⇔ (P1,2 ∨ P2,1)

Cons of propositional logic All students know arithmetic. AlicelsStudent-AliceKnowsArithmetic BoblsStudent-BobKnowsArithmetic 44 Propositional logic is very clunky.What's missing? Objects and relations:propositions (e.g., AliceKnowsArithmetic)have more internal structure (alice, Knows,arithmetic) Quantifiers and variables:all is a quantifier which applies to each person,don't want to enumerate them all... 4口◆4⊙t1三1=,¥9QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Cons of propositional logic ▶ All students know arithmetic. ▶ AliceIsStudent → AliceKnowsArithmetic ▶ BobIsStudent → BobKnowsArithmetic ... ▶ Propositional logic is very clunky. What’s missing? ▶ Objects and relations: propositions (e.g., AliceKnowsArithmetic) have more internal structure (alice, Knows, arithmetic) ▶ Quantifiers and variables: all is a quantifier which applies to each person, don’t want to enumerate them all

First-order logic 采用命题逻辑的基础一陈述式、上下文无关和合成语义,并借用 自然语言的思想。 Whereas propositional logic assumes the world contains facts, first-order logic(like natural language)assumes the world contains ~Objects(对象):people,houses,.numbers,colors,,baseball games,wars,.. Relations(关系):red,round,prime, brother of,bigger than,part of,comes between,. ~Functions(函数):father of,best friend,one more than,plus, 谓词用来描述个体(可以独立存在的事物)之间的关系或属性 口卡回+·三色是分Q
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . First-order logic 采用命题逻辑的基础—陈述式、上下文无关和合成语义,并借用 自然语言的思想。 Whereas propositional logic assumes the world contains facts, first-order logic (like natural language) assumes the world contains ▶ Objects (对象): people, houses, numbers, colors, baseball games, wars, … ▶ Relations (关系): red, round, prime, … brother of, bigger than, part of, comes between, … ▶ Functions (函数): father of, best friend, one more than, plus, … 谓词用来描述个体(可以独立存在的事物)之间的关系或属性

Logics in general 本体论约定 认识论约定 语言 (世界中存在的) (智能体对事实 所相信的内容) 命题逻辑 Propositional logic 事实 真/假/未知 一阶逻辑 First-order logic 事实、对象、关系 真/假/未知 时序逻辑 Temporal logic 事实、对象、关系、时间 真/假/未知 概率逻辑 Probability logic 事实 信度∈[0,1] 4口404三·1=,生9QG
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Logics in general 语言 本体论约定 (世界中存在的) 认识论约定 (智能体对事实 所相信的内容) 命题逻辑 Propositional logic 事实 真/假/未知 一阶逻辑 First-order logic 事实、对象、关系 真/假/未知 时序逻辑 Temporal logic 事实、对象、关系、时间 真/假/未知 概率逻辑 Probability logic 事实 信度 ∈[0,1]
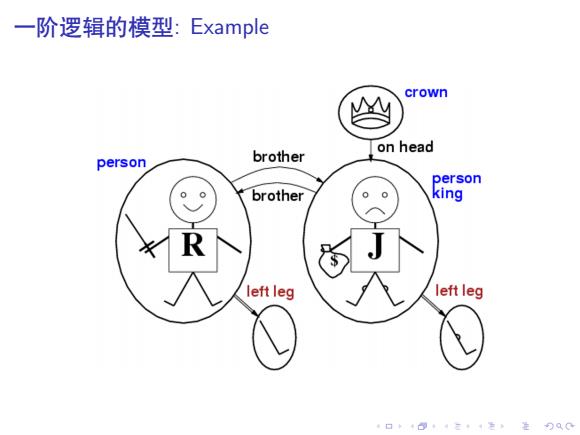
一阶逻辑的模型:Example crown M on head person brother person brother king left leg left leg 口·三,4色,进分Q0
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 一阶逻辑的模型: Example