
Introduction to Compiling CS308 Compiler Theory
Introduction to Compilin g CS308 Compiler Theory 1
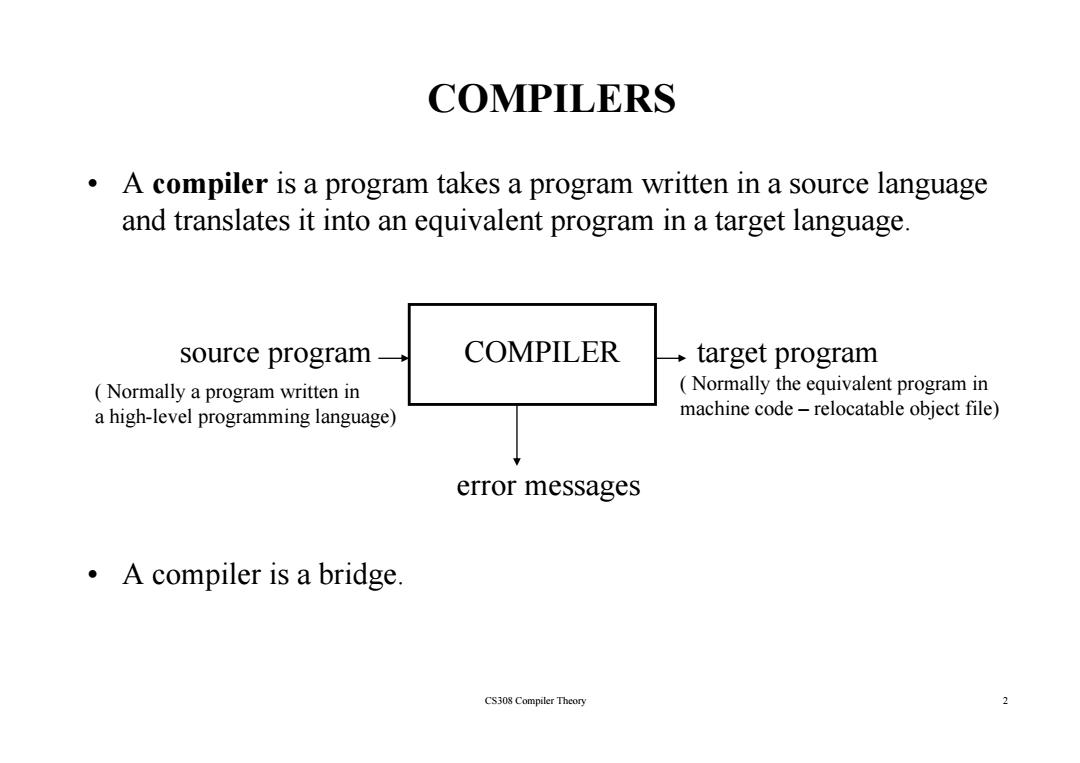
COMPILERS A compiler is a program takes a program written in a source language and translates it into an equivalent program in a target language. source program COMPILER target program Normally a program written in Normally the equivalent program in a high-level programming language) machine code-relocatable object file) error messages A compiler is a bridge. CS308 Compiler Theory 2
COMPILERS • A compiler is a program takes a program written in a source language and l ii i l i l d translates it into an equivalent program in a target language. source program COMPILER target program ( Normally the equivalent program in ( Normally a program written in a high-level programming language) ( Normally the equivalent program in machine code – relocatable object file) error messages • A compiler is a bridge. CS308 Compiler Theory 2

Compiler Architecture In more detail: Intermediate Language Source Front End- Back End- 一Target Language Language language specific machine specific Analysis Synthesis .Separation of Concerns .Retargeting CS308 Compiler Theory 3
Compiler Architecture In more detail: Intermediate Language Front End – language specific Back End – machine specific Source Language Target Language Analysis Synthesis •Separation of Concerns •Retar getin g 3 g g CS308 Compiler Theory

Phases of A Compiler Source LexicalSyntax Semantic Intermediate Code Code Target Program AnalyzerAnalyzer Generator Optimizer GeneratorProgram Each phase transforms the source program from one representation into another representation. They communicate with error handlers. They communicate with the symbol table. CS308 Compiler Theory 4
Phases of A Compiler Lexical Analyzer Semantic Analyzer Syntax Analyzer Intermediate Code Generator Code Optimizer Code Generator Target Program Source Program • Each phase transforms the source program from one representation into another re presentation. • They communicate with error handlers. • They communicate with the symbol table. CS308 Compiler Theory 4
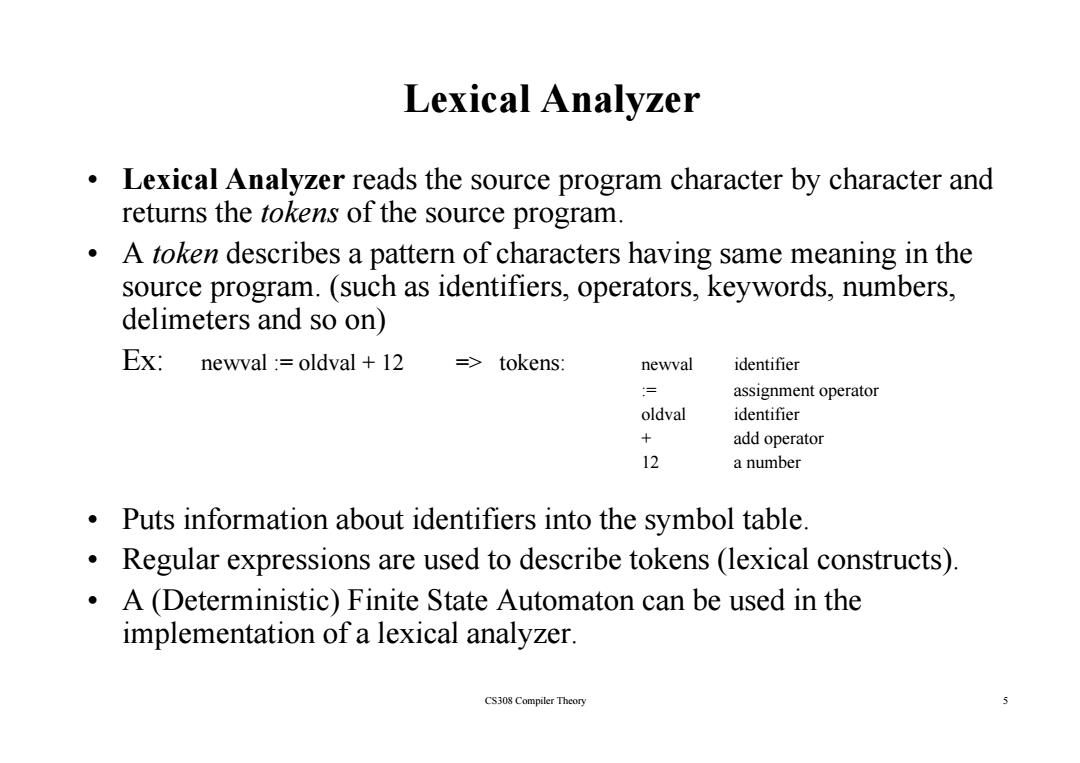
Lexical Analyzer Lexical Analyzer reads the source program character by character and returns the tokens of the source program. A token describes a pattern of characters having same meaning in the source program.(such as identifiers,operators,keywords,numbers, delimeters and so on) Ex: newval :oldval 12 => tokens: newval identifier = assignment operator oldval identifier + add operator 12 a number Puts information about identifiers into the symbol table. Regular expressions are used to describe tokens(lexical constructs). A (Deterministic)Finite State Automaton can be used in the implementation of a lexical analyzer. CS308 Compiler Theory 5
Lexical Analyzer • Lexical Analyzer reads the source program character by character and ret rns the returns the t ko ens of the so rce program of the source program. • A token describes a pattern of characters having same meaning in the source program. (such as identifiers, operators, keywords, numbers, source program. (such as identifiers, operators, keywords, numbers, delimeters and so on) Ex: newval := oldval + 12 => tokens: newval identifier := assignment operator oldval identifier + add operator 12 a number • Puts information about identifiers into the symbol table. • R l i d t d ib t k (l i l t t ) Regular expressions are used to describe tokens (lexical constructs). • A (Deterministic) Finite State Automaton can be used in the implementation of a lexical analyzer. 5 implementation of a lexical analyzer. CS308 Compiler Theory