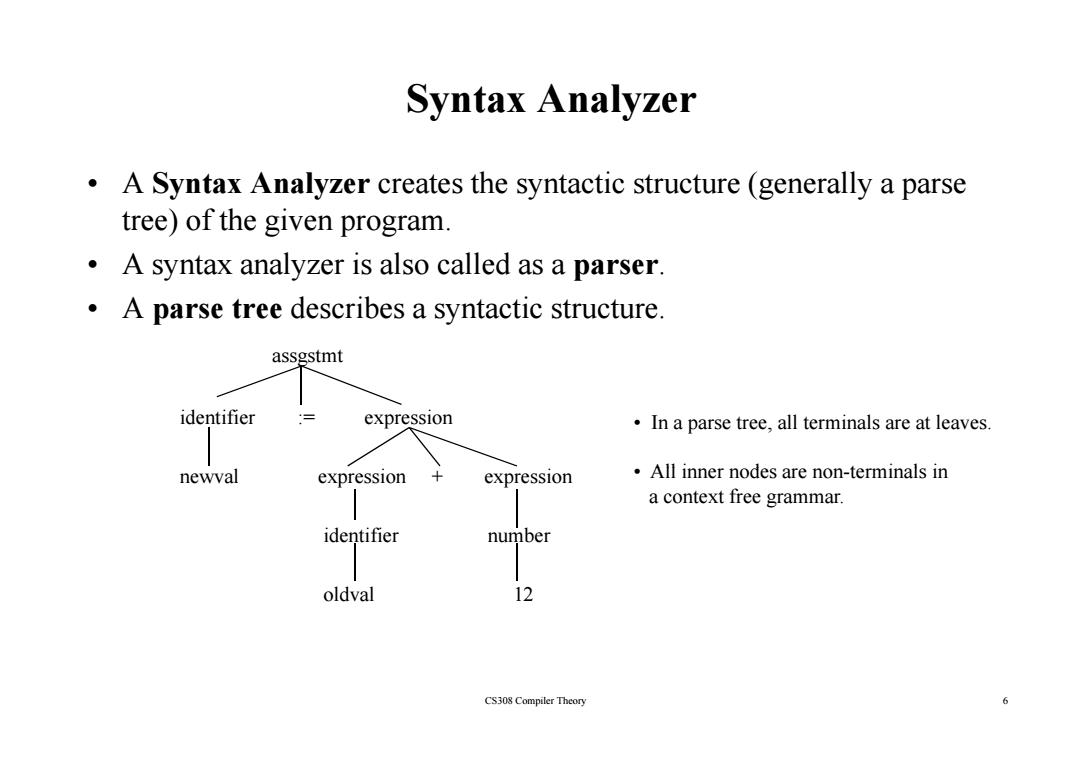
Syntax Analyzer A Syntax Analyzer creates the syntactic structure(generally a parse tree)of the given program. A syntax analyzer is also called as a parser. .A parse tree describes a syntactic structure. assgstmt identifier expression In a parse tree,all terminals are at leaves. newval expression expression All inner nodes are non-terminals in a context free grammar. identifier number oldval 12 CS308 Compiler Theory 6
Syntax Analyzer • A Syntax Analyzer creates the syntactic structure (generally a parse tree) fh i o t e given program. • A syntax analyzer is also called as a parser. • A parse tree describes a syntactic structure. assgstmt identifier := expression • In a parse tree, all terminals are at leaves. newval expression + expression All i d t i li identifier number • All inner nodes are non-terminals in a context free grammar. oldval 12 CS308 Compiler Theory 6

Syntax Analyzer (CFG) The syntax of a language is specified by a context free grammar (CFG). The rules in a CFG are mostly recursive. A syntax analyzer checks whether a given program satisfies the rules implied by a CFG or not. If it satisfies,the syntax analyzer creates a parse tree for the given program. Ex:We use BNF(Backus Naur Form)to specify a CFG assgstmt -identifier :=expression expression -identifier expression -number expression -expression expression CS308 Compiler Theory 7
Syntax Analyzer (CFG) • The syntax of a language is specified by a context free grammar ( ) CFG ). • The rules in a CFG are mostly recursive. • A syntax analyzer checks whether a given program satisfies the rules implied by a CFG or not. – If it satisfies the syntax analyzer creates a parse tree for the given program If it satisfies, the syntax analyzer creates a parse tree for the given program. • Ex: We use BNF (Backus Naur Form) to specify a CFG We use BNF (Backus Naur Form) to specify a CFG assgstmt -> identifier := expression ex pression -> identifie r expression -> number expression -> expression + expression CS308 Compiler Theory 7