
Parameter Passing Mechanisms CS308 Compiler Theory
Parameter Passing Mechanisms CS308 Compiler Theory
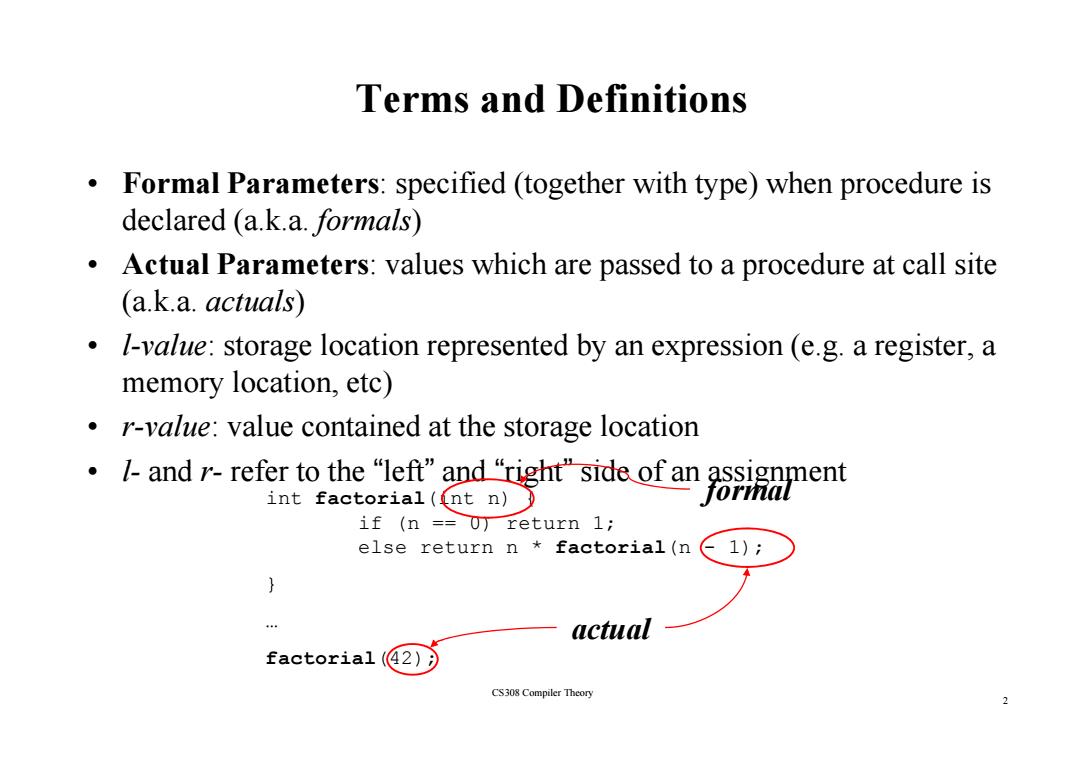
Terms and Definitions Formal Parameters:specified(together with type)when procedure is declared (a.k.a.formals) Actual Parameters:values which are passed to a procedure at call site (a.k.a.actuals) I-value:storage location represented by an expression (e.g.a register,a memory location,etc) r-value:value contained at the storage location ·I-andr-refer to the“left”and“right"side of an assignment int factorial((nt n) formal if (n =0)return 1; else return n factorial(n 1) } actual factorial(42) CS308 Compiler Theory 2
Terms and Definitions • Formal Parameters: specified (together with type) when procedure is d l d( k dec lare d (a. k.a. f l orma ls ) • Actual Parameters: values which are passed to a procedure at call site ( k a. k.a. act l ua ls ) • l-value: storage location represented by an expression (e.g. a register, a memory location etc) memory location, etc) • r-value: value contained at the storage location • l - and r - refer to the refer to the “left ” and “right ” side of an assignment side of an assignment int factorial(int n) { if (n == 0) return 1; else return n * factorial(n - 1); formal } … actual 2 factorial(42); CS308 Compiler Theory
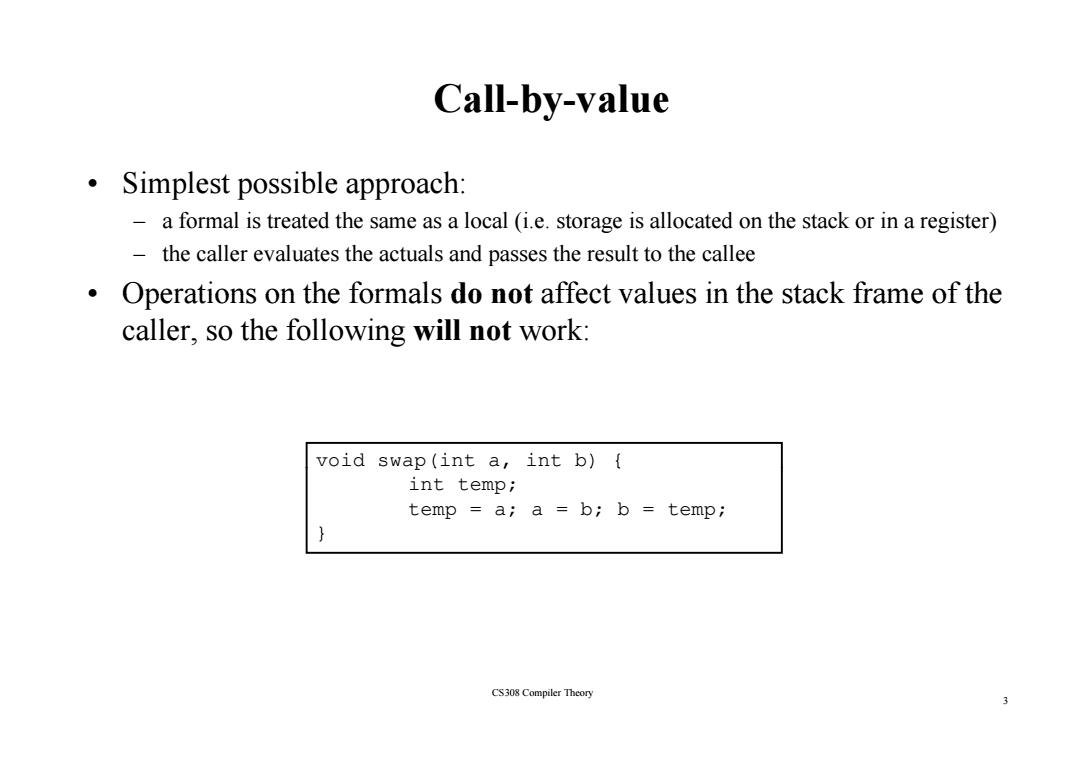
Call-by-value Simplest possible approach: a formal is treated the same as a local (i.e.storage is allocated on the stack or in a register) the caller evaluates the actuals and passes the result to the callee Operations on the formals do not affect values in the stack frame of the caller,so the following will not work: void swap(int a,int b){ int temp; temp a;a =b;b temp; CS308 Compiler Theory 3
Call-by-value • Simplest possible approach: – a formal is treated the same as a local (i.e. storage is allocated on the stack or in a register) – the caller evaluates the actuals and passes the result to the callee • Operations on the formals Operations on the formals do not affect values in the stack frame of the affect values in the stack frame of the caller, so the following will not work: void swap( , ) { int a, int b) { int temp; temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } 3 CS308 Compiler Theory

Call-by-reference Also known as:call-by-address,call-by-location The location of the actual is passed,rather then its value: if the actual is a variable (i.e.corresponds to an assignable location in memory)its address is passed -if the actual is an expression,the expression is evaluated to a temporary location and the address of that location is passed (the compiler will warn you since this is not what you usually want) Operations on the formals do affect the values in the caller,so procedure swap now works: void swap(int&a,int&b){ int temp; temp =a;a =b;b temp; CS308 Compiler Theory 4
Call-by-reference • Also known as: call-by-address, call-by-location • The location of the actual is passed, rather then its value: – if the actual is a variable (i.e. corresponds to an assignable location in memory) its address is passed is passed – if the actual is an expression, the expression is evaluated to a temporary location and the address of that location is passed (the compiler will warn you since this is not what you usually want) usually want) • Operations on the formals do affect the values in the caller, so p ocedu e rocedure sw pa now wo s: rk void swap(int& a, int& b) { int temp; temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } 4 CS308 Compiler Theory

Copy-restore Also known as:copy-in copy-out,value-result Combination of call-by-value and call-by-reference: the actuals are evaluated before the call the expressions having only r-values, the expressions having l-values are passed by reference CS308 Compiler Theory 5
Copy-restore • Also known as: copy-in copy-out, value-result • Combination of call-by-value and call-by-reference: – the actuals are evaluated before the call – the e pressions ha ing onl r the expressions having only r-val es u , – the expressions having l-values are passed by reference 5 CS308 Compiler Theory