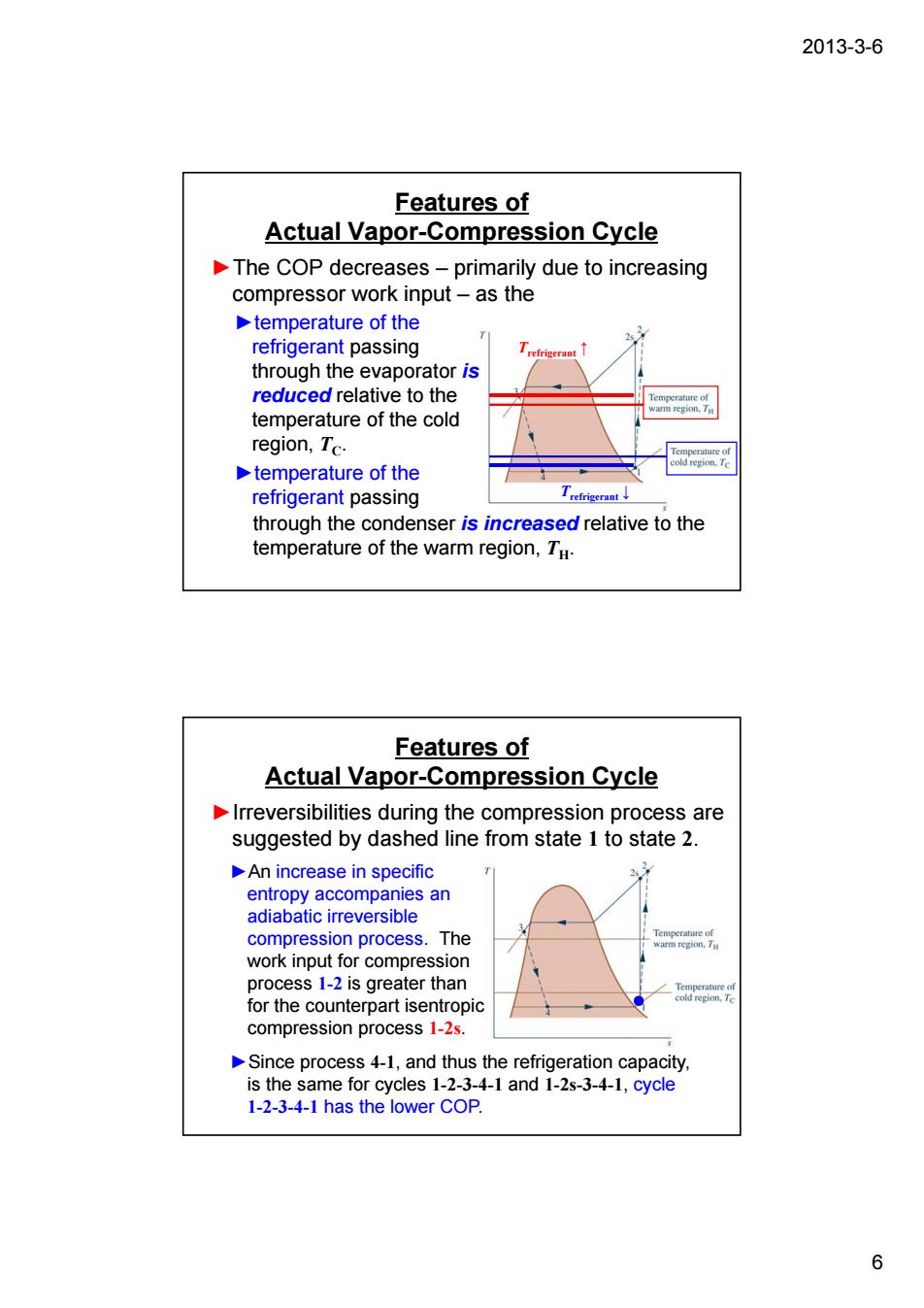
2013-3-6 Features of Actual Vapor-Compression Cycle The COP decreases-primarily due to increasing compressor work input-as the temperature of the refrigerant passing thro ough the ator is reduced relative to the temperature of the cold region,Tc. temperature of the refrigerant passing through the condenser is increased relative to the temperature of the warm region,Tu Features of Actual Vapor-Compression Cycle Irreversibilities during the compression process are suggested by dashed line from state 1 to state 2. An increase in specific ompani compres on process work input r compre ess 1-2 is greater than or the counterpart is compression process 1-2s. Since process 4-1,and thus the refrigeration capacity is the same for cycles 1-2-3 4-1and1-2s-3-4-1,cycle 1-2-3-4-1 has the lower COP 6
2013-3-6 6 Features of Actual Vapor-Compression Cycle ►The COP decreases – primarily due to increasing compressor work input – as the ►temperature of the refrigerant passing through the evaporator is reduced relative to the temperature of the cold region, TC. ►temperature of the refrigerant passing through the condenser is increased relative to the temperature of the warm region, TH. Trefrigerant ↓ Trefrigerant ↑ Features of Actual Vapor-Compression Cycle ►Irreversibilities during the compression process are suggested by dashed line from state 1 to state 2. ►An increase in specific entropy accompanies an adiabatic irreversible compression process. The work input for compression process 1-2 is greater than for the counterpart isentropic compression process 1-2s. ►Since process 4-1, and thus the refrigeration capacity, is the same for cycles 1-2-3-4-1 and 1-2s-3-4-1, cycle 1-2-3-4-1 has the lower COP
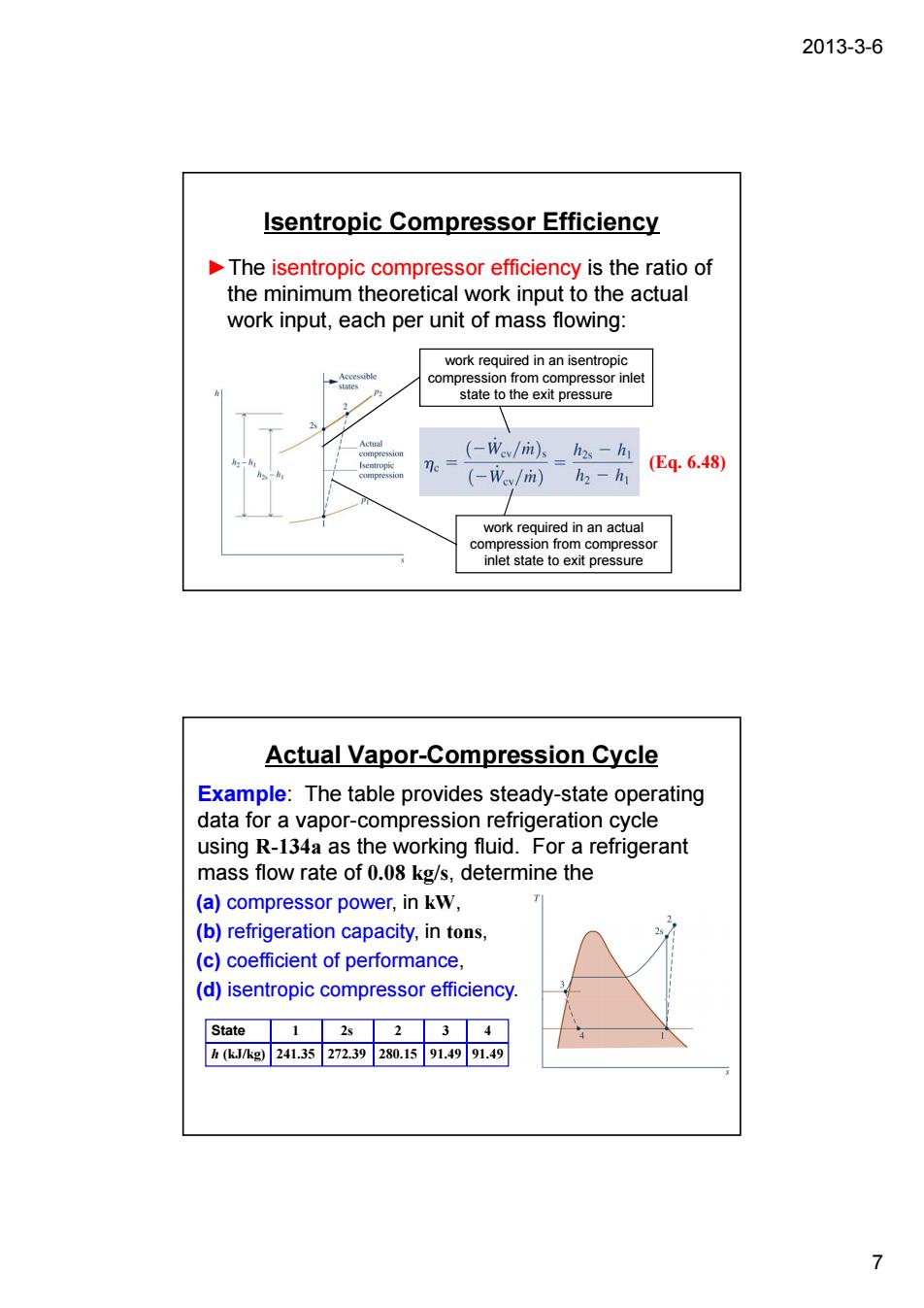
2013-3-6 Isentropic Compressor Efficiency The isentropic compressor efficiency is the ratio of the minimum theoretical work input to the actual work input,each per unit of mass flowing: work required in an isentropic n from r inlet (-Wev/rit)s h2s m (Eq.6.48 (-W/m)h-h red in an actual Actual Vapor-Compression Cycle Example:The table provides steady-state operating data for a vapor-compression refrigeration cycle using R-134a as the working fluid.For a refrigerant mass flow rate of 0.08 kg/s,determine the (a)compressor power,in kW, (b)refrigeration capacity,in tons, (c)coefficient of performance. (d)isentropic compressor efficiency 岛 7
2013-3-6 7 Isentropic Compressor Efficiency ►The isentropic compressor efficiency is the ratio of the minimum theoretical work input to the actual work input, each per unit of mass flowing: (Eq. 6.48) work required in an actual compression from compressor inlet state to exit pressure work required in an isentropic compression from compressor inlet state to the exit pressure Actual Vapor-Compression Cycle (a) compressor power, in kW, (b) refrigeration capacity, in tons, (c) coefficient of performance, (d) isentropic compressor efficiency. Example: The table provides steady-state operating data for a vapor-compression refrigeration cycle using R-134a as the working fluid. For a refrigerant mass flow rate of 0.08 kg/s, determine the State h (kJ/kg) 1 241.35 2s 272.39 2 280.15 3 91.49 4 91.49