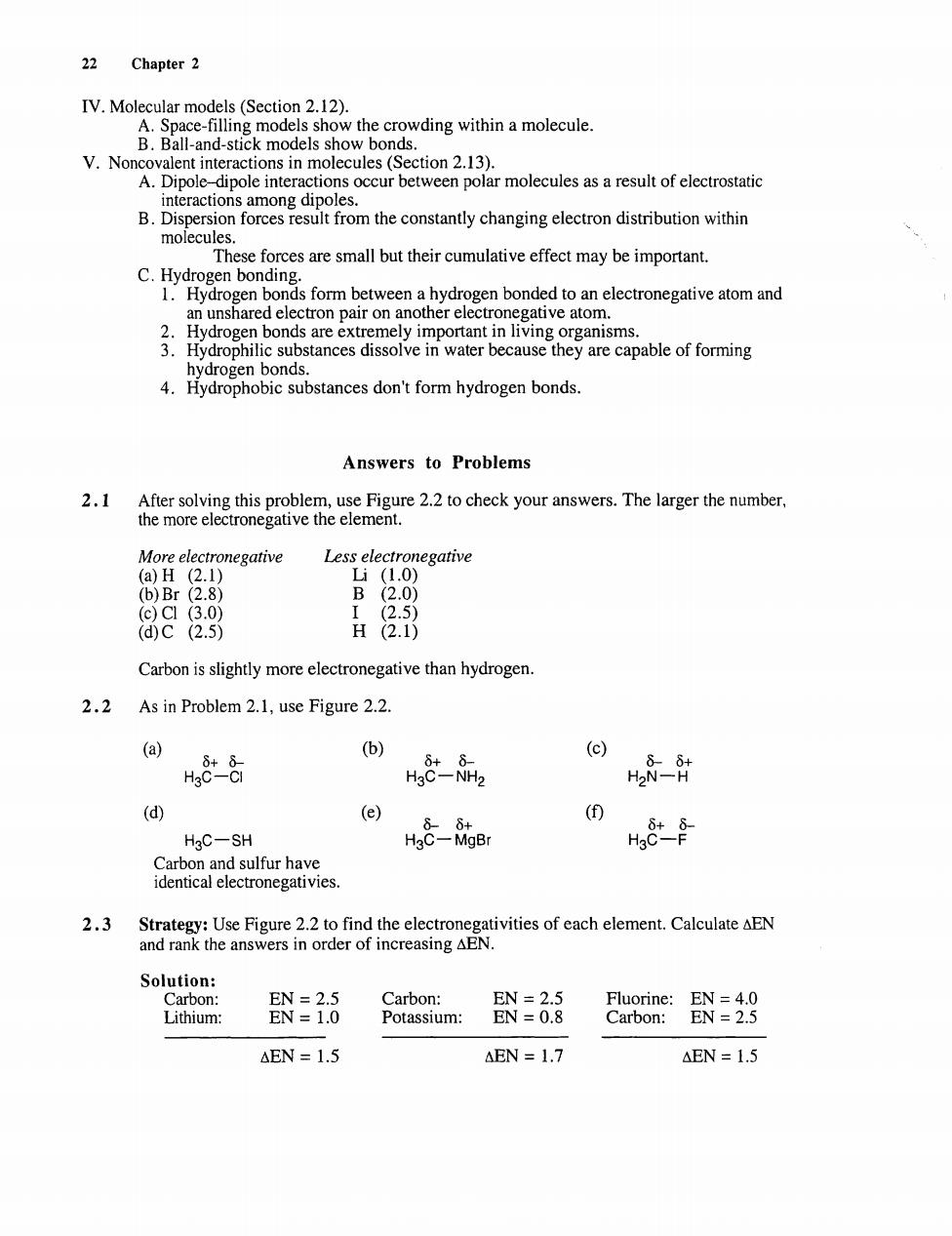
22 Chapter 2 IV.Molecular models(Section 2.12). A.Space-filling mod s show the crowding within a molecule. nd-sti K m V.No i i0n2.13) A.Dipole dipole interactions occur between polar molecules as a result of electrostatic nteraction B. ion forcesesu from the constantly changing electron distribution within These forces are small but their cumulative effect may be important. C.Hydrogen bonding 1.Hydrogen bonds form between a hydrogen bonded to an electronegative atom and tron pair on another ele hydrogen bonds. 4.Hydrophobic substances don't form hydrogen bonds. Answers to Problems 2.1 Mor electronegative Less electronegative 2.1 .8 B ac2.5 H2.1) Carbon is slightly more electronegative than hydrogen 2.2 As in Problem 2.1,use Figure 2.2. (b) H,88 k82 ⊙ 8计 (e) HgC-SH ho8-防e H8t手 Carbon and sulfur have identical electronegativies. 2.3 Strategy:Use Figure 2.2 to find the electronegativities of each element.Calculate AEN and rank the answers in order of increasing AeN EN=2.5 Carbon: EN=2.5 Lithium: EN=1.0 Potassium: EN=0.8 Caroone EN AEN =1.5 AEN 1.7 AEN=1.5
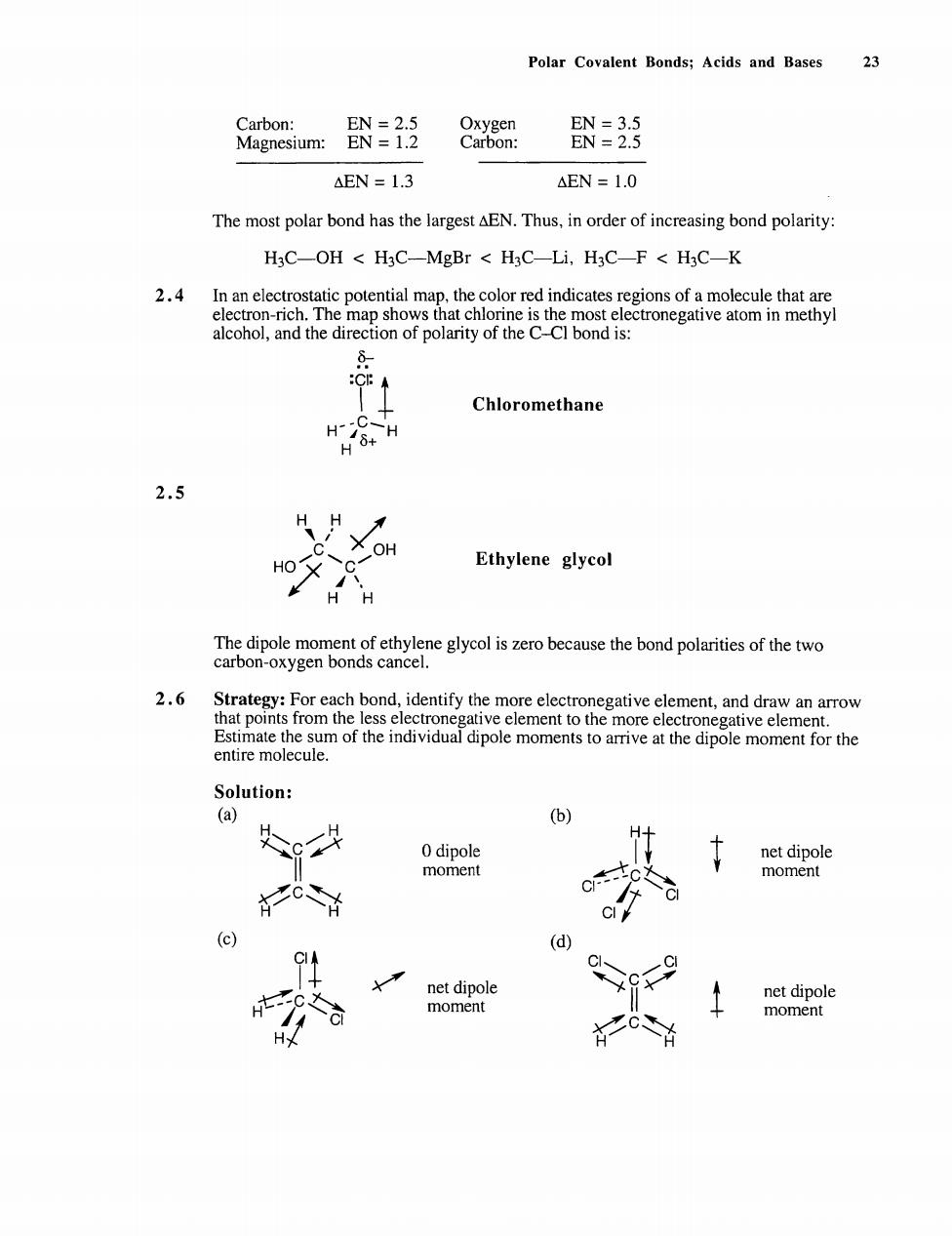
Polar Covalent Bonds;Acids and Bases 23 Carbon: Magnesium: 删 删:器 AEN 1.3 AEN=1.0 The most polar bond has the largest AEN.Thus,in order of increasing bond polarity: HC-OH HC-MgBr HaC-Li,HaC-F HC-K 2.4 alcohol,and the direction of polarity of the C-Cl bond is: 0- Chloromethane 2.5 HO Ethylene glycol The dinole t of ethylene glycol is zero because the bond polarities of the two caron-ygcn bonds cancel. 2.6 Strategy:For each bond,identify the more electronegative element,and draw an arrow entire molecule. Solution: (b) 0 dipole net dipole moment moment (c) (d) xc

24 Chapter 2 2.7 Use the formula in Section 2.3 to confirm the formal charges shown for nitromethane. :0 Nitromethane Fomal chage (F)eo 2 L electrons :FC=5-号-0=+1 Foroxygen:FC=6-6=-1 2.8 Strategy:To find the formal charge of an atom in a molecule,follow these two steps: (1)Draw an electron-dot structure of the molecule. (2)Use the for henumer of ondingandro Fomal charge (F)of bondng clectronsn 2 L electrons Solution 12 H2C=N=N:H:C::N:N: For carbon:FC=40 For nitrogen 1:FC 5-3-0=+1 For nitogen 2:FC5 cific eler those electrons in lone pairs

Polar Covalent Bonds;Acids and Bases 25 HgC-C=N-0:H:C:C::N:0: H For carbon 1:FC=4-0 For carbon 2:FC=4- For nitrogen FC=5+1 For oxygen:FC=6-2-6=-1 HaC-NC:=HiC:N:::C: H For carbon 1:FC=40 For carbon 2:FC=4--2=-1 For nitrogen:FC=5-+ 2.9 electrons- 12 Methyl phosphate For oxygen 1:FC =6--4=0 For oxygen 2:FC=6--0 For oxygen 3:FC=6-2-6=-1 Foroxygen 4:FC6 Oxygen atoms 3 and 4 each have a formal charge of-1
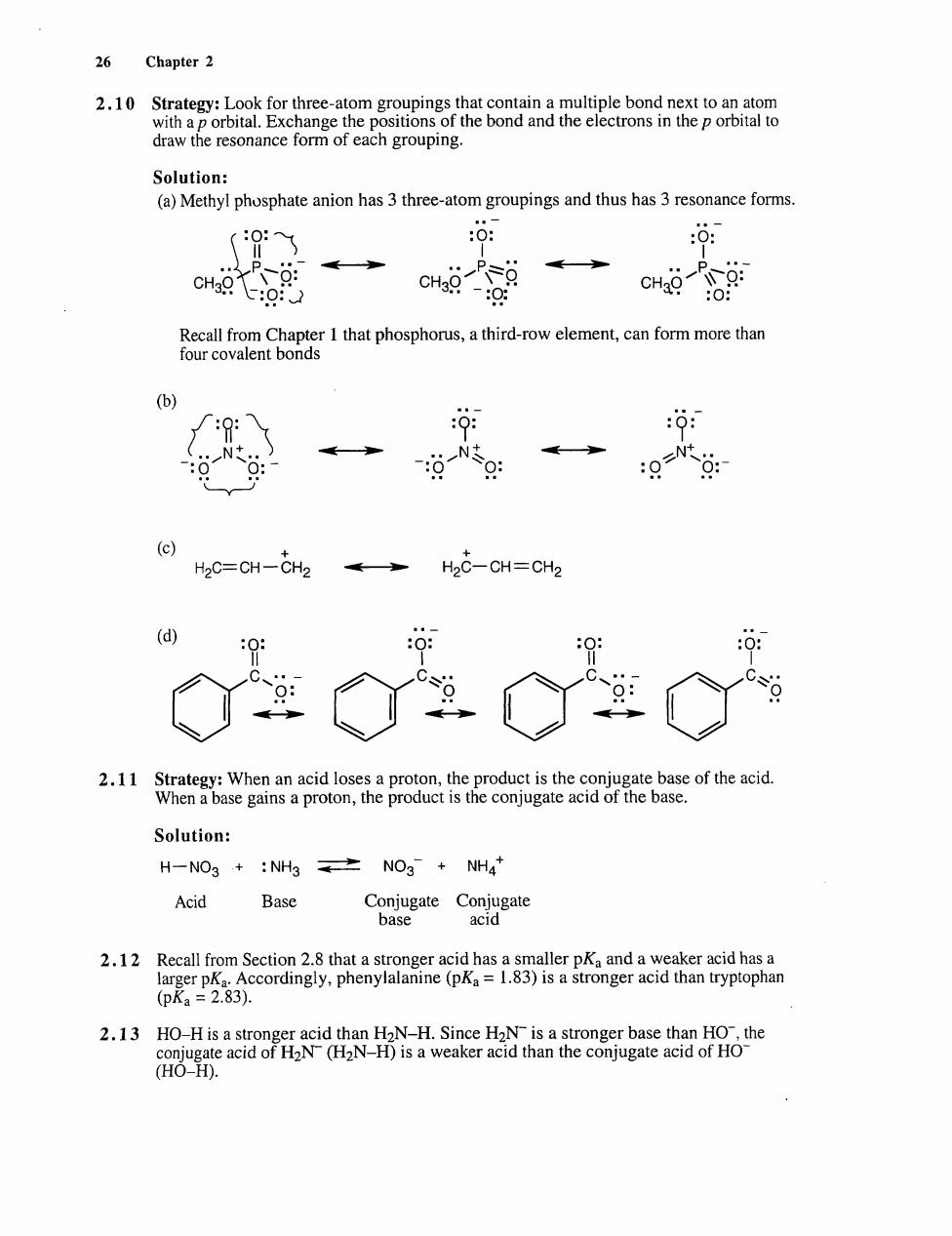
26 Chapter 2 Solution: (a)Methyl phosphate anion has 3 three-atom groupings and thus has 3 resonance forms. 0: o: c的 CH -ctaaCboREr1thlphoepionus,ahindowcemeL,canfommacthan (b) Nt. H2C=CH-CH2 H2C-CH=CH2 d 2.11 Strategy:When an acid loses a proton,the product is the conjugate base of the acid. When a base gains a proton,the product is the conjugate acid of the base. Solution: H-NO3+:NH3NOg+NH4 Acid Base CoC 2.12 Recall from Section 2.8 that a stronger acid has a smaller pKa and a weaker acid has a Accordingly,phenylalanine(pKa=1.83)is a stronger acid than tryptophan (pRa=2.83) (HO-H)