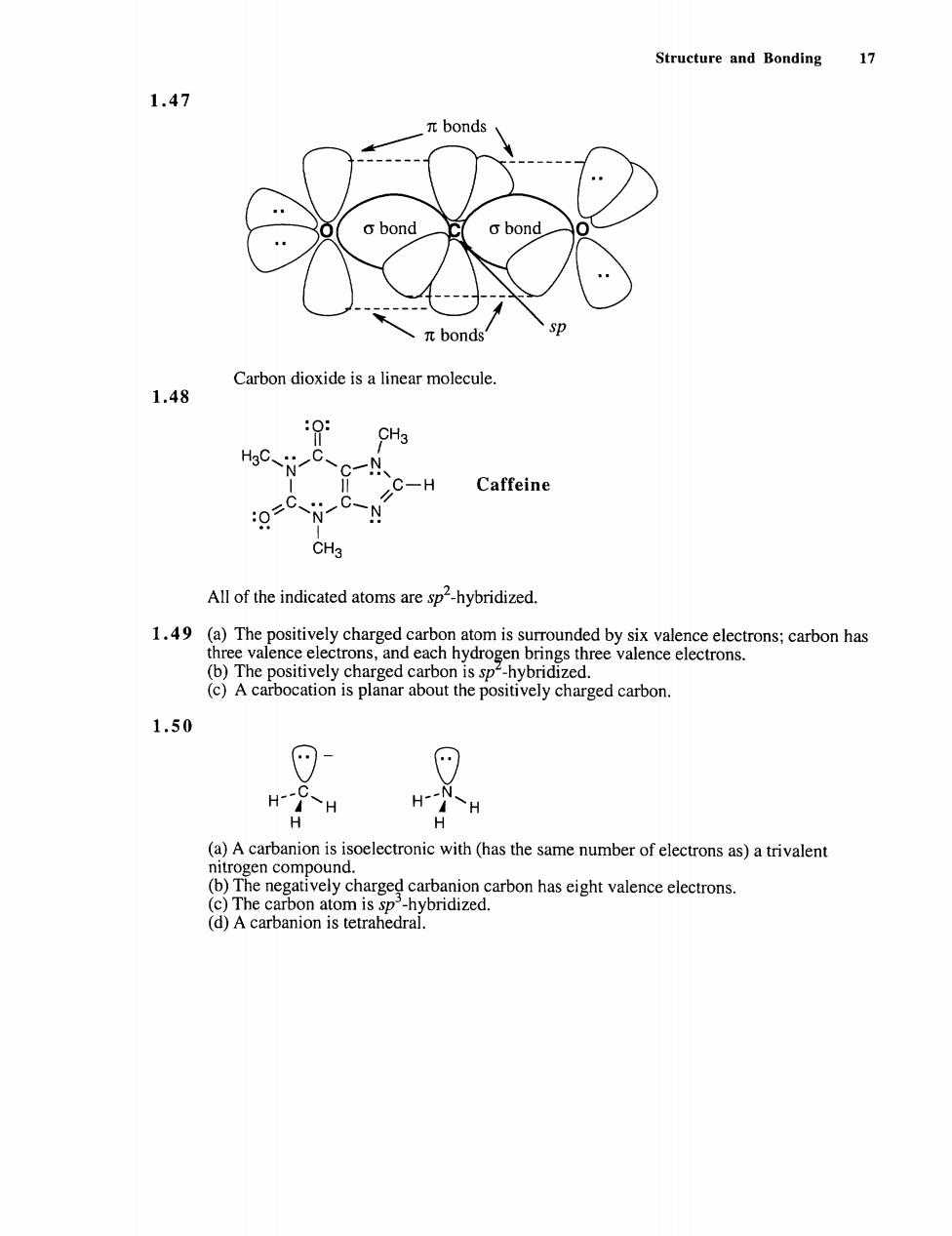
Structure and Bonding 17 1.47 πbonds o bond πbonds Carbon dioxide is a linear molecule. 1.48 C-H Caffeine C N-C-N CH3 All of the indicated atoms are sp2-hybridized. 1.49(a)The )The positively charged (c)A carbocation is planar about the positively charged carbon. 1.50 (a)A carbanion is isoelectronic with(has the same number of electrons as)a trivalent (d)A carbanion is tetrahedral
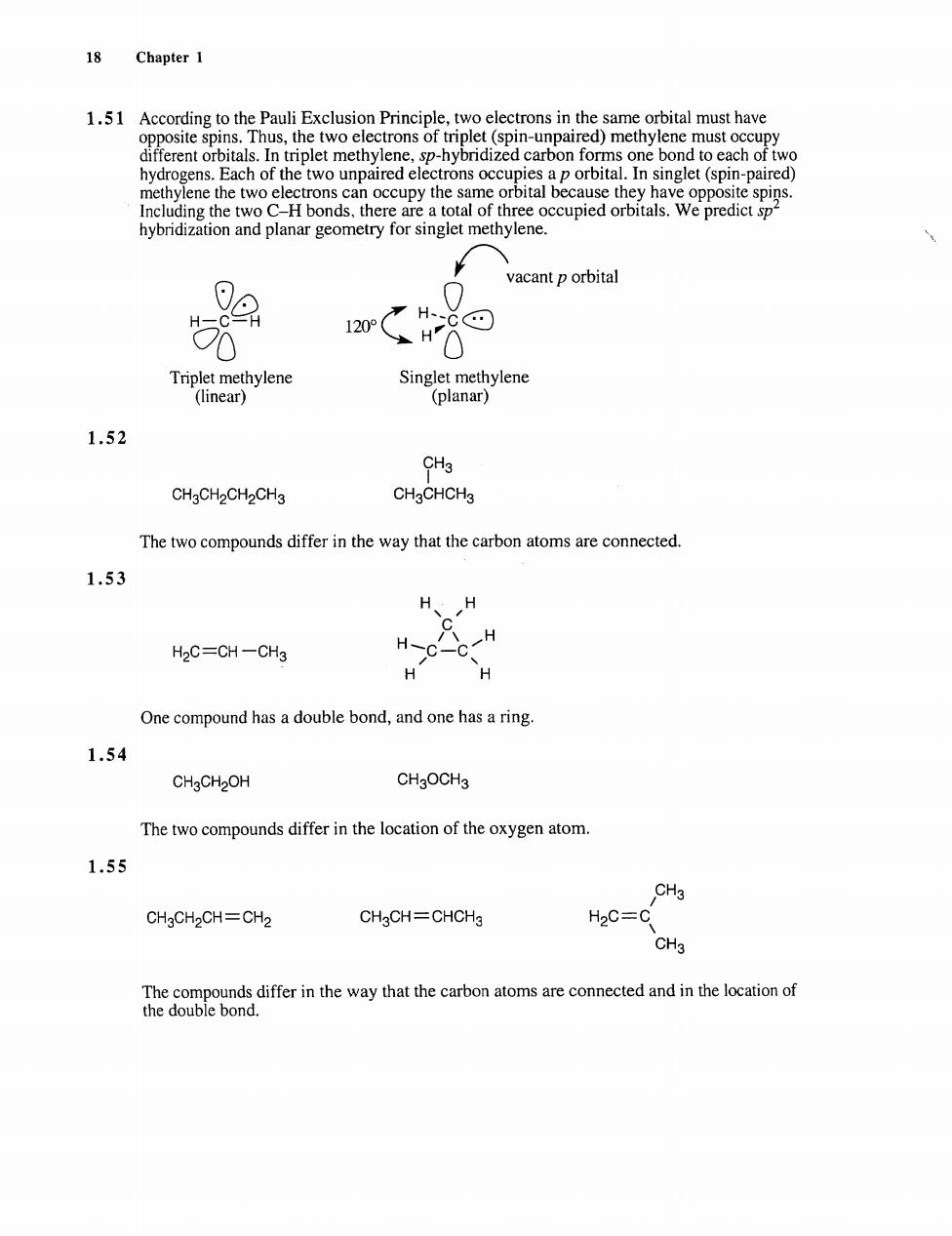
8 Chapter 1 1.51 According to the Pauli Exclusion Principle,two electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins. different OrsTthe two electrons ot tpedd carbon forms one bond to each of two triplet methylene.sp-hyn the two CH bonds.there are a total of three occupied orbitals.We predicts hybridization and planar geometry for singlet methylene vacant p orbital m Triplet methylene (linear) 1.52 CH3 CHgCH2CH2CH3 CHgCHCH3 The two compounds differ in the way that the carbon atoms are connected 1.53 H、H H2C=CH-CH3 H C C H H H One compound has a double bond,and one has a ring 1.54 CH3CH2OH CHgOCH3 The two compounds differ in the location of the oxygen atom. 1.55 CH3 CHgCH2CH=CH2 CH3CH=CHCH H2C=C CH3
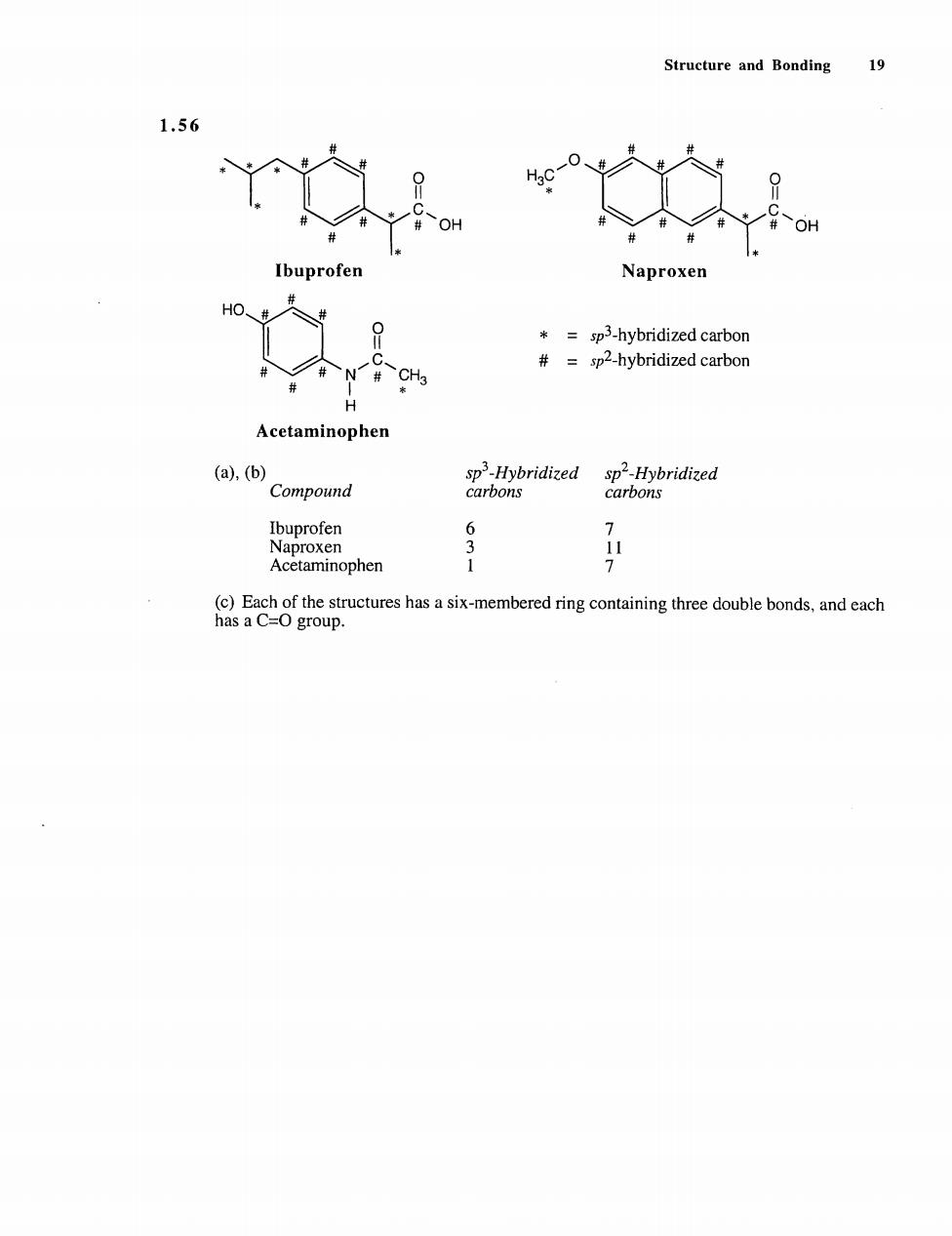
Structure and Bonding 19 1.56 Ibuprofen Naproxen *=sp3-hybridized carbon #=sp2-hybridized carbon H Acetaminophen (a,(b) spHybridized sp2-Hybridized Compound carbons carbons 7 Acetaminophen f520fgpnctehsacnba时igcoainighedobebank.andeah

Chapter 2-Polar Covalent Bonds;Acids and Bases Chapter Outline I.Polar covalent bonds(Sections 2.1-2.3). A.Elec y (Section 2.D. 1.hoomodetotally ionicad omere totally covalent,most chemical bonds are polar covalent bonds. In these 2.Bond eme electrons are attracted to one atom more than to the other atom. electronegative than elements on the left side Carbon has an EN of 2.5. Blements with 2.5 are more electronegative than carbon sean ca o pr et the polarity of a bond f AEN <0.4,a bond is no polar covalent If AEN S and 0,a bond is polar covalent d.The symbols+a nd are sed to indicate I partial charges e. A crossed arrow is used to indicate bond The ta I of the a sta maps are also use 5.nnducuve effect isn to polarize a bond. B.Dipole moment(Section 2.2). moment is the measure of a molecule's overall polarity. -oxr.w d in 3.Dipole moment can be used to measure charg e separation . Water and an monia have large values of D:methane and ethane have D=0. C. harge (FC)indicates electron"ownership"in a molecule 2 (FC)=#of val 3.Molecules that are neutral overall but that have+and-charges on individual atoms are dipola II.Resonance(Sections 2.4 -2.6 1.Son n,fo (Sce 02 le) an be drawn as two(or more)different electron-dot structures. hese structures are called reso ure is called a te ate between the structures nance 2.Resonance structures differ only in the placement of and nonbonding electrons All atoms occupy the same positions. 3.Resonance is an important concept in organic chemistry

Polar Covalent Bonds;Acids and Bases 21 2.Re iffe ry.not real. nt of their n or nonbonding electrons. row is used to indicate the mover ent of electrons.not atoms 3.Different resonance forms of a molecule don't have to be equivalent. If resonance forms are e nonequivalent,the st ructure of the actual molecule 4.Rest ene form st he valid Lewis structure es and obey normal rules of valency 5.The resonance hybrid is more stable than any individual resonance form. C.A useful technique for drawing resonance forms(Se ct10n2.6 1.Any three-atom grouping with a multiple bond adjacent to a nonbonding porbita 2.0 atom in theg ng has a lone electron pair.a vacant orbital or a single lectron. -atom pieces,resonance forms can be generated. III.Acids .Bro red-D definitior A Bronsted-Lowry acid donates an Hion:a Bronsted-Lowry base accepts H'. 2.The product that results when a that resu hen an a the eeoe te B. 含 4.0st4 6 A strong acid has a small pKa,and a weak acid has a large pKa c.Ihe te base of a strong acid is a weak base,and the conjugate base of a cid h stro a.An acid with a low pka reacts v gate base of an acid with a high 6.ph words,the products of an acid-base reaction are more stable than the 6.Organic acids and organic bases (Section 2.10). a. There are two main types of organic acids: Is that contain hydroge ed to oxygen. b.The n on nded to the car on ne O group. ogen C. and bases(Section 2.11). ron pair a. acid pts ither a vacant low-energy orbital or a polar bond to hydroger b.Examples include metal cations,halogen acids,Group 3 compounds and s ha on-metal compounds Most oxygen-and nitre ic eo unds are Lewis bases Many organic Lewis bases have more than one basic site. 3. edow shows the movement of co froma Lewis base toa Lewis