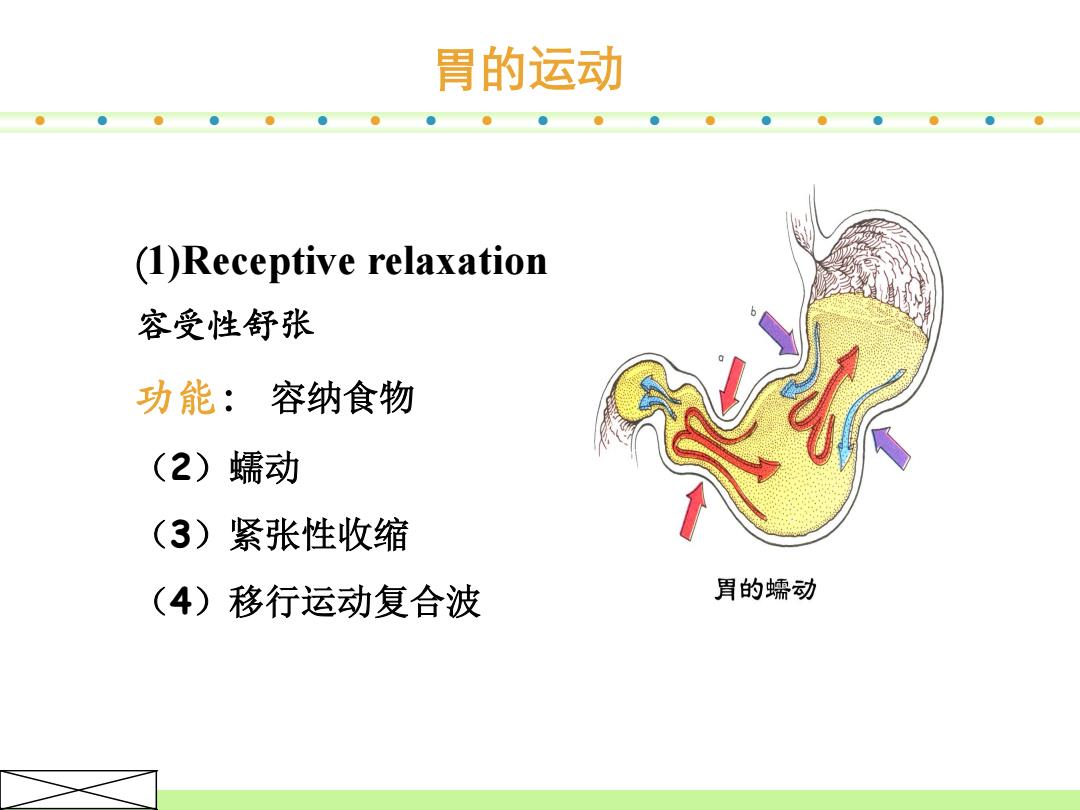
胃的运动 (1)Receptive relaxation 容受性舒张 功能:容纳食物 (2)蠕动 (3)紧张性收缩 (4)移行运动复合波 胃的蠕动
(1)Receptive relaxation 容受性舒张 功能: 容纳食物 (2)蠕动 (3)紧张性收缩 (4)移行运动复合波 胃的运动

思考:为什么吃油腻的食物不易咸到饥饿?
思考:为什么吃油腻的食物不易感到饥饿?
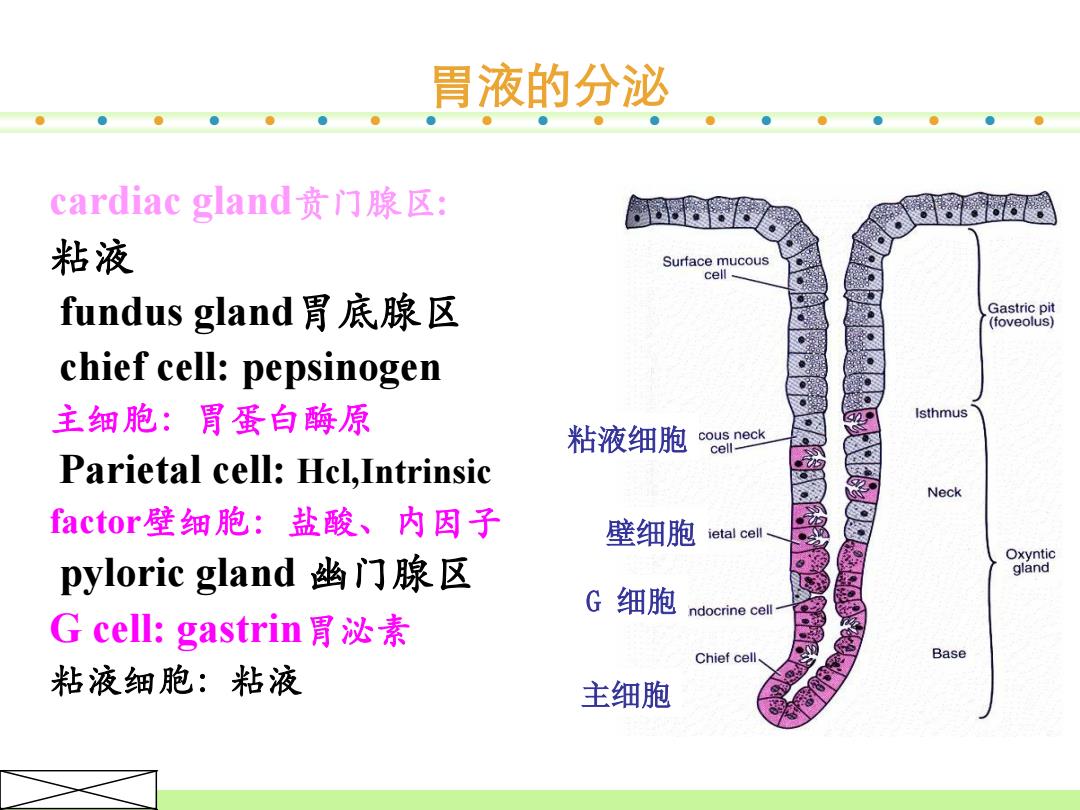
胃液的分泌 cardiac gland贲门腺区: 粘液 Surface mucous cell fundus gland胃底腺区 Gastric pit (foveolus) chief cell:pepsinogen 主细胞:胃蛋白酶原 Isthmus 粘液细胞 cous neck cell- Parietal cell:Hcl,Intrinsic Neck factor.壁细胞:盐酸、内因子 壁细胞 ietal cell- pyloric gland幽门腺区 Oxyntic gland G细胞 ndocrine cell Gcel:gastrin胃泌素 Chief cell Base 粘液细胞:粘液 主细胞
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● cardiac gland贲门腺区 : 粘液 fundus gland胃底腺区 chief cell: pepsinogen 主细胞:胃蛋白酶原 Parietal cell: Hcl,Intrinsic factor壁细胞:盐酸、内因子 pyloric gland 幽门腺区 G cell: gastrin胃泌素 粘液细胞:粘液 主细胞 粘液细胞 壁细胞 G 细胞 胃液的分泌

HC分泌的机制 Hydrochloric Acid Production by Parietal w Cells in the Gastric Glands of the Stomach 00 4 Play Pause Audio Text Hydrochloric acid is produced in parietal cells through a complex series of reactions. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● HCl分泌的机制
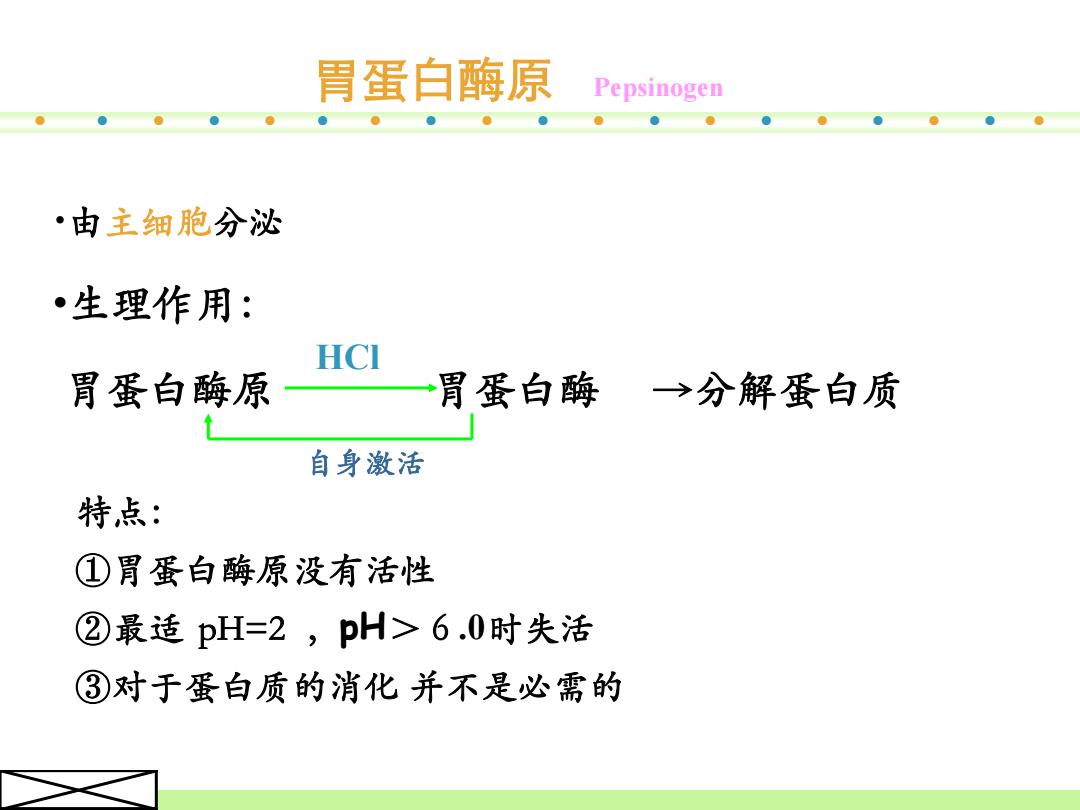
胃蛋白酶原 Pepsinogen ·由主细胞分泌 生理作用: HCI 胃蛋白酶原 胃蛋白酶 →分解蛋白质 自身激活 特点: ①胃蛋白酶原没有活性 ②最适pH=2,pH>6.0时失活 ③对于蛋白质的消化并不是必需的
•由主细胞分泌 •生理作用: 胃蛋白酶原 胃蛋白酶 →分解蛋白质 HCl 特点: ①胃蛋白酶原没有活性 ②最适 pH=2 ,pH>6.0时失活 ③对于蛋白质的消化 并不是必需的 自身激活 胃蛋白酶原 Pepsinogen