The t Test(cont) Knowing the sampling distribution for the standardized estimator allows us to carry out hypothesis tests Start with a null hypothesis ◆For example,Ho:BO If accept null,then fail to reject that x,has no effect on y,controlling for other x's Econometrics 15-Zhuxi@SJTU 11
Econometrics 15 - Zhuxi@SJTU 11 The t Test (cont) Knowing the sampling distribution for the standardized estimator allows us to carry out hypothesis tests Start with a null hypothesis For example, H0 : bj=0 If accept null, then fail to reject that xj has no effect on y, controlling for other x’s

The t Test(cont) To perform our test,we first need to form he1 statistic for月:Ta=e(a厂 We will then use our t statistic along with a rejection rule to determine whether to accept the null hypothesis,Ho Econometrics 15-Zhuxi@SJTU 12
Econometrics 15 - Zhuxi@SJTU 12 The t Test (cont) j ˆ 0 To perform our test, we first need to form ˆ ˆ the statistic for : . ˆ We will then use our statistic along with a rejection rule to determine whether to accept the null hypothesis, H j j j t T se t b b b b

t Test:One-Sided Alternatives Besides our null,Ho,we need an alternative hypothesis,H,and a significance level H may be one-sided,or two-sided ◆Hi:B>0andH:阝<0 are one-sided ◆Hi:B≠0 is a two-sided alternative If we want to have only a 5%probability of rejecting Ho if it is really true,then we say our significance level is 5%(Type I error <5%) Econometrics 15-Zhuxi@SJTU 13
Econometrics 15 - Zhuxi@SJTU 13 t Test: One-Sided Alternatives Besides our null, H0 , we need an alternative hypothesis, H1 , and a significance level H1 may be one-sided, or two-sided H1 : bj > 0 and H1 : bj < 0 are one-sided H1 : bj 0 is a two-sided alternative If we want to have only a 5% probability of rejecting H0 if it is really true, then we say our significance level is 5% (Type I error < 5%)

One-Sided Alternatives (cont) Having picked a significance level,a,we look up the (1-a)th percentile in a t distribution with n-k -1 df and call this c,the critical value We can reject the null hypothesis if the t statistic is greater than the critical value If the t statistic is less than the critical value then we“fail to reject'the null,.not“accept'”the null, Econometrics 15-Zhuxi@SJTU 14
Econometrics 15 - Zhuxi@SJTU 14 One-Sided Alternatives (cont) Having picked a significance level, , we look up the (1 – ) th percentile in a t distribution with n – k – 1 df and call this c, the critical value We can reject the null hypothesis if the t statistic is greater than the critical value If the t statistic is less than the critical value then we “fail to reject” the null, not “accept” the null
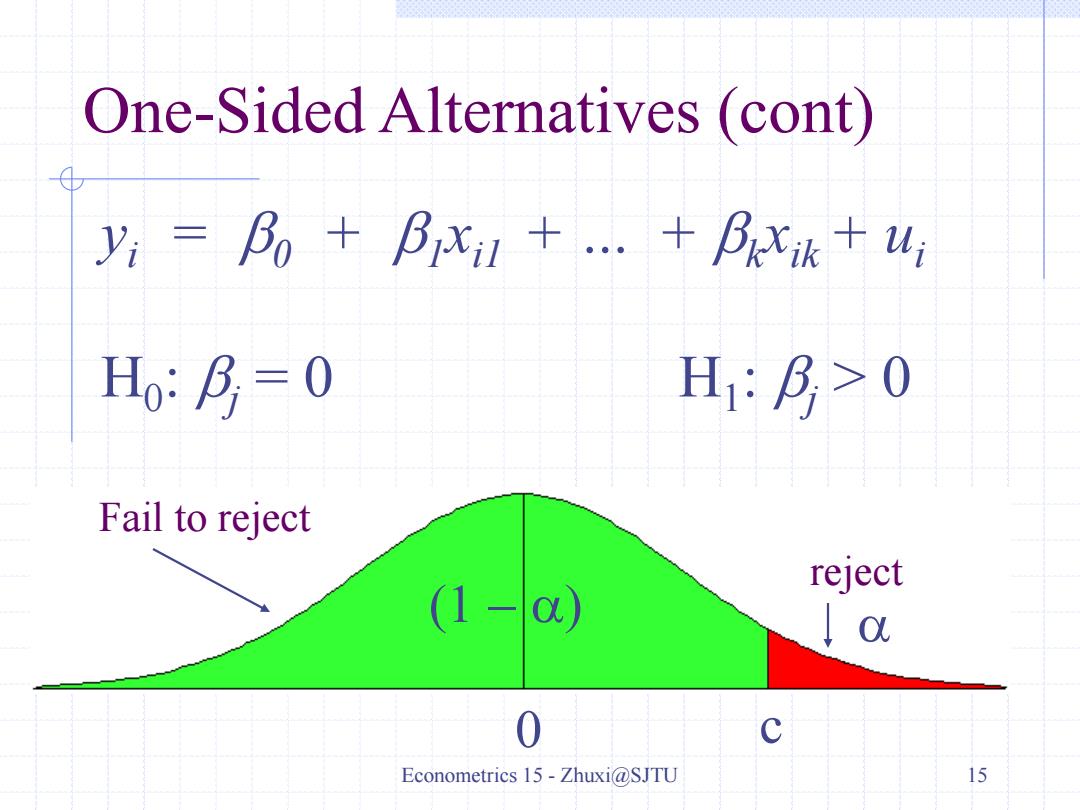
One-Sided Alternatives (cont) yi=Bo+Bxi+.+Bxik+ui Ho:月=0 H:月>0 Fail to reject reject (1-) ↓0 Econometrics 15-Zhuxi@SJTU 15
Econometrics 15 - Zhuxi@SJTU 15 yi = b0 + b1 xi1 + … + bk xik + ui H0 : bj = 0 H1 : bj > 0 0 c 1 One-Sided Alternatives (cont) Fail to reject reject