One-sided ys Two-sided Because the t distribution is symmetric, testing H:B<0 is straightforward.The critical value is just the negative of before We can reject the null if the t statistic <-c, and if the t statistic than-c then we fail to reject the null For a two-sided test.we set the critical value based on a/2 and reject H:阝≠Oif the absolute value of the t statistic >c Econometrics 15-Zhuxi@SJTU 16
Econometrics 15 - Zhuxi@SJTU 16 One-sided vs Two-sided Because the t distribution is symmetric, testing H1 : bj < 0 is straightforward. The critical value is just the negative of before We can reject the null if the t statistic < –c, and if the t statistic > than –c then we fail to reject the null For a two-sided test, we set the critical value based on /2 and reject H1 : bj 0 if the absolute value of the t statistic > c
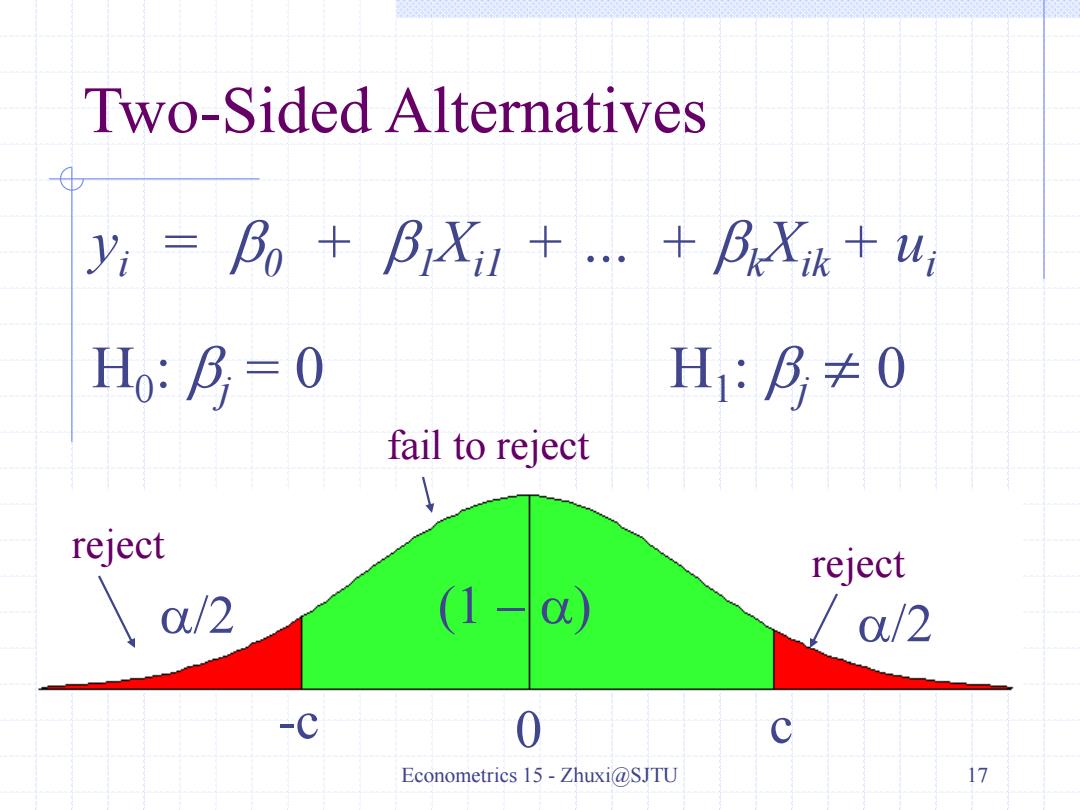
Two-Sided Alternatives yi=Bo +BXi+..+BXik+ui Ho:月=0 H:月≠0 fail to reject reject reject \0/2 (1-o) 0/2 Econometrics 15-Zhuxi@SJTU 17
Econometrics 15 - Zhuxi@SJTU 17 yi = b0 + b1Xi1 + … + bkXik + ui H0 : bj = 0 H1 : bj 0 0 c /2 1 -c /2 Two-Sided Alternatives reject reject fail to reject