
三、病理(Pathology) Normal VS > Chest wall deformity:Invagination of the lower end of the sternum and the connected ribs,rib cartilages.The anteroposterior diameter of the thorax becomes shorter. >Displacement and deformation of the thoracic viscera
三、病理(Pathology) ➢ Chest wall deformity: Invagination of the lower end of the sternum and the connected ribs, rib cartilages.The anteroposterior diameter of the thorax becomesshorter. ➢ Displacement and deformation of the thoracic viscera
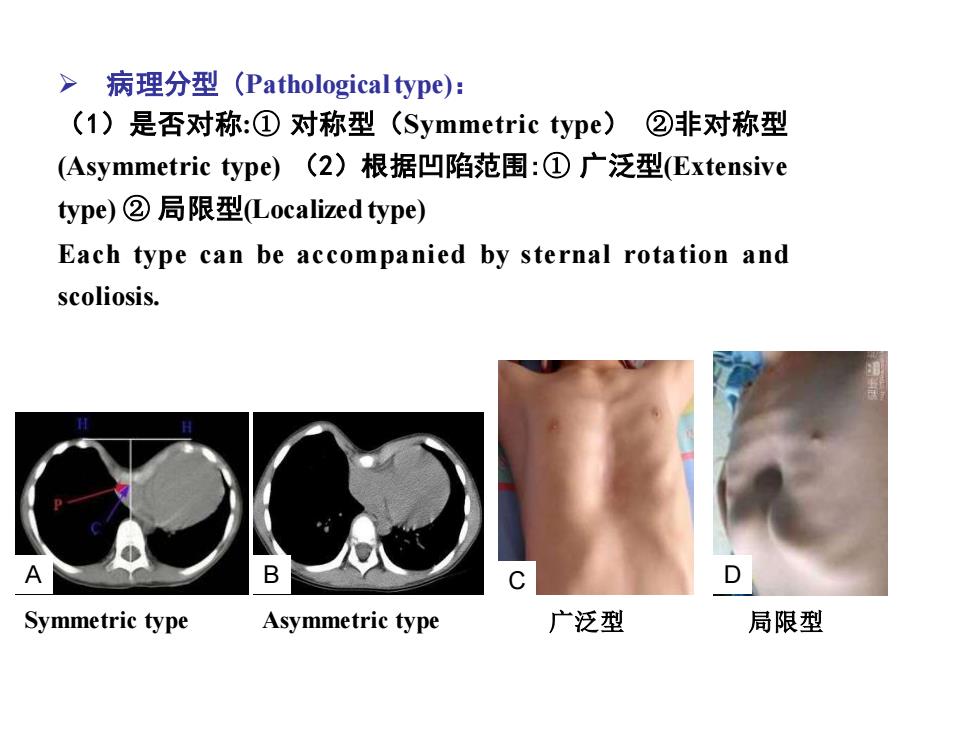
> 病理分型(Pathological type): (1)是否对称:①对称型(Symmetric type).②非对称型 (Asymmetric type))(2)根据凹陷范围:①广泛型(Extensive ype)②局限型Localized type) Each type can be accompanied by sternal rotation and scoliosis. A D Symmetric type Asymmetric type 广泛型 局限型
➢ 病理分型 (Pathological type): (1)是否对称:① 对称型(Symmetric type) ②非对称型 (Asymmetric type) (2)根据凹陷范围:① 广泛型(Extensive type) ② 局限型(Localized type) Each type can be accompanied by sternal rotation and scoliosis. Symmetric type Asymmetric type 广泛型 局限型 A B C D

四、病理生理(Pathophysiology) (一)肺功能损害(Lung function damage) >通气功能损害(Ventilatory impairment) >通气储备功能降低(Decreased ventilatory reserve function) (二)心功能损害(Cardiac dysfunction) >舒张功能受损(Impaired diastolic function) >瓣膜及传导功能异常(Valve and conduction dysfunction) >心脏储备功能降低(Decreased cardiac reserve function)
(一)肺功能损害(Lung function damage) ➢ 通气功能损害 (Ventilatory impairment) ➢ 通气储备功能降低(Decreasedventilatory reserve function) (二)心功能损害(Cardiac dysfunction) ➢ 舒张功能受损(Impaired diastolic function) ➢ 瓣膜及传导功能异常(Valveand conduction dysfunction) ➢心脏储备功能降低(Decreasedcardiac reserve function) 四、病理生理(Pathophysiology)

五、临床表现(Clinical maifestation) (一)症状(Symptoms) 1.The hallmark of the condition is a sunken appearance of the sternum.The most common form is a cup-shaped concavity,involving the lower end of the sternum and costal cartilages.It can either be present at birth or not develop until puberty. Patients may also experience chest and back pain,which is usually of musculoskeletal origin. The symptoms also include recurrent respiratory infections,wheezing or coughing
五、临床表现(Clinical manifestation) (一)症状(Symptoms) 1. The hallmark of the condition is a sunken appearance of the sternum. The most common form is a cup-shaped concavity, involving the lower end of the sternum and costal cartilages. It can either be present at birth or not develop until puberty. Patients may also experience chest and back pain, which is usually of musculoskeletal origin. The symptoms also include recurrent respiratory infections, wheezing or coughing

Pectus excavatum is a progressive deformity.This patient progressed from mild to severe asymmetric before puberty.At the time of puberty, the chest becomes more rigid and patients start to exhibit cardiopulmonary symptoms.(漏斗胸畸形常随年龄的增长而逐渐加重。)
Pectus excavatum is a progressive deformity. This patient progressed from mild to severe & asymmetric before puberty. At the time of puberty, the chest becomes more rigid and patients start to exhibit cardiopulmonary symptoms.(漏斗胸畸形常随年龄的增长而逐渐加重。)