
Feature of diastolic HF: impaired ventricular relaxation and filling a normal-sized chamber with normal emptying ventricular EF is in normal range 0 typical symptoms and sighs of HF related principally to the elevation of filling pressure
Feature of diastolic HF: ◼ impaired ventricular relaxation and filling ◼ a normal-sized chamber with normal emptying ◼ ventricular EF is in normal range ◼ typical symptoms and sighs of HF related principally to the elevation of filling pressure
ACUTE VERSUS CHRONIC HEART FAILURE ACUTE: the sudden reduction in cardiac output often results in acute pulmonary edema and/or systemic hypotension CHRONIC: develops or progresses slowly Vascular congestion is common arterial pressure is ordinarily well maintained
ACUTE VERSUS CHRONIC HEART FAILURE ACUTE: the sudden reduction in cardiac output often results in acute pulmonary edema and/or systemic hypotension CHRONIC: develops or progresses slowly Vascular congestion is common arterial pressure is ordinarily well maintained

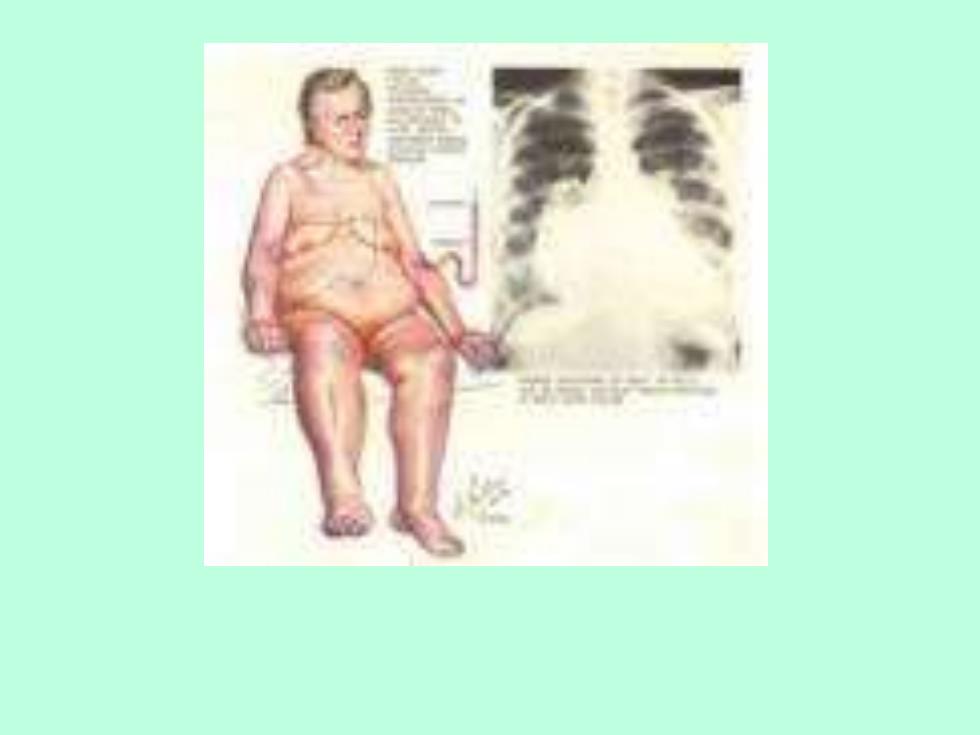
RIGHT-SIDED VERSUS LEFT-SIDED HF In left-sided HF,underlying abnormality affects the left ventricle primarily.the main clinical manifestations are exertional dyspnea,nocturnal dyspnea and orthopnea,common sign is pulmonary rales In right sided HF,underlying abnormality affects the right ventricle primarily,but right-sided HF is often secondary to left-sided HF.The main manifestations are peripheral edema and gastrointestinal symptoms. Common signs are distended neck vein and positive hepatojugular reflux,congestive hepatomegely, pleural effusion and ascites 28
28 RIGHT-SIDED VERSUS LEFT-SIDED HF In left-sided HF, underlying abnormality affects the left ventricle primarily. the main clinical manifestations are exertional dyspnea , nocturnal dyspnea and orthopnea, common sign is pulmonary rales . In right sided HF, underlying abnormality affects the right ventricle primarily, but right-sided HF is often secondary to left-sided HF. The main manifestations are peripheral edema and gastrointestinal symptoms. Common signs are distended neck vein and positive hepatojugular reflux, congestive hepatomegely, pleural effusion and ascites

rOfu im1itt