
7.2 The ABZs of DNA Secondary Structure Structure Overview of Nucleic Acids Unlike three dimensional structures of proteins,DNA molecules assume simple double helical structures independent on their sequences.There are three kinds of double helices that have been observed in DNA:type A,type B,and type Z,which differ in their geometries.The double helical structure is essential to the coding functional of DNA.Watson (biologist)and Crick(physicist)first discovered double helix structure in 1953 by X-ray crystallography. RNA,on the other,can have as diverse structures as proteins,although they can also hand form double helix of type A.The ability of being both informational and diverse in structure suggests that RNA was the prebiotic molecule that could function in both replication and catalysis (The RNA World Hypothesis).In fact,some virus encode their genetic materials by RNA(retrovirus)
7.2 ·The ABZs of DNA Secondary Structure Structure Overview of Nucleic Acids Unlike three dimensional structures of proteins, DNA molecules assume simple double helical structures independent on their sequences. There are three kinds of double helices that have been observed in DNA: type A, type B, and type Z, which differ in their geometries. The double helical structure is essential to the coding functional of DNA. Watson (biologist) and Crick (physicist) first discovered double helix structure in 1953 by X-ray crystallography. RNA, on the other, can have as diverse structures as proteins, although they can also hand form double helix of type A. The ability of being both informational and diverse in structure suggests that RNA was the prebiotic molecule that could function in both replication and catalysis (The RNA World Hypothesis). In fact, some virus encode their genetic materials by RNA (retrovirus)
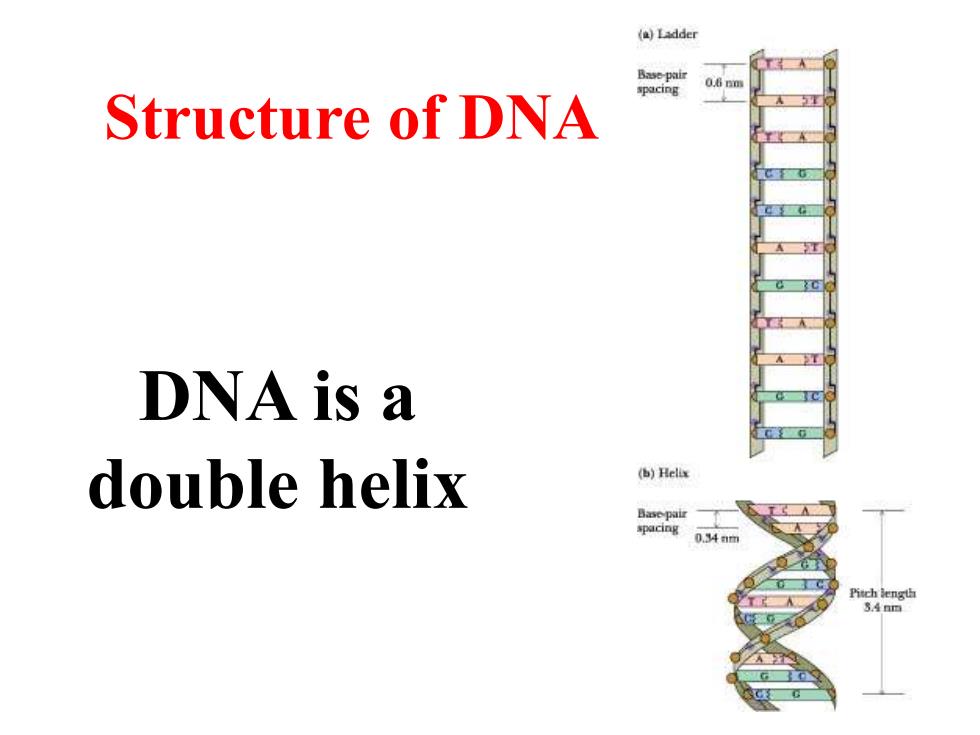
(a)Ladder Base-pair spacing Structure of DNA DNA is a double helix (b)Helix Base-pai 034m itch eng
DNA is a double helix Structure of DNA
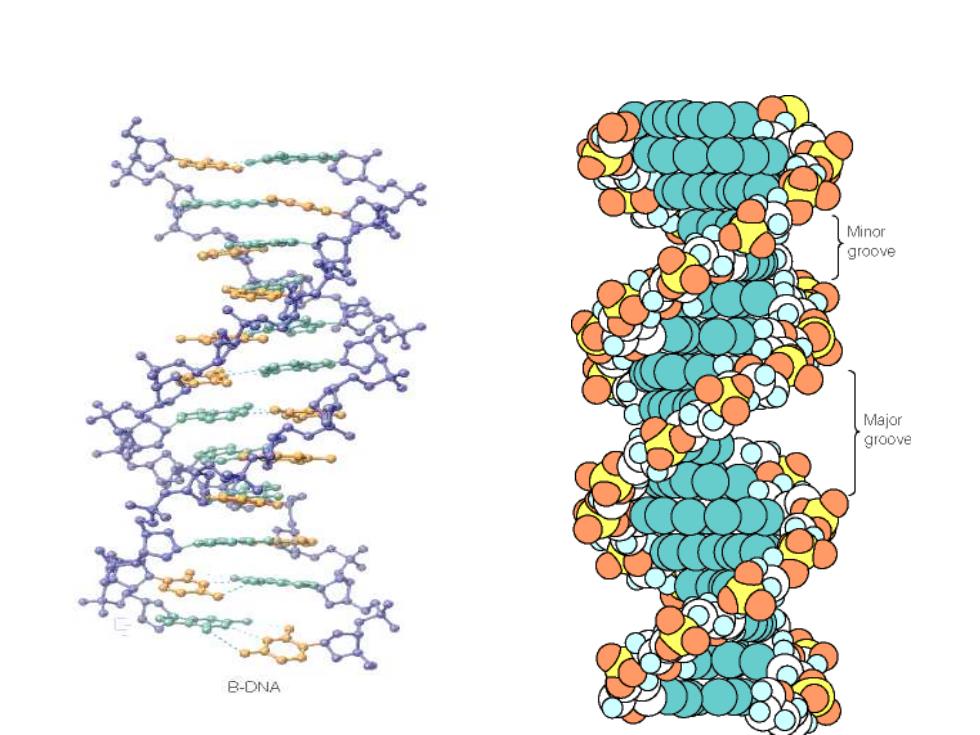
Minor groove Major groove B-DNA
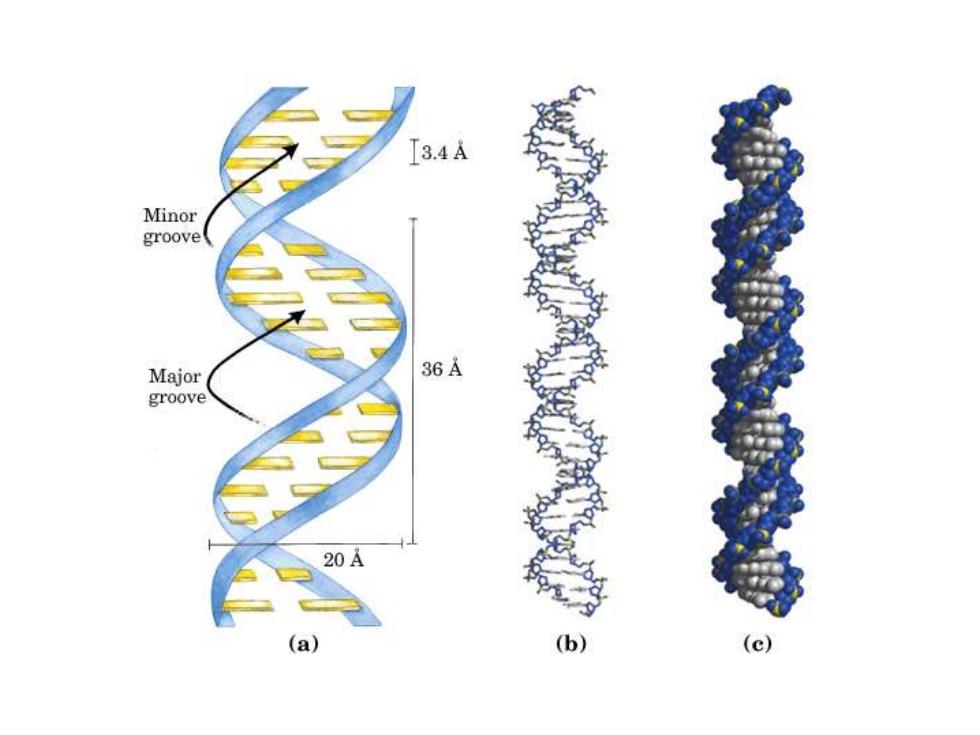
3.4A Minor groove Major 36A groove 20A (a)】 (b) (c)

Major groove Major groove -0.29nm- 030m 030 029nm 111am Minor groove Minor groove Structural Equivalence of Watson-Crick Base Pairs; the A:T pair and G:C pair have virtually identical dimensions
Structural Equivalence of Watson–Crick Base Pairs; the A:T pair and G:C pair have virtually identical dimensions