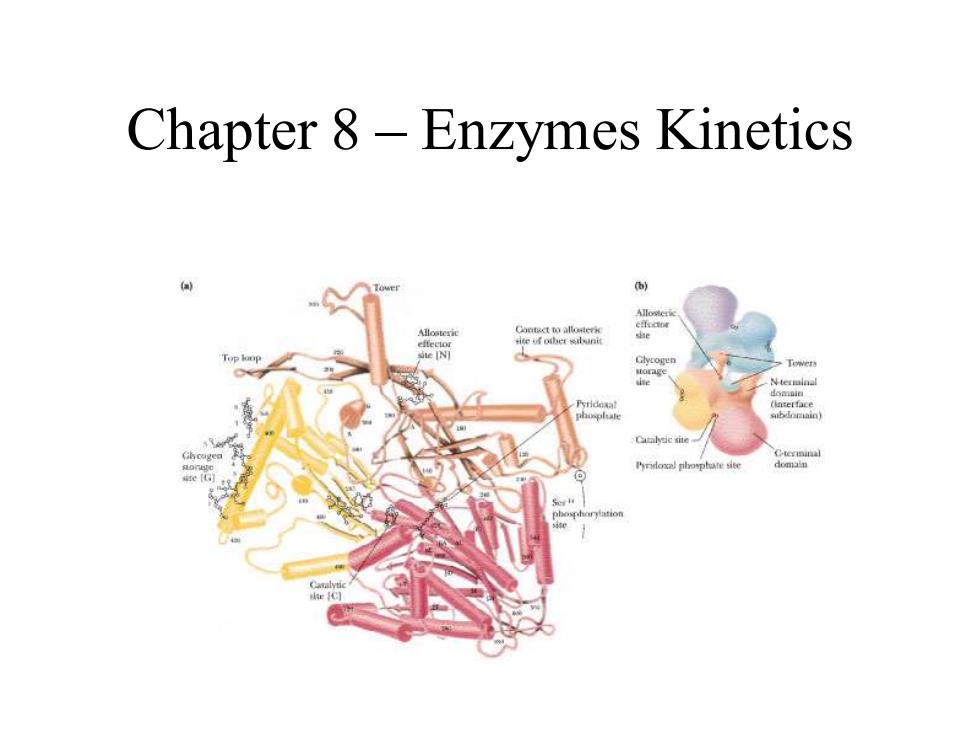
Chapter 8-Enzymes Kinetics Contact to allorteric ite of ofer bni
Chapter 8 – Enzymes Kinetics
Introduction to Enzymes Thousands of biochemical reactions proceed at any given instant within living cells.These reactions are catalyzed by en☑ymes, Enzymes are mostly proteins.But two important enzymes are most certainly to be RNA(ribozymes).One is the ribosome (peptidyl transfer)and the other is the splicesome (splicing of intron); Enzymes are the agents of metabolic function.Enzymes play key functions in controlling rate of reaction,coupling reactions,and sensing the momentary metabolic needs of the cell
Introduction to Enzymes • Thousands of biochemical reactions proceed at any given instant within living cells. These reactions are catalyzed by enzymes; • Enzymes are mostly proteins. But two important enzymes are most certainly to be RNA (ribozymes). One is the ribosome (peptidyl transfer) and the other is the splicesome (splicing of intron); • Enzymes are the agents of metabolic function. Enzymes play key functions in controlling rate of reaction, coupling reactions, and sensing the momentary metabolic needs of the cell

8.1.Enzymes-Catalytic Power, Specificity,and Regulation Enzymes are characterized by three distinctive features: catalytic power, specificity, regulation
8.1 • Enzymes—Catalytic Power, Specificity, and Regulation Enzymes are characterized by three distinctive features: catalytic power, specificity, regulation
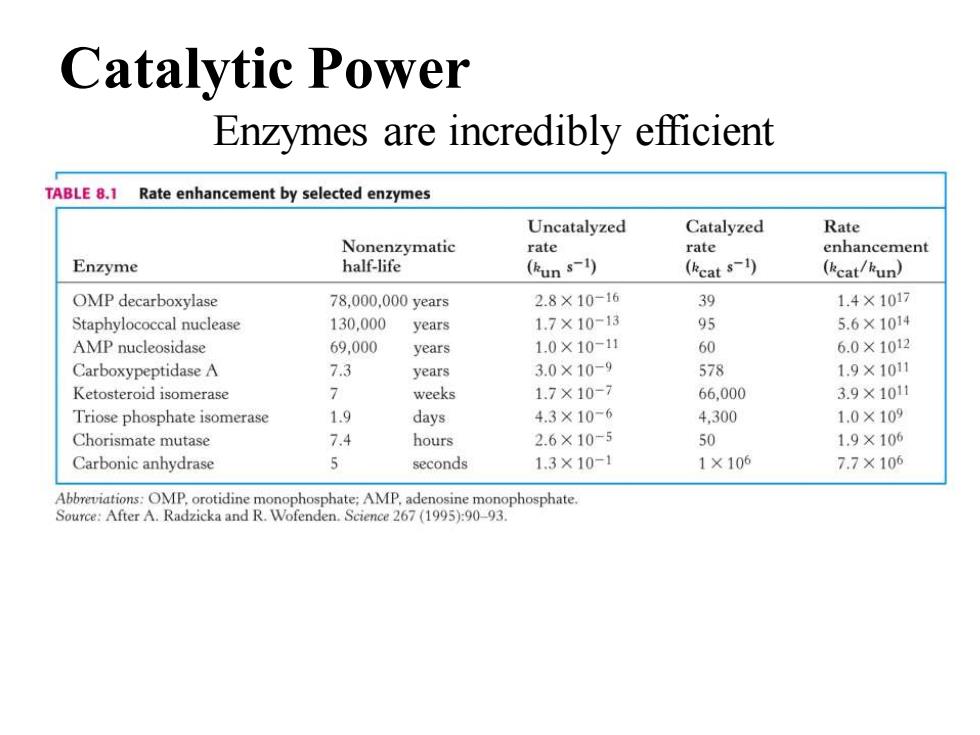
Catalytic Power Enzymes are incredibly efficient TABLE 8.1 Rate enhancement by selected enzymes Uncatalyzed Catalyzed Rate Nonenzymatic rate rate enhancement Enzyme half-life (kun s-1) (kcat s-1) (kcat/kun) OMP decarboxylase 78,000,000 years 2.8×10-16 39 1,4×1017 Staphylococcal nuclease 130.000 years 1.7×10-13 95 5.6×1014 AMP nucleosidase 69,000 years 1.0×10-11 60 6.0×1012 Carboxypeptidase A 7.3 years 3.0×10-9 578 1.9×1010 Ketosteroid isomerase 7 weeks 1.7×10-7 66,000 3.9×10日 Triose phosphate isomerase 1.9 days 4.3×10-6 4,300 1.0×109 Chorismate mutase 7.4 hours 2.6×10-5 50 1.9×106 Carbonic anhydrase seconds 1.3×10-1 1×106 7.7×106 Abbreviations:OMP,orotidine monophosphate:AMP.adenosine monophosphate. Source:After A.Radzicka and R.Wofenden.Science 267 (1995):90-93
Enzymes are incredibly efficient Catalytic Power
Enzyme Specificity The selective qualities of an enzyme are collectively recognized as its specificity. Intimate interaction between an enzyme and its substrates occurs through molecular recognition based on structural complementarity;such mutual recognition is the basis of specificity.The specific site on the enzyme where substrate binds and catalysis occurs is called the active site
Enzyme Specificity The selective qualities of an enzyme are collectively recognized as its specificity. Intimate interaction between an enzyme and its substrates occurs through molecular recognition based on structural complementarity; such mutual recognition is the basis of specificity. The specific site on the enzyme where substrate binds and catalysis occurs is called the active site