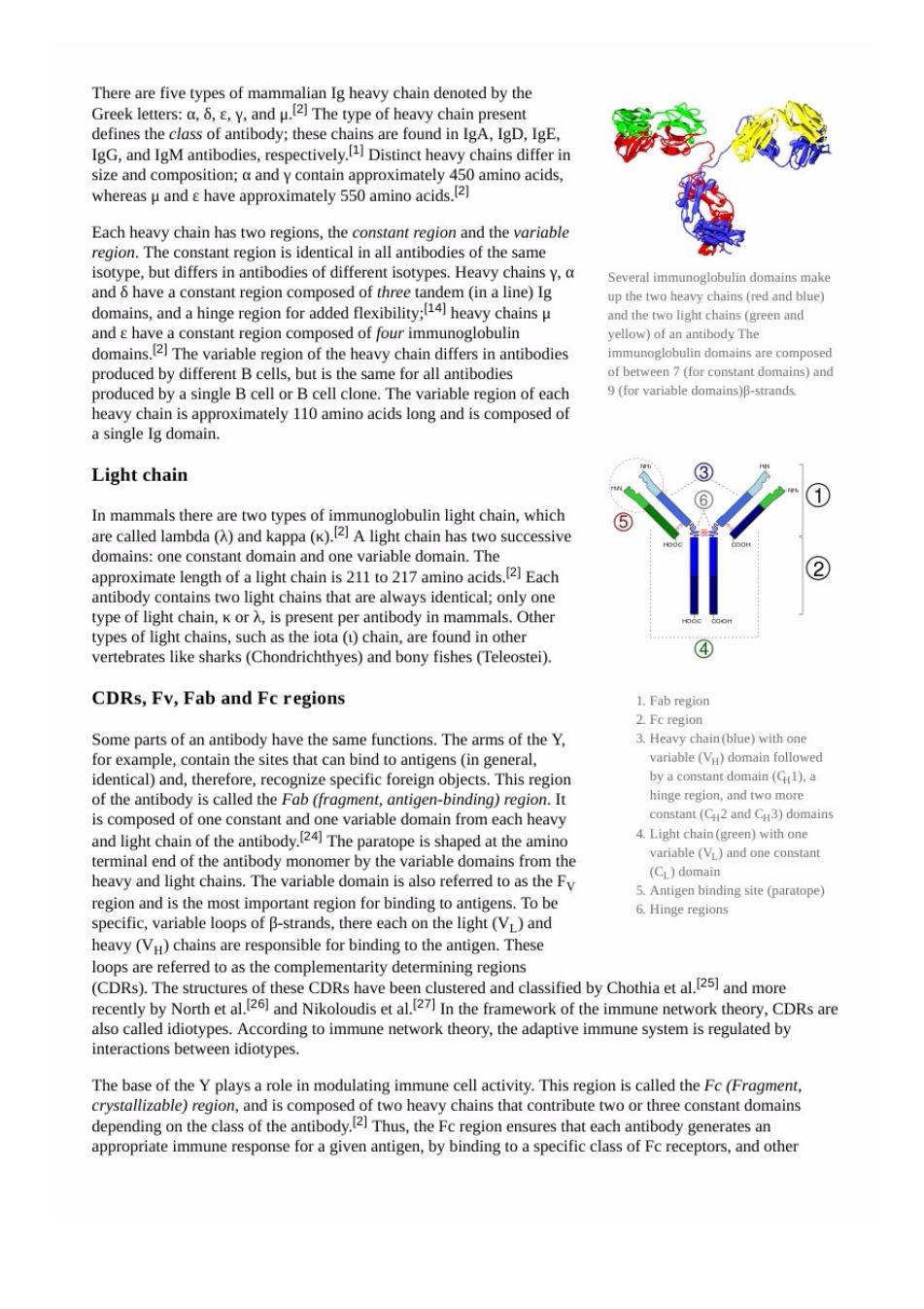
There are five types of mammalian Ig heavy chain denoted by the Greek letters:a.8..Y.and u.(2]The type of heavy chain p sent defines the class of antibody:these chains are found inA,ID,IgE. IgG,and IgM antibodies,respectively Distinct heavy chains differ in Each heavy chain has two regions,the constant region and the variable region. stantregon I in all antibo of the same and 6 ha Several domains mak domains.and a hinge region for added flexibility:heavy chains p the two口 and have a constant region composed of four immunoglobulin ellow)of an domains The variable region of the heavy chain differs in antibodies cell clo or al 9(for variable domains)-strand a single Ig domain. Light chain ① in mammals there s two successive domains:one constant domain and one variable domain.The approximate lengh of a light chain acids.Each antibod s two light chains that are always identical;only one type on Ch K or vertebrates like sharks (Chondrichthyes)and bony fishes (Teleostei). ④ CDRs,Fv,Fab and Fc regions 1.Fab region Some parts of an have the s.The arms of the Y. Fc region the sit variable V doman followed identical)and,therefore,recognize specific foreign objects.This region byaconstan domain(G).a of the antibody is called the Fab (fragment,antigen-binding)region.It and light 4.Light chain (green)with one chain of【he ody. riable (VL)and one constant and is the most in aion for hinding To be binding site(paratope) specific.variable loops of B-strands.there each on the light (and 6.Hinge regions heavy(Vu)chains are responsible for binding to the antigen.These loops are referred to as the complementarity determining regions couy Nor and的Ch mon In the framework of the immune network theory.CDRs are otype 8 ol he pay水hiis@ able compost 2)Th 0 s that con bute two or constant do nain

immune molecules.such as complement proteins.by doing this.it mediates different physiological effects aam时n l In summary.the fab region of the antibody determines antigen specificity while the fc region of the antibody determines the antibody's class effect.Since only the constant domains of the heavy chains make up the Fc region o fects.Possible classes of e alpha. ntib nd M of antibodies include:Opsonisation,agglutination,haemolysis,complement activation,mast cell degranulation and neutralisation (though this class e ffect may be mediated by the Fa st Fc mediated effects are directed a Function The main categories of antibody action include the following ggutination,in which antibodies"lue together"foreign cells into clumps that are attractive targets for phagocytosis e or ph soluble antigens,forcing them to precipitate ou tion (fix ation),in which an ntibodie that are vitn a membrane complex,w hiletoinfoiegnoalencourage i .Encouragement of inflammation by chemotactically attracting inflammatory cells Activated b cells differentiate into either antibody roducing cells called plasma cells that secrete soluble antibody or memory cells that survive in the body for years afte rememerded inde to allow the immun system to vided by oassive immunization from lating antibodies are prod by clor al B ce protein ute to i ty in t macrophages and other cells by coating the pathogen:and the trigger destruction of pathogens bysmothermmune rponsuhas the compeme paybesoier oactive amine degranulation to contributetoimmunity against certain types of antigens(helminths, Activation of complement res ling of bacteria in two ways. First,the binding of the antibo dy and complement molecule a pro 559 op nese pnag components for embrae tack complex tt antibodie to kl the bacerdi

Activation of effector cells To combat pathogens that replicate outside cells,antibodies bind to pathogens to link them together,causing them to agglutinate.Since an 2 antibody has at least two paratopes,it can bind more than one antigen l epitopes cam oe sur es of these antigen ogens have Fo receptor on a particular cell triggers an effector function of that cell; eutrophils will microbe The activation of natural killer cells by antibodies initiates a cytotoxic mechanism known as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)-this process may explain the effica oclonal antibodies us d in bio system approp Natural antibodies Humansand higher"that re viral en d the classica complement pathway leading to lysis of enveloped virus particles ong before the adaptive immune response is activated.Many natural antibodies are directed against the disaccharide galactose (1,3)-galactose(a-Gal), which is found satemitnlsgaronghcovlhlodcelsurfaoeP9lesandgCneatedinponseo s sugar by bac ting in the serumo antigen Immunoglobulin diversity an antibody resp of mic aries allowin them to interact with many different antigens 34 It has been estimated that humans generate about 10 billion different antibodies,each capable of binding a distinct epitope of an antigen.Although a huge repertoire of different antibodies is generated in a single individual,the number of genes available to make th ese proteins is limited by the size of the humar genome entaieBoestogmerateadesepeol antibody genes.36 Domain variability The chromosomal region that encodes an antibody is large and contains several distinct gene loci for each domain of the ound on )are 22 and 2 in hur of these domai hich nt in heavy and light chain of every antibody,but can differ in different antibodies generated from distinct B cells (C)D